
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
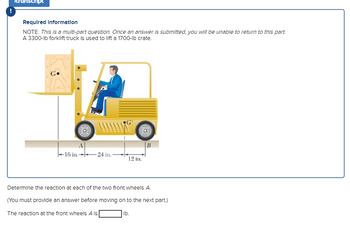
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part.
A 3300-lb forklift truck is used to lift a 1700-lb crate.
A
16 in.24 in.
12 in.
B
Determine the reaction at each of the two front wheels A.
(You must provide an answer before moving on to the next part.)
The reaction at the front wheels A is
lb.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The figure shows a traffic-light assembly with three identical 100-lb traffic lights at B, C, and D. The vertical and horizontal poles have negligible weight. Calculate the support reactions at the fixed support O. (Ignore the thickness of all poles when calculating distances.)arrow_forward4.8 m 2. The frame shown below is loaded with an unknown horizontal force, P. At point E, the surface exerts a force of 130 lb. on the roller. a) Draw and label all the reactions and forces acting on the frame and on the individual components, using the diagrams provided on the back of this handout. b) Determine the magnitude of the force, P, required for the frame to be in equilibrium. c) Determine the x- and y- components of the force acting at point C on member CDE, and specify the directions (→, +, t. 1). Note: For each calculation, state which diagram number (1, 2, 3, 4) you are using. Ans: P = 80 lb, C = 100 lb , C, = 75 lb 1 (by the way, FBC = 125 lb (T)) 4 in. 8 in. C 3 in. В 6 in. 1 3arrow_forward5arrow_forward
- Learning Goal: Part A - Finding the vertical component of the reaction at A To determine the reaction forces at supports on a horizontal beam by using the equations of equilibrium for a static application. Determine the vertical reaction at A. As shown, beam ABC is supported by the roller at A and pin at C. The geometry of the beam is given by a = 2.0 ft, b= 6.0 ft. and c= 10.5 ft. The applied forces are F = 1.50 kip and F = 1.00 kip. Force F, is applied at an angle 0 = 55° with the horizontal. Neglect the weight of the beam.(Figure 1) Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. • View Available Hint(s) A, = Value Units Submit Part B - Finding the horizontal component of the reaction at C Determine the horizontal component of the pin reaction at C. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. • View Available Hint(s) HẢ ? Figure C, = Value Units y Submit Part C - Finding the vertical component of the reaction…arrow_forwardIn the diagram below shows a truss structure which is subjected to an applied load and supported by joints namely pin and rollers. A) draw the fbd of the given truss system in the diagram below and solve for the unknown support reactionsarrow_forwardDo not give answer in image formet and hand writingarrow_forward
- Solve for A and Barrow_forwardQUESTION 13 The lifting pulley in Figure Q13 consists of a small crank of diameter d = 0.13 m and a large crank of diameter D (m). A worker can pull the rope of the large crank with a maximum force F = 243 N. Determine the minimum diameter D of the large crank (in metres) that will allow the worker to lift the item of mass m = 76 kg. Provide the numerical value only to two decimal places (e.g. 0.25) and do not include the units in the answer box. D F Figure Q13: Lifting pulley marrow_forwardThe 150-kg uniform crate rests on the 10-kg cart (see Figure 1). Determine the maximum force P that can be applied to the handle without causing the crate to slip or tip on the cart. The coefficient of static friction between the crate and cart is us = 0.2. P 0.5 m Prob. 17-38 Figure 1 1 marrow_forward
- 9 in. 30° x 6 in. 3 in. * B 3 in. 3 in. 4 in. The top cylinder weighs 100 lbs., the middle cylinder weighs 150 lbs. and the bottom cylinder weighs 200 lbs. A) Compute the forces on the L shaped support rack from each cylinder. Include free body diagram of each cylinder. B) Compute the reactions on the L shaped support rack at A and B. Include a free body diagram of the support rack.arrow_forwardLearning Goal: To analyze a rod assembly in three-dimensional space and determine the support reactions by using the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. The rod assembly shown has smooth joumal bearings at A, B, and C. The forces F 600 N. F-480 N. F 460 N, and F-900 N are applied as shown in the figure. The geometry of the rod assembly is given as a 0.900 m, &0.650 m, and c 0.800 m Neglect the weight of the rod Determine the magnitude of the 2 component of the reaction on the rod at A Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) Submit PA A₁ = Value Submit Part F- Finding the x component of the reaction at A Determine the magnitude of the x component of the reaction on the rod at A Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) Units μÁ Value ? Units ?arrow_forwardA man having a weight of 195 lb attempts to hold himself using one of the two methods shown in (Figure 1). Neglect the weight of the platform. a) Determine the total force the man must exert on bar AB in case a. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. b) Determine the normal reaction he exerts on the platform at C in case a. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. c) Determine the total force the man must exert on bar AB in case b. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. d) Determine the normal reaction he exerts on the platform at C in case b. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY