
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
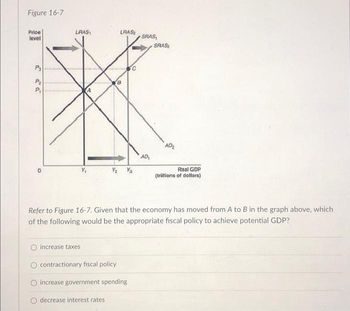
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 16-7
Price
level
P3
a
P₂
P₁
0
LRAS
A
increase taxes
LRAS
8
с
Y₂ Ya
contractionary fiscal policy
O increase government spending
O decrease interest rates
SRAS₁
AD₁
SRAS
AD₂
Refer to Figure 16-7. Given that the economy has moved from A to B in the graph above, which
of the following would be the appropriate fiscal policy to achieve potential GDP?
Real GDP
(trillions of dollars)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Real GDP Consumption (dollars) expenditure (dollars) 10 22.5 20 30 30 37.5 40 45 50 52.5 60 60 2 LAS 160 * SAS 150 140 130 120 AD 4 8 12 16 20 24 Real GDP (trillions of 2000 dollars) In the above table and figure, supposed that there is no import or proportional tax. To pull the economy back to the long-run equilibrium, the government can conduct a balanced budget operation by spending $ trillion. O 1) 1 O 2) 2 O 3) 4 4) 8 el (GDP deflator, 2000 = 100) Coarrow_forwardWhat would happen to output, employment, and the price level if the government increased spending on infrastructure, ceteris paribus? O Output would decrease, employment would decrease, and the price level would decrease O Output would decrease, employment would decrease, and the price level would increase O Output would decrease, employment would increase, and the price level would increase Output would increase, employment would increase, and the price level would decrease. O Output would increase, employment would increase, and the price level would increase Question 2(Multiple Choice Worth 5 points) (03.06 MC) Assume the price level is increasing, real GDP is decreasing, and the unemployment rate is increasing. Which event would explain this macroeconomic situation? OA positive supply shock OA negative supply shock A positive demand shock OA negative demand shock O insufficient dataarrow_forwardIn the United States, from the most recent fiscal data we reviewed in class, total government spending is roughly 39% of GDP; yet, using the expenditure method for calculating GDP, government expenditures on goods and services were only 17% of GDP. Which of the following most likely explains the difference? Select one: O a. Transfer payments are included in the second figure, but not the first one. O b. Transfer payments are included in the first figure, but not the second one. O c. Military (i.e. defense) spending on goods and services is included in the second figure, but not the first one. O d. Military (i.e. defense) spending on goods and services is included in the first figure, but not the second one.arrow_forward
- A Moving to another question will save this response. Question 23 Fiscal policy can move us to equilibrium at Full Employment by O a. these are all possible fiscal policies to bring us to full employment. O b. bailing out troubled industries with special subsidies like the "paycheck protection" during the pandemic. O c. making changes in G, net government spending. O d. changing tax rates people have to pay. A Moving to another question will save this response. tab 1 Q ABA 2 W E R Tarrow_forward8arrow_forwardSuppose the level of potential GDP is $6,000 billion, but the equilibrium level of GDP is $7,500 billion. If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.67, how much should government spending be decreased to eliminate the inflationary gap? O $250 billion $1500 billion O $500 billion O $125 billionarrow_forward
- If people expected that a fiscal policy in the form of a tax cut was temporary, then this policy's effect on the economy will tend to be: Select one: O a. Stronger O b. Weaker O c. The exact opposite of what was intended O d. As the multiplier effect would predict O e. None of the choicesarrow_forwardThe government budget constant for an economy is given below: G + TRị + rDt-1-7; = D¿ – Di-1 where G = government spending, TR is transfer payments, rD;-1 is interest payments on public debt, T is tax revenue and D is the stock of public debt. According to the government budget constraint in what way (or ways) can government expenditures be funded? O a. by a combination of tax revenue and borrowing from the public O b. by printing money O c. by tax revenue O d. by borrowing from the public O e. by borrowing from the central bankarrow_forward5. Expenditure Gaps The following graph shows the planned expenditure line (AE) for an economy where current equilibrium income is $400 billion and full-employment income is $650 billion. REAL EXPENDITURE (Billions of dollars) 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 0 100 45-degree line The economy is experiencing the income gap would require a $ this economy is PE Full-Employment Income 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 INCOME (Billions of dollars) billion PE ? billion. Closing in government spending. Thus the value of the multiplier for with the absolute value of the gap equal toarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education