Question
Given that the glass is semicircular, what happens to the ray of light (bends towards the normal, bends away from the normal, or no refraction) as it passes through the curved surface (only) in cases (a) and (b)?
Write answer for each case. Use the figures for additional information.
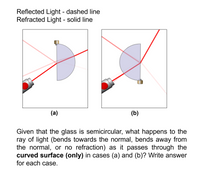
Transcribed Image Text:Reflected Light - dashed line
Refracted Light - solid line
(a)
(b)
Given that the glass is semicircular, what happens to the
ray of light (bends towards the normal, bends away from
the normal, or no refraction) as it passes through the
curved surface (only) in cases (a) and (b)? Write answer
for each case.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- For each ray (#1-4) what is the total phase shift of the ray along the path just due to reflection or refraction at the interfaces. (Your answer will either be zero or pi. Don't need to include phase shift differences due to path length differences).arrow_forward( Please type answer note write by hend )arrow_forwardCalculate the critical angle for the light traveling from glass (n glass= 1.54) to air (n=1.00). Express your answer in degrees. Normal format with 3 SF. airarrow_forward
- A ray of light travels through air until it strikes the interface between the air and another medium. The incident ray makes an angle of 0, = 32.0° with the normal, as shown in the figure below. Upon passage into the second medium, the ray is refracted, emerging from the interface at an angle 0, with respect to the normal. Air Second medium (a) Suppose that the second medium is polystyrene. What is the angle of refraction, 8, (in degrees)? (Enter your answer to at least one decimal place.) (b) Suppose that the second medium is sodium chloride. What is the angle of refraction, 8,, in this case (in degrees)? (Enter your answer to at least one decimal place.) (c) Finally, suppose that the second medium is glycerine. What is the angle of refraction, 0,, in this case (in degrees)? (Enter your answer to at least one decimal place.)arrow_forwardA beam of light both reflects and refracts at the surface between air and glass as shown in the figure below. If the refractive index of the glass is na, find the angle of incidence 0, in the air that would result in the reflected ray and the refracted ray being perpendicular to each other. (Use the following as necessary: n.:) 0, ng 0,arrow_forwardQuestion #1: Two plane mirrors are place perpendicular to each other. A laser hits mirror M1 30cm above the origin (0,0) as shown in the figure below. a) Find the distance from the origin where the laser will incident at mirror M2. b) How long it will take the laser to travel (in nano-second) from mirror M2 to the screen(situated 50 cm parallel to M1)? M1 25° Screen 300M M2 (0,0) is 5o cmarrow_forward
- Using the figure below, find the angles of refraction for a light ray passing from air into glass with the following angles of incidence: 5°, 10°, and 20°. 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 Angle in air (*) O10° %3D 020° Do you notice a trend in the resulting values? If so, describe it. O Doubling the angle of incidence approximately halves the angle of refraction. O Doubling the angle of incidence approximately doubles the angle of refraction. O Doubling the angle of incidence approximately quadruples the angle of refraction. There is no trend in the resulting values. Based on your observations, what would you predict the angle of refraction to be for an angle of incidence of 40°? How does your value compare with that inferred from the figure? () ssed u asuyarrow_forwardPlease Asaparrow_forwardA goldfish is swimming inside a spherical bowl of water having an index of refraction n = 1.333. Suppose the goldfish is p = 10.7 cm from the wall of a bowl of radius |R| = 19.2 cm, as in the figure below. Neglecting the refraction of light caused by the wall of the bowl, determine the apparent distance of the goldfish from the wall according to an observer outside the bowl.cm behind the glassarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios