
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
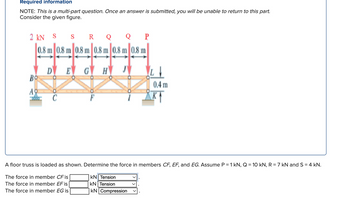
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part.
Consider the given figure.
2 kN
S
S
R Q
Q
P
0.8 m 0.8 m 0.8 m 0.8 m 0.8 m 0.8 m
D
E
GH
Bo
Απ
C
0.4 m
A floor truss is loaded as shown. Determine the force in members CF, EF, and EG. Assume P = 1 kN, Q = 10 kN, R = 7 kN and S = 4 kN.
The force in member CF is
The force in member EF is
The force in member EG is
KN Tension
KN | Tension
KN Compression
✓
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Answer with Complete Solution.arrow_forwardBegin with reading he brief description of zero-force members in a truss that was provided earlier in this assignment and linked here again. ZeroForce Truss Text.pdf V Based on that reading, try and identify all the zero-force members in the below truss. Explain your choices in the handwritten file.arrow_forwardI need DE,DF,GFarrow_forward
- A Look at the truss below. Fill in the correct magnitude with sign for each tension force acting on joint C. Keep the values in fractions. Ex. 250/3 Diagram TCD= Magnitude KN B TCE = Magnitude KN Enter both values before submission F E 10 KN 40 KN 3 panels at 4m = 12m 000 3 marrow_forwardFor the truss below, label members AB, CF, and EF as either "T" (tension), "C" (compression), or "zero-force." If there are none of a particular type, place it next to "none." 6ft (TYP) T *6* 2 T C 2k Zero-force 3k NONE: 12.54arrow_forwardRequired Information NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. A Howe roof truss is shown. Take P₁= P₂= P3 = 600 lb. P2 300 b P1 BY CI P3 E SASHSA→→SA- The force in member AB (FAB) is The force in member AC (FAC) is The force in member BC (FBC) is The force in member CE (FCE) is The force in member BD (FBD) is The force in member BE (FB) is The force in member DF (FDA) is The force in member DE (FDE) is The force in member EF (FEA) is The force in member EG (FEG) is The force in member FG (FFG) is The force in member FH (FFH) is The force in member GH (FGH) is 300 lb 6 ft G H 6 ft Determine the force in each member of the Howe roof truss shown. State whether each member is in tension (7) or compression (C). lb (Click to select) V lb (Click to select) lb (Click to select) lb (Click to select) lb (Click to select) lb (Click to select) lb (Click to select) lb (Click to select) lb (Click to select) V lb (Click to select) lb…arrow_forward
- Solve the problem shown below. Each answer is worth equal credit. Show all necessary steps of your work clearly to obtain credit. Final answer must be to 3 significant figures and contain units and be in the box. Using P1= 6.0 kips, then determine the reactions and member forces of the truss. a) List reactions at A and K? (Use positive, +, to indicate a reaction that is up, to the right, and counterclockwise.) [30 pts] RAX: RAY: Rkx: Rky: b) Determine the member forces using either the method of joints or method of sections. (Include Units and the correct sign in the answer, (Use: '+'= tension, & '-' = compression) J I H G 4 ft K A -3 ft- B P1 -3 ft- C P1 -3 ft D P1 E -3 ft 3 ft- P1 P1 F FBC: FCJ: FI: FEG: FDH: FIC:arrow_forwardNeed help on all questions. Please include all units, steps to the problem and information such as its direction or if it is in compression or tension. Thx.arrow_forwardcalculate the forces on PQ and QG use sections method .arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY