
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Refer to the graph shown below. At point A:
Which is true?
A: the economy has full employment
B: economic growth is declining
C: inflation tends to be declining
D: wages can be lowered due to worker surplus
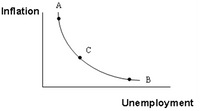
Transcribed Image Text:Inflation
B
Unemployment
A:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- While economists measure unemployment at the macroeconomic level, microeconomic forces are often responsible for this macro aggregate. In other words, the tie between microeconomics and macroeconomics is inevitable when discussing the level of unemployment in an economy. Suppose the following graph represents the market for unskilled labor in a fictional economy. These workers typically represent the young, inexperienced, or uneducated part of the labor force and are therefore most effected by changes in the unemployment rate. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this grapharrow_forwardThe Black Death: (a) Wages were higher after the Black Death because of diminishing returns. Our production model exhibits diminishing returns to labor: each additional unit of labor increases output by less and less. So if the amount of labor is reduced, the marginal product of labor — and hence the wage — increases. The reason is that capital stays the same: each remaining worker is able to work with more machines, so his productivity rises. In fourteenth-century Europe, the marginal workers could move to better land and discard old broken-down tools. Graphically, this can be seen by considering the supply-and-demand diagram for labor in Figure 4.2(b). If the supply of labor shifts back (because a large number of workers die), the equilibrium wage rate increases. Draw this graph — including the shift in the labor supply curve — to see the result for yourself. Mathematically, the result can be seen in the solution for the wage rate in our production model,…arrow_forwardThe graphs below depict the initial market for labor (on the left) and the macroeconomic production function (on the right). You will use these graphs to identify the effect of an increase in the number of available workers on employment, Potential GDP, and per-worker productivity. Suppose that a substantial increase in labor force participation increases the supply of labor by 40,000 workers at every value of the real wage. (1) Identify the effect of this event on equilibrium employment in the market for labor, and identify the specific new equilibrium level of employment. (2) Identify the effect of this event on Potential GDP, and identify the specific new level of Potential GDP. (3) Finally, identify the effect of this event on per-worker productivity, and identify the specific new level of per-worker productivity. You should embed a graph that clearly depicts (1) the correct supply shift in the market for labor, (2) the new equilibrium real wage, and (3) the new equilibrium…arrow_forward
- Assume that aggregate demand curve can be expressed by the following function: W = 55 - 3Q, while the aggregate supply curve can be expressed by the following function: W = 5+7Q. Here W denotes wage level in thousand dollar and Q denotes unit of labours in million people. What is labour equilibrium wage level and units of labour?arrow_forwardq5arrow_forwardWhich of these issues falls into the scope of microeconomics? a. The impact of interest rates on household purchases b. The impact of interest rates on gross domestic product c. The movement of the aggregate demand curve once interest rates rise d. The effect of an increase in interest rates on the price levelarrow_forward
- This is an intermediate macroeconomics subject question. Please explain clearly.arrow_forwardIf real GDP grows by 8% and population grows by 12%, then... a) the economy is in a recession b) inflation rate is stable c) standard of living is decreasing d) unemployment rate is increasingarrow_forwardWe live in a world where computers and other items of technology seem to get ever cheaper to produce. Such technology is important in the production of a vast range of consumer goods. We wish to analyse the impact of this phenomenon on two key pieces of economic data. The main impact of the decreasing cost of technology is that (select from consumption/investment/government spending/exports/imports/economy-wide production costs/wage costs) would (Select increase/decrease) This would shift the (Select one from the picture attached) which (Select: Increse or decreases the price level) and (Select: increases or decreases GDP) Suppose that the economy is now away from long run equilibrium (GDP is above Yf). The way that the economy adjusts back to equilibrium is that (Select: interest rates/the exchange rate/factor prices such as wages/governement spending) (Select: Increases/decreases). This shifts the (Select one from the picture attached)arrow_forward
- The following graph illustrates the market for cashews. It plots the monthly supply of cashews and the monthly demand for cashews. Suppose an increase in pests destroys a major portion of cashew trees. Show the effect this shock has on the market for cashews by shifting the demand curve, supply curve, or both. Note: Select and drag one or both of the curves to the desired position. Curves will snap into position, so if you try to move a curve and it snaps back to its original position, just drag it a little farther. PRICE (Dollars per ton) 30 24 18 12 6 0 0 4 8 12 Supply Demand QUANTITY (Thousands of tons) 16 Total Revenue (Thousands of Dollars) 20 Demand Supply ? One of the growers is pleased with the price increase caused by the pests because she believes it will lead to increased revenue. Using elasticities, you will be able to determine whether this price change will lead to a rise or fall in total revenue in this market. Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand…arrow_forwardWhich of the following is INCORRECT? In a typical month more than 5 percent of workers leave their jobs. Frictional unemployment is inevitable in a dynamic economy. Although the unemployment created by sectoral shifts is unfortunate, in the long run such changes lead to higher productivity and higher living standards. At least 10 percent of U.S. manufacturing jobs are destroyed every year.arrow_forwardRead the following passage to answer the question: Various countries, including South Africa, China and India, have established Special Economic Zones (SEZs) within their domestic economies. Firms that operate within these SEZS receive several incentives including tax relief, rent- free land, capital investment and training. This is done with the expectation to increase exports and to create job opportunities for local communities. Based on the passage, which one of the following statements regarding supply factors and demand factors that affect economic growth, is true? Select one: a. Tax relief, capital investment and training are not supply factors, nor demand factors. b. Creation of job opportunities for local communities will be positively influenced by demand factors. C. The fact that companies operating in SEZs do not have to pay rent, is a demand factor that will affect economic growth. d. Exports by firm's operating in SEZs form part of supply factors.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education