
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
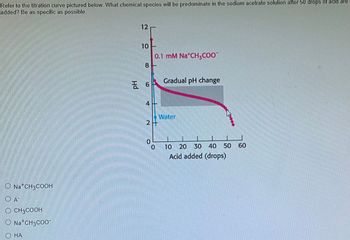
Transcribed Image Text:Refer to the titration curve pictured below. What chemical species will be predominate in the sodium acetrate solution after 50 drops of acid are
added? Be as specific as possible.
O Na+ CH3COOH
A
O CH3COOH
O Na+ CH3COO-
ⒸHA
12
10
8
6
0.1 mM Na CH3COO
4-
2+
0
0
Gradual pH change
Water
20 30 40 50
Acid added (drops)
10
10 20
60
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Circle true or false for each of the following T F Addition of sodium cyanide (NaCN) to hydrocyanic acid (HCN) would increase the pH. TFAbuffer solution can be made from a weak base and its conjugate acid. T F A buffer solution can be made from a strong acid and its conjugate base. T F The equivalence point of a strong acid-weak base titration will occur below pH 7.arrow_forwardExplain why pH is observed:● prior to titration● before the equivalence point is reached● at the equivalence point● past the equivalence pointarrow_forward65.0 mL of 0.575 M HNO, is titrated by 0.450 M KOH. Calculate the pH of the acid solution before any titrant is added. pH = 0.240 Calculate the pH after 50.29 mL of 0.450 M KOH is added to 65.0 mL of 0.575 M HNO pH = 0.882 3 Calculate the pH after 83.06 mL of 0.450 M KOH is added to 65.0 mL of 0.575 M HNO3. pH = 9.10 Calculate the pH after 154 mL of 0.450 M KOH is added to 65.0 mL of 0.575 M HNO3. pH = 13.18arrow_forward
- An aqueous solution contains 0.30 M ammonium bromide. One liter of this solution could be converted into a buffer by the addition of: (Assume that the volume remains constant as each substance is added.) 0.14 mol HCI O0.30 mol HCI O0.07 mol Ba(OH)2 0.29 mol NH3 0.29 mol CaBr2arrow_forwardSketch an accurate titration curve by plotting pH as a function of mL of HCl added when a 40 mL solution of 0.100 M ammonia is titrated with 0.100 M HCl include pH values when:0mL of HCl is added, 10 mL, 20 mL, 30mL and 40 mLarrow_forwardwrite legibly or typewritten for upvote unclear solutions will get downvotearrow_forward
- Which solution would be considered a buffer solution? 1) 0.50M NaF + 0.25M KF 2) 0.38M CH3COOH + 0.15M CH3COOH 3) 0.25M H2SO4 + 0.25M Na2SO4 4)1.25M LiNO3 + 0.50M HNO3 5) 0.50M NaCl + 0.50M HClarrow_forward4 Volume HCI Added (mL) Strong Base/Weak Acid Strong Acid/Strong Base Strong Acid/Weak Base Weak Acid/VWeak Basearrow_forwardA 25.0-mL sample of 0.30 M HCI is titrated with 0.30 M KOH. What is the pH of the solution after 3.3 mL of KOH have been added to the acid? Please report with 1 decimal place.arrow_forward
- A buffer solution contains dissolved C6H5NH2 and C6H;NH3CI. The initial concentration of C6H5NH2 is 0.50 M and the pH of the buffer is 4.20. Determine the concentration of C6H5NH3* in the solution. The value of Kb for C6H5NH2 is 3.8 x 10 10. ( PREV 1 3 NEXT > Based on your ICE table and definition of Kb, set up the expression for Kb in order to determine the unknown. Do not combine or simplify terms. Kp 3.8 x 10-10 %3D %3D 5 RESET [0] [0.50] [x] [2x] [4.20] [6.3 x 10-5) [1.6 x 10-10] [3.8 х 1011 [x + 4.20] [x - 4.20] [x + 6.3 x 10-51 [x - 6.3 х 10-5] [x + 1.6 x 101°] [x - 1.6 x 10-10] [x + 3.8 x 10-101 [x - 3.8 x 101°]arrow_forwardConsider a solution of a weak acid being titrated with a solution of a strong base to beyond the equivalence point. Which of the following statements is incorrect? a. The pH will increase intially and then change very little until the equivalence point is reached b. Only a small percentage of the weak acid will react with the added base c. The volume of the base solution required to reach the equivalence point can be less than, equal to, or more than the volume of the acid solution. d. At the equivalence point, the solution will be basic e. Beyond the equivalence point, the solution will be basic f. None of the above g. The pH of the solution in the tiration flask is affected by the total volume at any given pointarrow_forwardPlease answer all 3 questionsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY