
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
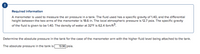
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
A manometer is used to measure the air pressure in a tank. The fluid used has a specific gravity of 1.40, and the differential
height between the two arms of the manometer is 18.6 in. The local atmospheric pressure is 12.7 psia. The specific gravity
of the fluid is given to be 1.40. The density of water at 32°F is 62.4 Ibm/ft3.
Determine the absolute pressure in the tank for the case of the manometer arm with the higher fluid level being attached to the tank.
The absolute pressure in the tank is
13.96 psia.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Atmospheric pressure at this location is 102.0 kPa and fluid temperature is presently 30°C. Oil (sg = 0.90) C Water 125 mm 475 mm 250 JU mm 50 mm Mercury (sg = 13.54) Figure 1: Compound manometer (note: sg = specific gravity)arrow_forwardThe Venturi meter shown in the sketch below, contracts the flow down to one quarter of its original area. Cold air at 0 deg C flows in the pipe through the Venturi meter. The velocity of the air upstream of the Venturi meter is equal to 40 ft/s and the pressure at the same point is equal to 30 psia. What is the manometer reading if the fluid of the manometer is water with density 1000 kg/m3 . Assume that the air behaves as an ideal gas with molecular weight equal to Mw=29 kg/kmol and constant density evaluated at upstream conditions. Use Bernoulli's equation for your calculations. please respond asap!arrow_forwardPage 3 Ethyl alcohol flows in a pipe at 20°C. The pipe is not open to the atmosphere. The manometer fluid is mercury. Both manometers are open to the atmosphere. Elevations are given in cm. Find the pressure [Pa, gage] and velocity [m/s] at Point 1. 100 68 Assume steady, ideal flow. 58 50 39 Elev in cm NOT TO SCALEarrow_forward
- A 12-inch by 6-inch Venturi meter is installed in a vertical pipeline carrying water as shown inthe Figure C. The flow is upward through the meter. A differential manometer containing fluid,with sp.gr 1.67, is attached to inlet and throat, the difference z in gage levels being 5.76 ft.Neglecting loss of head, write energy equation from inlet to throat of meter. Also write stepby step equation of the differential gage between inlet and throat and combine the twoequations to compute the dischargearrow_forward! Required information A manometer is used to measure the air pressure in a tank. The fluid used has a specific gravity of 1.40, and the differential height between the two arms of the manometer is 19.8 in. The local atmospheric pressure is 12.7 psia. The specific gravity of the fluid is given to be 1.40. The density of water at 32°F is 62.4 lbm/ft³. Determine the absolute pressure in the tank for the case of the manometer arm with the higher fluid level being attached to the tank. The absolute pressure in the tank is psia.arrow_forwardA manometer is attached to a water tank as shown in the figure. Find the height of the free water surface above the bottom of the tank. water 0.2m 0.15m 0.15m Hg(13.6)arrow_forward
- You are required to design a barometer that uses water instead of mercury to operate under standard sea-level conditions. Draw a conceptual diagram of your barometer design. Show on your diagram what the pressures will be at all liquid-gas interfaces, and where the barometer reading will be taken.Calculate the minimum height requirement of the barometer tube to measure standard sealevel atmospheric pressure.arrow_forward1) A manometer is attached to two pipes as shown. If knowing mercury SG is 13.6, sea water SG is 1.035, and fresh water p is 1,000 kg/m³, determine the pressure difference between two pipelines at the centers. Fresh Water h. -60 cm Air hair -70 cm hea <- 40 cm Mercury Sea Water hi -10 cmarrow_forwardWater flows at 0.07 cubic meter per second through a pipe. A horizontal venturi meter with throat diameter of 150-mm was used to measure the velocity inside the pipe. Based on manometer reading, the differential gauge is deflected 1.2 meter. If the specific gravity of the manometer fluid is 1.60, the velocity, in meter per second (m/s), of water inside the pipe is ____ ANSWER ASAParrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning