
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
. Refer to Figure 3-3. Tanek’s
|
|
a. |
3/4 taco and Barb’s opportunity cost of one burrito is 1/2 taco. |
|
|
b. |
3/4 taco and Barb’s opportunity cost of one burrito is 2 tacos. |
|
|
c. |
4/3 tacos and Barb’s opportunity cost of one burrito is 1/2 taco. |
|
|
d. |
4/3 tacos and Barb’s opportunity cost of one burrito is 2 tacos. |
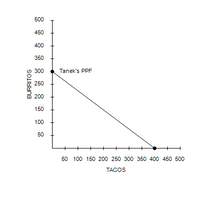
Transcribed Image Text:500
450
400
350
300
Tanek's PPF
250
200
150
100
50
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
TACOS
BURRITOS
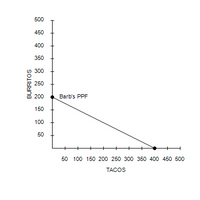
Transcribed Image Text:500
450
400
350
300
250
200
Barb's PPF
150
100
50
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
TACOS
BURRITOS
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Opportunity cost indicates the forgone benefits from the next best alternative.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6. The interaction of individual choices Immediately after an ice storm brought down power lines throughout the region, hardware stores were sold out of batteries and flashlights. However, within a couple of days, special deliveries brought in extra batteries and flashlights, and everyone who wanted to buy a flashlight or batteries was able to do so. Which of the following principles of economic interaction best describes this scenario? O Markets allocate goods effectively. O All costs are opportunity costs. O When markets do not achieve efficiency, government intervention can improve overall welfare. There are gains from trade.arrow_forwardPlease no written by hand and no imagearrow_forward2. Determining opportunity cost Suppose that Ciana is deciding whether or not to buy a pair of sneakers that she has been researching online, and also the best place to make her purchase. Three different stores in the area sell the sneakers she likes, but some stores are more convenient for Ciana to reach than others. One option is her local shoe store located only 15 minutes away from where she works, where they charge a marked-up price of $112 for the sneakers: Ciana earns an hourly wage of $42 at her job. In order to purchase her sneakers she will have to take time off work, so each hour away from her job costs her $42 in lost income. Assume that Ciana’s travel time is the same each way (to and from the store) and that it will take her 30 minutes once she reaches a store to complete her shopping. Assume throughout the question that Ciana incurs no additional costs other than the sneakers, such as gas. Complete the following table by computing the opportunity cost of…arrow_forward
- Suppose that an economy produces only 2 goods, beer and pizza. Show a typical production possibilities frontier for this country and use it to define and explain the opportunity cost concept and the concept of increasing opportunity costs. If a technology was invented that made the production of beer much more efficient but had no effect on the production of pizza how would the production possibilities frontier change (show it). While all points on the production possibilities curves maximize production, which point maximizes satisfaction? 1. With reference to a diagram, show and explain how a market, left on its own, will tend toward an equilibrium in which there is neither a surplus nor a shortage of the product. 1. What condition must be met in order to conclude that an economy is maximizing social well-being? Do the equilibriums given by individual markets necessarily lead to the maximization of social well-being (that is, if demand is equal to supply, can you conclude that…arrow_forwardAndreas has 10 hours available for knitting scarves and hats. It takes him 10 minutes to knit a scarf and 20 minutes to knit a hat. His current plan is to make 3 scarves and1 hat. What is his opportunity cost (in terms of hats) of knitting one more scarf than is in his plan?arrow_forwardPrice for good A is $6 and good b is $8. Budget is $36. Good A Good B Quantity Total Utility Quantity Total Utility 1 18 1 32 2 30 2 56 3 38 3 72 4 42 4 80 5 44 5 84 6 3 6 2 7 2 7 1 If the price of A decreases to $4, then the utility maximizing combination of the two products is what?arrow_forward
- please do the questions and the chocies for the last question is (high, low) thankyou!!arrow_forwardWhich one is false? Explain why that is false. 1. The production possibilities curve is a simple device for summarizing the possible combinations of output that a society can produce if it employs its resources efficiently. 2. One person has a comparative advantage over another in the production of a good if she or he can produce more of that good than the other person. 3. The Cost-Benefit Principle says that a person should take an action if, and only if, the benefit of that action is at least as great as its cost. 4. Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity buyers demand at the market price is exactly the same as the quantity that sellers offer. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for surearrow_forwardSuppose Liam's Automotive, a repair shop: offers two items: oil changes and tires. With all employees working diligently, the shop can produce these combinations each hour. Type of Product: Production Alternatives A B C D E Oil Changes 0 10 20 30 40 Tires. 80 60 40 35 0 Calculate the opportunity costs of moving from one point to each of the others (This is not a calculation provided in the text: What's the tradeoff?): Provide the answers after showing all work, and explain if theses costs are constant. What would it mean if the shop was actually doing 15 Oil Changes and 35 Tires? What would it mean if the shop was actually doing 35 Oil Changes and 35 tires?arrow_forward
- At one point along a PPF, 10 burgers and 7 sandwiches can be produced. At another point along the same PPF, 9 burgers and 10 sandwiches can be produced. The opportunity cost of a burger between these points is per burger. Select one: a. 7/10 of a sandwich b. 10/7 of a sandwich C. 3 sandwiches d. 1/3 of a sandwicharrow_forward5. Opportunity cost and production possibilities Raphael is a skilled toy maker who is able to produce both trucks and kites. He has 8 hours a day to produce toys. The following table shows the daily output resulting from various possible combinations of his time. Choice Hours Producing Produced (Trucks) (Kites) (Trucks) (Kites) A 8 0 4 0 B 6 2 3 10 C 4 4 2 16 D 2 6 1 19 E 0 8 0 20 On the following graph, use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot Raphael's initial production possibilities frontier (PPF). ( attached image) Suppose Raphael is currently using combination D, producing one truck per day. His opportunity cost of producing a second truck per day is( 1, 3, 16, 19 kites) per day. Now, suppose Raphael is currently using combination C, producing two trucks per day. His opportunity cost of producing a third truck per day is ( 1,6,10, or 16 kites) per day. From the previous analysis, you can determine that as…arrow_forwardThe production possibilities curve below shows the hypothetical relationship between the production of guns (national defense) and butter (social goods) in an economy. Combination A B C D E Guns O 20 60 80 100 Butter 8 6 4 2 0 Your response should be a number ONLY. 1. What is the marginal opportunity cost of moving from 2 to 4 units of butter? Guns. 2. What is the total opportunity cost of producing the four (4) unit of butter? Gunsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education