
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
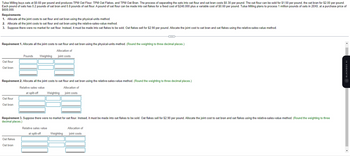
Transcribed Image Text:Tulsa Milling buys oats at $0.60 per pound and produces TPM Oat Flour, TPM Oat Flakes, and TPM Oat Bran. The process of separating the oats into oat flour and oat bran costs $0.30 per pound. The oat flour can be sold for $1.50 per pound, the oat bran for $2.00 per pound.
Each pound of oats has 0.2 pounds of oat bran and 0.8 pounds of oat flour. A pound of oat flour can be made into oat flakes for a fixed cost of $240,000 plus a variable cost of $0.60 per pound. Tulsa Milling plans to process 1 million pounds of oats in 20X0, at a purchase price of
$600,000.
Requirements
1. Allocate all the joint costs to oat flour and oat bran using the physical-units method.
2. Allocate all the joint costs to oat flour and oat bran using the relative-sales-value method.
3. Suppose there were no market for oat flour. Instead, it must be made into oat flakes to be sold. Oat flakes sell for $2.90 per pound. Allocate the joint cost to oat bran and oat flakes using the relative-sales-value method.
Requirement 1. Allocate all the joint costs to oat flour and oat bran using the physical-units method. (Round the weighting to three decimal places.)
Allocation of
joint costs
Oat flour
Oat bran
Requirement 2. Allocate all the joint costs to oat flour and oat bran using the relative-sales-value method. (Round the weighting to three decimal places.)
Relative sales value
Allocation of
at split-off
joint costs
Oat flour
Oat bran
Pounds Weighting
Oat flakes
Oat bran
Weighting
Requirement 3. Suppose there were no market for oat flour. Instead, it must be made into oat flakes to be sold. Oat flakes sell for $2.90 per pound. Allocate the joint cost to oat bran and oat flakes using the relative-sales-value method. (Round the weighting to three
decimal places.)
Relative sales value
at split-off
Weighting
Allocation of
joint costs
BLACKBOX AI
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Based on the below examples (1&2), how can I figure out which contribution margin is needed to calculate the required Break-even? Between (Contribution Margin Per Unit) or (Contribution Margin Ratio). Example (1) (Why we didn't take CM/unit, but instead, CMR is calculated?) Northern Pacific Fixtures Corporation sells a single product for $28 per unit. If variable expenses are 65% of sales and fixed expenses total $9,800, the break-even point is? Example (2) (this one I know how to calculate). Mishoe Corporation has provided the following contribution format income statement. All questions concern situations that are within the relevant range. Sales (1,000 units)...................... $50,000 Variable expenses...................... 32,500 Contribution margin..................... 17,500 Fixed expenses.......................... 12,250 Net operating income.................. $5,250 The break-even point in unit sales is closest…arrow_forwardPlease solvearrow_forwardComplete the table below for contribution margin per unit, total contribution margin, and contribution margin ratio: E (Click the icon to view the table.) Compute the missing information, starting with scenario A, then for scenarios B and C. (Enter the contribution margin ratio to nearest percent, X%.) A Number of units 1,510 units Sale price per unit $ 1,600 Variable costs per unit 1, 120 Calculate: Contribution margin per unit Total contribution margin Contribution margin ratio Data Table A Number of units 1,510 units 14,390 units 2,450 units Sale price per unit 1,600 $ 4.400 5,000 Variable costs per unit 1,120 880 3,750 Calculate: Contribution margin per unit Total contribution margin Contribution margin ratio Print Done Enter any number in the edit fields and then click Check Answer. parts remaining Clear All Final Checkarrow_forward
- Required:1. Compute the contribution margin per unit from (a) using the new material and (b) using the new material and increasing the selling price. (Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) All of the empty spaces needs numbers, please use the same format at the photosarrow_forwardThe following terms are used to describe various economic characteristics of costs.a. Opportunity costb. Out-of-pocket costc. Sunk costd. Differential coste. Marginal costf. Average costRequired: Choose one of the terms listed above to characterize each of the amounts described below.1. The cost of feeding 500 children in a public school cafeteria is $800 per day, or $1.60 per child per day. What economic term describes this $1.60 cost?2. The cost of including one extra child in a day-care center.3. The cost of merchandise inventory purchased two years ago, which is now obsolete.4. The management of a high-rise office building uses 2,500 square feet of space in the building for its own management functions. This space could be rented for $250,000. What economic term describes this $250,000 in lost rental revenue?5. The cost of building an automated assembly line in a factory is $800,000. The cost of building a manually operated assembly line is $375,000. What economic term is used to…arrow_forwarda. What is the traditional unit product cost for the deluxe model now? (round your intermediate calculations and final answer to 2 decimal places.) b. What is the traditional unit product cost for the tourist model? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to 2 deimal places) c. What is the ABC unit product cost for the deluxe model now? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to 2 decimal places.) d. What is the ABC product cost for the tourist model? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forward
- Royal Lawncare Company produces and sells two packaged products - Weedban and Greengrow. Revenue and cost information relating to the products follow: \ table[[, Product], [, Weedban,Greengrow], [Selling price per unit,$8.00, $39.00arrow_forwardPlease help mearrow_forwardanswer in text form please both a and b (without image)arrow_forward
- Gladstorm Enterprises sells a product for $50 per unit. The variable cost is $32 per unit, while fixed costs are $9,504. Determine the break-even point in sales units. Round answer to the nearest whole number. units Determine the break-even point in sales units if the selling price was increased to $65 per unit. Round answer to the nearest whole number. unitsarrow_forwardSBD Phone Company sells its waterproof phone case for $98 per unit. Fixed costs total $182,000, and variable costs are $44 per unit. (1) Determine the contribution margin ratio. per unit Contribution margin Contribution Margin Ratio Choose Numerator: Choose Denominator: Contribution Margin Ratio Contribution margin ratio (2) Determine the break-even point in dollars. Choose Numerator: Choose Denominator: Break-Even Point in Dollars Break-even point in dollarsarrow_forward(e) When sales increase by 1%, which of the following should increase by more than 1% in a merchandising company? (You may select more than one answer. Single click the box with the question mark to produce a check mark for a correct answer and double click the box with the question mark to empty the box for a wrong answer. Any boxes left with a question mark will be automatically graded as incorrect.) V Variable cost Fixed cost ces Gross margin Contribution margin Net operating incomearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education