
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Refer to the attached figure. A loop of wire sits in a uniform magnetic field, everywhere pointing toward you. Due to a changing magnetic flux through the loop, an induced current flows in the wire, clockwise as shown. The area of the loop is 0.490 m^2 , and the magnetic field initially has magnitude 0.360 T. Suppose that, over a time period of 2.98 s, the magnetic field changes from its initial value, producing an average induced voltage of 0.036 V. What is the final value of the magnetic field after this time period?
0.695 T
0.579 T
0.290 T
0.463 T
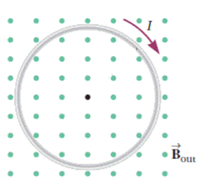
Transcribed Image Text:**Transcription for Educational Website:**
**Diagram Description:**
The image illustrates the concept of magnetic fields around a current-carrying wire using the right-hand rule. The diagram features a circular loop with an inward magnetic field denoted as \( \mathbf{B}_{\text{out}} \), represented by green dots uniformly distributed across the background, indicating the direction of the magnetic field going outward.
**Components:**
- **Circular Loop:** The loop is depicted as a grey circle, representing a wire carrying an electric current.
- **Current Direction (\( I \)):** Shown by a purple arrow along the loop, the current flows in a clockwise direction.
- **Magnetic Field (\( \mathbf{B}_{\text{out}} \)):** The magnetic field is indicated by the green dots that symbolize field lines directed outward from the plane of the loop.
**Magnetic Field & Current Relationship:**
The diagram underscores the principle that a current-carrying conductor (the loop) generates a magnetic field around it, which can be determined by the right-hand rule. According to the rule, if the thumb of the right hand points in the direction of the current, the fingers curl in the direction of the generated magnetic field outside the loop, in this case, out of the plane.
This illustration aids in understanding the interaction between current and magnetic fields, foundational to electromagnetic theory and its applications.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A single loop (N=l) of wire of radius r = 0.0300 m lies with its face parallel to the page. It is in an external uniform perpendicular magnetic field pointing OUT as shown in the diagram below by the dot surrounded by a circle ⊙. Suppose the external magnetic field magnitude is with rate △B/△t = 10.00 What is the area A of the wire loop? What is the magnitude IεI of the voltage induced in the wire loop ? The loop has resistance R = 40.0 Ω. What is the current I in the loop? In the figure below, indicate the direction of the current I, clockwise or counter-clockwise, in the loop. Draw a labeled curved arrow on the loop representing the current direction. In the figure below, indicate the direction of the induced magnetic field , in or out. Indicate this direction by drawing a labeled IN (×) or OUT ⊙ symbol within the circle.arrow_forwardA loop of wire sits in a uniform magnetic field, everywhere pointing toward you. Due to a changing magnetic flux through the loop, an induced current flows in the wire, clockwise as shown. The area of the loop is 0.610 m^2 , and the magnetic field initially has magnitude 0.950 T. Suppose that, over a time period of 2.23 s, the magnetic field changes from its initial value, producing an average induced voltage of 0.104 V. What is the final value of the magnetic field after this time period? 596 T 330 T 665 T 0.798 Tarrow_forwardA flat circular coil with 153 turns, a radius of 2.46 x 10-² m, and a resistance of 0.597 £ is exposed to an external magnetic field that is directed perpendicular to the plane of the coil. The magnitude of the external magnetic field is changing at a rate of AB/At = 0.743 T/s, thereby inducing a current in the coil. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at the center of the coil that is produced by the induced current. Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- 104 loops of wire lie in the plane of this page. A magnetic field pointing out of the page is increased from 0 → 4.5 T in 0.15 seconds. The loops each enclose an area of 1 m2. (a) What is the change in magnetic flux (∆ΦB) through one of the loops of wire in this time? (b) What is the induced voltage in the loops? (c) If the loops (combined) have a total resistance of 5 Ω, what will be the induced current in the loops? (d) In what direction will the induced current flow (clockwise or counterclockwise)?arrow_forwardA 185‑turn circular coil of radius 3.79 cm and negligible resistance is immersed in a uniform magnetic field that is perpendicular to the plane of the coil. The coil is connected to a 14.5 Ω resistor to create a closed circuit. During a time interval of 0.147 s, the magnetic field strength decreases uniformly from 0.537 T to zero. Find the energy ? in millijoules that is dissipated in the resistor during this time interval.arrow_forwardA loop of wire of radius a = 35 mm has an electrical resistance R = 0.038 Ω . The loop is initially inside a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B0 = 1.8 T parallel to the loop's axis. The magnetic field is then reduced slowly at a constant rate, which induces a current I = 0.20 A in the loop. How long does it take for the magnitude of the uniform magnetic field to drop from 1.8 T to zero? Find the time Δt it takes the magnetic field to drop to zero.arrow_forward
- A loop of wire sits in a uniform magnetic field, everywhere pointing toward you. Due to a changing magnetic flux through the loop, an induced current flows in the wire, clockwise as shown. The area of the loop is 0.300 m^2 , and the magnetic field initially has magnitude 0.300 T. Suppose that, over a time period of 2.30 s, the magnetic field changes from its initial value, producing an average induced voltage of 0.020 V. What is the final value of the magnetic field after this time period?arrow_forwardA coil of wire is made of 520 turns and has an area of 0.30 m². It is placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.40 T. This magnetic field flips its orientation from 0.40 T in the +y-direction to 0.40 T in the-y-direction in 2.0 s. (a) What is the change in magnetic flux and (b) the magnitude of the induced emf in the coil of wire?arrow_forwardProblem 3. A conducting rectangular loop is rotating in an external magnetic field as shown. B= 1 T,r= 0.1 m, f= 60 Hz. The length of the loop in the direction perpendicular to the picture is I = 0.3 m. (a) Find the voltage induced in this rotating loop. (b) Suppose that a 10 2 resistor is connected as a load across the terminals of the loop. Express the current flowing through the resistor as a function of time. You will need to make one simplification assumption; explain what it is. (c) For the conditions in (b), calculate the instantaneous and average electric power generated by the loop. (d) Same for mechanical power consumed by the loop. S N Barrow_forward
- A circular coil of wire has radius 0.37 m, with 979 turns of wire in the coil. It is located in a magnetic field of 1.90 T, directed perpendicular to the plane of the loop. (a) What is the magnetic flux through the loop (in T m²)? (b) Now suppose the coil is attached to a 160 ohm resistor, and the magnetic field decreases to 0 in 1 second. What is the induced current in the circuit?arrow_forwardYou are given a straight piece of conductor that is 5.0 cm long and moves in a region of uniform magnetic field of 1.6 T along the z-direction. If the conductor is oriented along the x-axis and moves in the y-direction with a velocity of 5.0 m/s, find the magnitude of induced voltage that will be produced between the ends of this moving conductor.arrow_forwardA square conducting hoop with side length 1.41 m is placed in a uniform magnetic field that points out the page. The loop lies perpendicular to the field. If the resistance of the loop is 4 w what is the magnitude and direction of the induced current as the magnetic field increases steadily from 2.0 T to 4.0 T in 10.0 secondsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON