
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
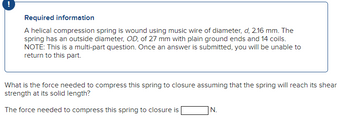
Transcribed Image Text:Required information
A helical compression spring is wound using music wire of diameter, d, 2.16 mm. The
spring has an outside diameter, OD, of 27 mm with plain ground ends and 14 coils.
NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to
return to this part.
What is the force needed to compress this spring to closure assuming that the spring will reach its shear
strength at its solid length?
The force needed to compress this spring to closure is
|N.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Problem 3: Design a helical compression spring to be used to return a pneumatic cylinder to its original position after being actuated. At a length of 10.50 in, the spring must exert a force of 60 lb. At a length of 4.00 in, it must exert a force of 250 Ib. Severe service is expected. Use ASTM A231 steel wire.arrow_forwardi.Considering the rod diagrammed below; calculate an equivalent spring constant or the rod using the length of the rod 1, its area A, and Young's nodulus E for a compressive force F that compresses the rod a distance x. Additionally, is a linear spring a useful model for a rod under compression? What if the rod is under tension? compressed rodarrow_forwardThree springs are connected to a mass and to fixed supports. When the coordinate y is equal to zero, there is no spring force. Your tasks: Tw m k3 assume Staur C équilibrition Fload Figure 1: System schematic for Problem 1. A Draw the free body diagram for the mass m including all 3 spring forces and the load force Fload). B Draw the free body diagram for the mass m, but combine the springs into one equivalent spring with spring constant keq. Write the equivalent stiffness of the spring keq in terms of the other spring constants. (3 C Given that k₁ = 300 N/m, k₂ = 100 N/m, and k3 = 200 N/m, and Fload = 300 N, calculate the loaded deflection SA Yloaded- D Compute the amount of potential energy stored in each spring. E Compute the forces, in Newtons, in each spring and denote them as F₁, F2, and F3 when the load from Part D is applied. wwwarrow_forward
- View In: English v In the below arrangement, all the string and pulleys are massless and the inclined plane is frictionless. At t 0, spring is unstretched and a constant force F = mg starts to act. Find the maximum extension in the spring. (Assume incline to be sufficiently long). Question 11 F=mg Options 8mg 1. O k 4 mg 2. O 5 k 8 mg 3. O 15 k 8mg 4. O 3karrow_forwardPlease help with all thank you!!arrow_forwardA helical compression spring with squared and ground ends has an outside diameter of 1.100 in, a wire diameter of 0.085 in, and a solid height of 0.563 in.Compute the ID, the mean diameter, the spring index, and the approximate number of coils.arrow_forward
- Item 2 Consider the following hanging mass system for the following problems. Before answering the questions below, draw two separate free-body diagrams of ring C and then ring B. Be sure the FBDS are neat a properly labeled. You will turn them in with your written work. (Figure 1) Figure 30° E 45° F 1 of 1 Part A cb Deturmine the tension developed in cable if cylindar E weighs 40 lb and 0= 15°. FCB= Submit ▾ Part B WF = 5 ΑΣΦ 11 vec Submit Request Answer If cylinder E weighs 40 lb and 0 = 15°, determine the weight of cylinder F. Express your answer with the appropriate units. 15. ΑΣΦ ↓↑ vec ? Request Answer ? lb 2 of 5arrow_forwardTOPIC: Machine Design Multiple choice Note: Please also provide a solution that proves the correct answer.arrow_forward6. It is desired to design a valve spring of I.C. engine for the following details: (a) Spring load when valve is closed 80 N (b) Spring load when valve is open = 100 N (c) Space constraints for the fitment of spring are : Inside guide bush diameter = 24 mm Outside recess diameter= 36 mm (d) Valve lift 5 mm (e) Spring stcel has the following properties: Maximum permissible shear stress = 350 MPa Modulus of rigidity 84 kN/mm? ried: 1 Wire diameter; 2. Spring index; 3. Total number of coils; 4. Solid length of sprine: 5. Freearrow_forward
- Problem. Consider the following problem. Find the displacement of node 4. Assume F2=200 N, F3=300 N, F4=400 N and Kı= 100, K2= 200, and K3= 300 N/mm. F. 3 2 3 4 Note: The stiffness matrix of individual springs should be first written, then the equilibrium equations at each node should be written, expanded in terms of nodal displacement, and used to perform the assembly of the global stiffness matrix of the problem. Then, the appropriate boundary conditions should be applied and the nodal displacement vector should be found. Every step should be shown; missing any step would result in point deduction even if the final answer is correct.arrow_forwardA helical compression spring is subjected to a maximum force, Fmax of 1250 N. The deflection of the spring corresponding to the maximum force should be approximately 30 mm. The spring index is 6. The allowable shear stress is 350 MPa and the modulus of rigidity is 81 370 N/mm². Design the helical spring by calculating the wire diameter, mean coil diameter, number of active coils and the total number of coils. State all assumptions and decisions in your design.arrow_forwardHi, I have been given this pin-jointed frame analysis to solve (see pictures of the structure attached). Can you help me? The Figure 2 attached is a simplified structure to undertake a structural analysis on a concept design for a low cost stroller/buggy for children. The buggy consists of a number of metal sections that are pin-jointed together. The buggy is designed to accommodate a child of mass no more than 20 kg, sat on the seat which is supported at four points (Fc) on the frame of the buggy. Assume that the weight of the child is equally distributed across all of the points indicated on Figure 2 as Fc. Assume that there are no additional forces applied to the handle of the buggy, that the buggy is static (stationary) and that the buggy, and the elements of the frame have no mass. At points A and G, there are roll supports. At Points B, F and D there are the pin supports. I am required to determine the following: 1) Draw a free-body diagram of the structure 2) Simplify the Free…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY