
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
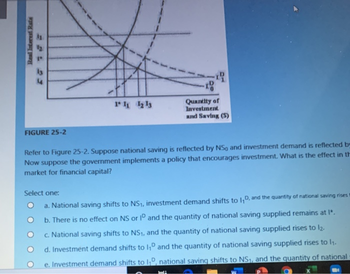
Transcribed Image Text:Real Interest Rate
1₂
1.
4
FIGURE 25-2
1 11 12 13
-10
Quantity of
Investment
and Saving (5)
Refer to Figure 25-2. Suppose national saving is reflected by NS, and investment demand is reflected by
Now suppose the government implements a policy that encourages investment. What is the effect in th
market for financial capital?
Select one:
a. National saving shifts to NS₁, investment demand shifts to 1₁D, and the quantity of national saving rises t
b. There is no effect on NS or ID and the quantity of national saving supplied remains at I".
c. National saving shifts to NS₁, and the quantity of national saving supplied rises to 12.
d. Investment demand shifts to 1₁D and the quantity of national saving supplied rises to 1₁.
e. Investment demand shifts to 1₁D, national saving shifts to NS₁, and the quantity of national
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION 2 Consider the closed-economy market-clearing model. Assume that the marginal propensity to consume is 0.8. Tax revenue decreases by $5 billion, while output and government spending remain the same (a) Calculate the dollar change in consumption. (b) Calculate the dollar change in national saving. (c) Does the equilibrium real interest rate increase, decrease, or stay the same? n toolhar nress ALT+F10 (PC) or ALT+FN+F10 (Mac).arrow_forwardpls also do the grapharrow_forwardRefer to the figure below to answer the following questions. Real interest rate (percent per year) CON 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 H H Select one: DLF₂ DLFO 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 Loanable funds (trillions of 2002 dollars) DLF₁ Refer to Figure 23.2.2. In Figure 23.2.2, a decrease the real interest rate will result in a movement from point E to A. point F. B. point G. C. point H. D. point. O E. either point G or point F. Figure 23.2.2arrow_forward
- During the financial crisis it was proposed that firms be provided with a tax credit for investment projects. Such a tax credit would shift: a. the demand for loanable funds left and shift the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange right. b. both the demand for loanable funds and the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange right. c. both the demand for loanable funds and the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange left. d. the demand for loanable funds right and shift the supply of dollars in the market for foreign-currency exchange left.arrow_forward41. Suppose that government institutes an investment tax credit and such policy generates an increase in the government budget deficit. This would: a. shift the saving curve (i.e. supply of loanable funds) to the left. b. cause the real interest rate to fall.arrow_forward4. Suppose gross saving in the United States is 20 percent of Gross National Product (GNP). a. If business saving is 15 percent of GNP and government saving is 4 percent of GNP, what percent of GNP is personal saving?b. Explain why a federal budget surplus increases national saving while a budget deficit decreases national saving.c. How can a federal budget deficit increase market equilibrium interest rates and reduce private investment and future economic growth?arrow_forward
- The diagram below show the market for financial capital assuming that national income is constant at potential GDP, Y*. Real Interest Rate I EL ME 14 FIGURE 25-2 NSO I 11 12 13 NS1 1 1 Quantity of Investment and Saving ($) Refer to Figure 25-2. Suppose national saving is reflected by NS, and investment demand is reflected by lo. Now suppose the government implements a revenue-neutral tax policy that encourages investment. What is the effect on the real interest rate? Select one: O a. There is no effect on NS or ID, and the interest rate remains at i*. O b. The real interest rate rises because of the decrease in the budget surplus. O C. National saving shifts to NS₁, and the real interest rate falls to i3. O d. Investment demand shifts to 1₁D, and the real interest rate rises to i₂. O e. The real interest rate falls because of the decrease in the budget surplus.arrow_forwardWhich group is most likely to demand funds from the financial (loanable funds) market? O financial institutions who lend funds to people. O the government when they run a budget surplus. O firms who want to borrow to pay for new capital. O people who have extra income they want to save. « Previous Next ASUS 16 5 6 7 Rarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education