
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Hi, im struggling with getting the right final answers for this question
part a) if the parallel pipes are replaced with a singular pipe, and entry and exit losses are ignored, what is the diameter of the pipe? the volume flux of this pipe is Q=0.3m3/s. (final answer should be 0.43m)?
part b) find the flow regime and the thickness of the viscous layer in pipe 1
if you could make notes to explain any significant steps so its easier for me to learn and apply to other questions that would be very helpful! thanks in advance :)

Transcribed Image Text:Pipe 1
L₁ = 1000 m
D₁ = 0.5 m
f₁ = 0.02
ks = 0.5 mm
U₁ = 1 m/s
Pipe 2
L₂ = 1000 m
D₂ = 0.3 m
f₂ = 0.015
ks = 0.5 mm
4₂ = ???
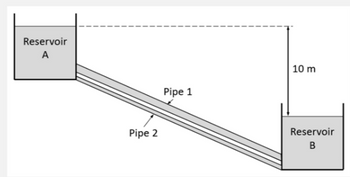
Transcribed Image Text:Reservoir
A
Pipe 2
Pipe 1
10 m
Reservoir
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Similitude Water flows through a 5 inch diameter pipe at 10 ft/s. If a test is performed using mercury moving at 4 ft/s, what diameter pipe (in inches) would be needed to maintain the same dynamic characteristics? Both fluids are at standard temperature and pressure. Hint: What dimensionless number do we use all the time for pipes?arrow_forwardHow to solve this question . Step-by step solution needed with explanation. ( Fill in the Blank)arrow_forwardPaint issues from the tank at a flow rate of 45 ft^3/s. Find the kinetic viscosity in ft^2/s. Assume the flow is laminar. Note: In answering the question, it must be in exponential form but in the text box just write the value no need to include the x10^-1.. A 9 ft L = 6 ft d = 1/2 in ܪ earrow_forward
- Problem 4: Laminar or Turbulent? Oil (s = 0.85 and v= 1.8x105 m²/s) flows through a 100 mm diameter pipe at 0.5 L/s. Part A Calculate the Reynolds number. Part B Is the flow laminar or turbulent, and why?arrow_forwardProblem 3. (15pts) Complete the following questions by analyzing the Water Phase Diagram. a) Water is heated from its initial condition (7=60°C, P=0.8atm) under constant pressure to the water vapor equilibrium curve. Specify the temperature and pressure at that equilibrium point. b) Water is depressurized from its initial condition (7=60°C, P=0.8atm) under constant temperature to the water vapor equilibrium curve. Specify the temperature and pressure at that equilibrium point. c) You are boiling water near the top of Longs Peak (P=0.6atm). At what temperature of the liquid water will the water begin to boil? d) While boiling water on Longs Peak, is it possible to heat the liquid water to a temperature above your answer in part c)? Explain.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning