
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:AutoSave Off HU
File Home
Paste
Clipboard
Page 1 of 1
Insert Design Layout
Calibri (Body) ✓11 A A Aa A E
A
BI U ab x₂ x² A
✓
Font
V
50 words m
Type here to search
Accessibility: Investigate
Document1 - Word
References Mailings Review
S
Paragraph
Search
↓
IT
View
¶
S
Help
AaBbCcDc AaBbCcDc AaBbC AaBbcct AaB
¶ Normal
1 No Spac... Heading 1
Heading 2
Title
Styles
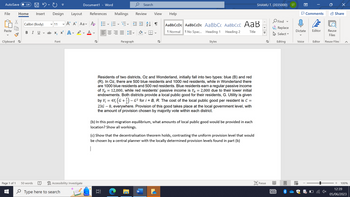
Residents of two districts, Oz and Wonderland, initially fall into two types: blue (B) and red
(R). In Oz, there are 500 blue residents and 1000 red residents, while in Wonderland there
are 1000 blue residents and 500 red residents. Blue residents earn a regular passive income
of YB = 12,000, while red residents' passive income is Y₁ = 2,000 due to their lower initial
endowments. Both districts provide a local public good for their residents, G. Utility is given
by Vi
23G-8, everywhere. Provision of this good takes place at the local government level, with
the amount of provision chosen by majority vote within each district.
į = 4Y₁ (G + ¹) − G² for i = B, R. The cost of the local public good per resident is C =
(b) In this post-migration equilibrium, what amounts of local public good would be provided in each
location? Show all workings.
(c) Show that the decentralisation theorem holds, contrasting the uniform provision level that would
be chosen by a central planner with the locally determined provision levels found in part (b)
SHAMU T. (2035000)
S
Focus
BA
DEI
Find
Replace
Select
Editing
ST
13
O
Dictate
V
A
Voice
Comments
Editor
Share
Reuse
Files
X
Editor Reuse Files
+ 100%
12:39
05/06/2023
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- b) Consider agent A with (inverse) demand curve for the public good and agent B with inverse demand , where prices are measured in £ per unit. The marginal cost of producing the public good is £10 per unit. What is the Pareto efficient level of the public good? Explain. Illustrate in a graph. [Hint: Compute the marginal social benefit of the public good by adding up the demand curves vertically, over the p’s]arrow_forwardPLEASE ANSWER PART b) and c) onlyarrow_forwardSuppose the government is trying to determine how to deal with pesticide contamination of its water supply. It wants to undertake a benefit-cost analysis of two alternative policy options for controlling pesticides: Upgrade its municipal water treatment plant to remove the pesticides, or Banning the use of the offending pesticides in the metropolitan area. Assume that either techniques reduces pesticides to a level which does not adversely affect human health. The cost of these control options are as follows: Municipal treatment upgrades: Capital Costs = $9 million. The new plant is constructed over one year. It starts operating at the beginning of year two. Once the plant begins operation, it has operating costs of $1 million per year. Once constructed, the plant lasts for 5 years, then it must be replaced with a new plant. Pesticide Ban: Annual operating costs due to substitution of non-toxic methods of controlling “pests” = $4 million per year. These costs would last forever. The…arrow_forward
- Assume that Matt, Joe, and Teresa are the only citizens in a community. A proposed public good has a total cost of $1,000. All three citizens will share an equal portion of this cost in taxes. The benefit of the public good is $380 for Matt, $360 for Joe, and $200 for Teresa. In a majority vote, this proposal will most likely be Multiple Choice accepted; the public good is produced, even though it is economically inefficient. defeated; the public good is not produced, which is the proper outcome. defeated; the public good is not produced, even though it would have been efficient to do so. accepted; the public good is produced, which is economically efficient.arrow_forwardAmaranda and Bartolo consume only two goods, X and Y. They can trade only with each other and there is no production. The total endowment of good X equals the total endowment of good Y. Amaranda's utility function is U(xA, YA) = min{xa, YA} and Bartolo's utility function is U(XB, YB) = max{xg, YB}. In an Edgeworth box for Amaranda and Bartolo, the set of Pareto optimal allocations is O the main diagonal. O both diagonals. O the whole Edgeworth box. O the edges of the box and the main diagonal. O the edges of the box.arrow_forwardConsider a two-agent two-good exchange economy. Assume the utility functions are given by U'(x}, x}) = x} + 4/x} and U²(x², x3) = x² + 2/x% with endowment vectors R' = (4, 12) and R? = (8, 8). Assume good x2 is the numeraire. a. Find the competitive equilibrium allocation and prices for this pure exchange economy.arrow_forward
- Consider an exchange economy with two types of agents, A and B, and two goods, x and y. Preferences are given by UA (XA, YA) = = A + 6 ln(y₁) and UB(TB, YB) = ln(TBYB). Suppose the government wants to reach the goal of XB = 5 with the competitive equilibrium by setting a redistribution r such that w₁ = (10,r) and wB = (0,20 - r). 1. Find r reaches the government's goal. Round your answer to 2 decimal points. Let Py = Answer:arrow_forwardFill all the blanks!arrow_forwardConsider a two-good economy (good z and good y) with two consumers and one firm. Consumer 1 has only 10 units of good x as her endowment. Consumer 2 has 25 units of good y as her endowment. The firm produces good x by using good y. Its production function is x = 2/y. Consumer 1 fully owns the firm. Consumer 1's utility function is given by U1[¤1, Yı] = In x+ln y1. Consumer 2's utility function is given by U2[c2, Y2] = VT2Y2. Let p be the price of good x and q the price of good y. Derive the general equilibrium.arrow_forward
- Consider two consumers (1; 2), each with income M to allocate between two goods. Good 1 provides 1 unit of consumption to its purchaser and units of consumption to the other consumer. Each consumer i, i = 1; 2, has the utility function is consumption of good 1 and is consumption of good 2. a. Provide an interpretation of α. b. Suppose that good 2 is a private good. Find the Nash equilibrium levels of consumption when both goods have a price of 1. c. By maximizing the sum of utilities, show that the equilibrium is Pareto-ancient if α = 0 but incident for all other values of α. d. Now suppose that good 2 also provides 1 unit of consumption to its purchaser and a, 0 ≤ α ≤ 1, units of consumption to the other consumer. For the same preferences, find the Nash equilibrium and show that it is ancient for all values of α. e. Explain the conclusion in part d.arrow_forwardConsider agent A with (inverse) demand curve for the public good and agent B with inverse demand , where prices are measured in £ per unit. The marginal cost of producing the public good is £10 per unit. What is the Pareto efficient level of the public good? Explain. Illustrate in a graph. [Hint: Compute the marginal social benefit of the public good by adding up the demand curves vertically, over the p’s - image attached that has the inverse demand functionarrow_forward5. Consider a monocentric model with fixed housing unit h and the utility of residents u=c, where c is the consumption of the composite goods. The budget constraint of each resident living at distance d from the CBD is c + ph = w-dt, where w is wage, p is housing rental rate, t is the unit commuting cost in distance. The city is open and free migration in and out. The external utility they obtain out of the city is ū= 10. The rental rate on agricultural land is pA. (a) Illustrate why the consumption of residents living in all parts of the city will be equalized. (b) Derive the housing rental rate (p) as a function of d, distance from the CBD, What is the slope? Draw a figure with p at the y-axis and d at the x axis. (c) Discuss how the boundary of the city is determined in this model, how would the boundary of the city respond to wage w and commuting cost t?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education