
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
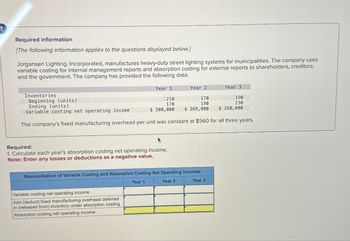
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.)
Jorgansen Lighting, Incorporated, manufactures heavy-duty street lighting systems for municipalities. The company uses
variable costing for internal management reports and absorption costing for external reports to shareholders, creditors,
and the government. The company has provided the following data:
Inventories
Beginning (units)
Ending (units)
Variable costing net operating income
Year 1
Year 2
Year 3
210
170
170
190
190
230
$ 300,000
$ 269,000
$ 260,000
The company's fixed manufacturing overhead per unit was constant at $560 for all three years.
Required:
1. Calculate each year's absorption costing net operating income.
Note: Enter any losses or deductions as a negative value.
Reconciliation of Variable Costing and Absorption Costing Net Operating Incomes
Variable costing net operating income
Add (deduct) fixed manufacturing overhead deferred
in (released from) inventory under absorption costing
Absorption costing net operating income
Year 1
Year 2
Year 3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3 manage costs? 10-31. Activity-Based Costing of Customers Rupert's Appliance Warehouse (RAW) delivers appliances to retailers throughout the city. The firm adds 6 percent to the cost of the appliances to cover the delivery cost. The delivery fee is meant to cover the cost of delivery. The finance team at RAW has analyzed the delivery service using activity-based costing methods and identified four activities. Data on these activities follow: 100 Activity Processing order.. Loading truck... Delivering order..... Billing..... Total overhead. .. Cost Driver Number of orders Number of items Number of orders Number of invoices Order value (total) . . . . . Number of orders.. Total number of items. Number of invoices. Activity Cost $ 90,000 180,000 108,000 70,000 $448,000 Two of Rupert's customers are McLean Designs and Neveux Appliances. Data for orders and deliveries to these two customers follow: .. Cost Driver Volume 3,000 orders 60,000 items 3,000 orders 2,500 invoices McLean Designs…arrow_forwardJorgansen Lighting, Incorporated, manufactures heavy-duty street lighting systems for municipalities. The company uses variable costing for internal management reports and absorption costing for external reports to shareholders, creditors, and the government. The company has provided the following data: Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Inventories Beginning (units) 220 160 180 Ending (units) 160 180 240 Variable costing net operating income $ 290,000 $ 269,000 $ 250,000 The company’s fixed manufacturing overhead per unit was constant at $560 for all three years. Required: 1. Calculate each year’s absorption costing net operating income. (Enter any losses or deductions as a negative value.)arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Kubin Company's relevant range of production is 18,000 to 22,000 units. When it produces and sells 20,000 units, its average costs per unit are as follows: Average Cost per Unit $ 7.00 $ 4.00 $ 1.50 $ 5.00 $ 3.50 $ 2.50 $ 1.00 $ 0.50 Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling expense Fixed administrative expense Sales commissions Variable administrative expensearrow_forward
- The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Jorgansen Lighting, Incorporated, manufactures heavy-duty street lighting systems for municipalities. The company uses variable costing for internal management reports and absorption costing for external reports. The company provided the following data: Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Inventories Beginning (units) 210 150 190 Ending (units) 150 190 230 Variable costing net operating income $ 290,000 $ 269,000 $ 260,000 The company's fixed manufacturing overhead per unit was constant at $550 for all three years. 2. Assume in Year 4 the company's variable costing net operating income was $250,000 and its absorption costing net operating income was $300,000. Did inventories increase or decrease during Year 4? How much fixed manufacturing overhead cost was deferred or released from inventory during Year 4 ?arrow_forward>>>>_____arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Jorgansen Lighting, Incorporated, manufactures heavy-duty street lighting systems for municipalities. The company uses variable costing for internal management reports and absorption costing for external reports. The company provided the following data: Year 1 Year 2 200 160 $ 290,000 Inventories Beginning (units) Ending (units) Variable costing net operating income The company's fixed manufacturing overhead per unit was constant at $560 for all three years. Year 3 160 180 $ 269,000 180 220 $ 250,000 2. Assume in Year 4 the company's variable costing net operating income was $240,000 and its absorption costing net operating income was $300,000. a. Did inventories increase or decrease during Year 4? b. How much fixed manufacturing overhead cost was deferred or released from inventory during Year 4?arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Arctica manufactures snowmobiles and ATVS. These products are made in different departments, and each department has its own manager. Each responsibility performance report includes only those costs that the department manager can control: direct materials, direct labor, supplies used, and utilities. Budget For Year Ended December 31 Direct materials Direct labor Totals Department manager salaries Supplies used Utilities Rent Totals Snowmobile $ 19,810 10,700 ▸ 4,600 3,630 Controllable Costs Responsibility Accounting Performance Report Manager, Snowmobile Department For Year Ended December 31 Budgeted $ 390 6,000 $ 45,130 Prepare a responsibility accounting performance report for the snowmobile department. Note: Under budget amounts should be indicated by a minus sign. 0 $ ATV $ 27,800 20,800 5,500 Actual 930 570 6,600 $ 62,200 Actual Snowmobile $ 19,720 10,990 4,700 3,470 360 5,600 $ 44,840 Over…arrow_forward! Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Martinez Company's relevant range of production is 7,500 units to 12,500 units. When it produces and sells 10,000 units, its average costs per unit are as follows: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling expense Fixed administrative expense Sales commissions Variable administrative expense Average Cost Per Unit $ 6.30 $ 3.80 $ 1.50 $ 4.00 $ 3.30 $ 2.00 Contribution margin per unit $ 1.00 $ 0.50 13. If the selling price is $22.30 per unit, what is the contribution margin per unit? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education