
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
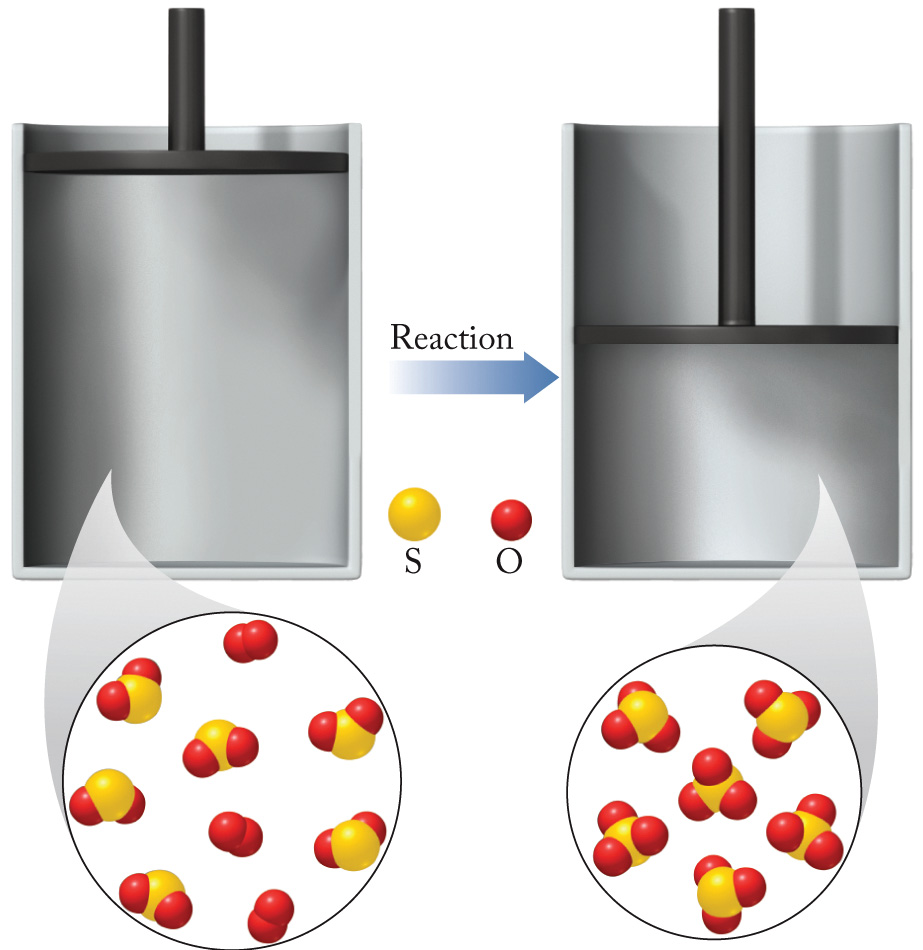
The process illustrated here takes place at constant pressure.
a.Write a balanced equation for the process. (Do not include states of matter. )
b. Is w positive, negative, or zero for this reaction?
A. Positive
A. Positive
B. Zero
C. Negative
c. Using data from the back of the textbook, calculate the ΔH°rxn for the formation of 6.00 moles of product.
kJ
kJ
Transcribed Image Text:Reaction
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 5.00 g of potassium hydroxide (molar mass = 56.1 g/mol) dissolves in 100.0 g of water and the temperature of the solution increases by 1.60oC. Calculate ΔH for the reaction in kJ/mol of KOH .The specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.18 J/goC ( Hint: the mass of the solution is 105g) (Hint #2: is this + or -?) Your answer should be in kJ/mol and have 3 sig figsarrow_forward-1. How much heat is released (in kJ) from 253 g of silver when it cools from 85 °C to 26 °C? The heat capacity of silver is 0.235 Jg C-¹. Hint: "heat released" means you should get a negative change in heat. But enter a positive number for this question.arrow_forwardOne mole of an ideal gas is contained in a cylinder with a movable piston. The temperature is constant at 78°C. Weights are removed suddenly from the piston to give the following sequence of three pressures. a. P₁ b. P2 c. P3 = 5.20 atm (initial state) = 2.53 atm = 1.00 atm (final state) What is the total work (in joules) in going from the initial to the final state by way of the preceding two steps? J What would be the total work if the process were carried out reversibly? Jarrow_forward
- A 2 mole sample of gas expands from a volume of 4 L to 10 L under a constant pressure of 12.5 atm before then dropping to a pressure of 5 atm (while remaining at 10 L). 2 moles of gas expands from a volume of 4L to 10 L under a constant temperature (300K). Which situation requires more work? Why?arrow_forwardWhen one mole of calcium carbonate reacts with ammonia, solid calcium cyanamide, CaCN2 and liquid water are formed. The reaction absorbs 90.1 KJ of heat. a. Write a balanced thermochemical equation for the reaction. b. Calculate ∆H°f for calcium cyanamide.arrow_forward4. Two solutions, initially at 24.60°C, are mixed in a coffee cup calorimeter (Ccal = 15.5 J/°C). When a 100.0 mL volume of 0.100 M AgNO3 solution is mixed with a 100.0 mL sample of 0.200 M NaCl solution, the temperature in the calorimeter rises to 25.30°C. Determine the AH°rxn for the reaction. Dsol'n = 1.00 g/mL. Csol'n = 4.184 J/g°C.arrow_forward
- General Chemistry 4th Edition McQuarrie • Rock • Gallogly University Science Books presented by Macmillan Learning Consider an ideal gas enclosed in a 1.00 L container at an internal pressure of 24.0 atm. Calculate the work, w, if the gas expands against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm to a final volume of 24.0 L. w = J Now calculate the work done if this process is carried out in two steps. 1. First, let the gas expand against a constant external pressure of 1.50 atm to a volume of 16.0 L. 2. From the end point of step 1, let the gas expand to 24.0 L against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm. w = Jarrow_forwardWhich of the following best defines molar heat capacity. a. The quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of a substance by 1K b. The quantity of heat required to lower the temperature of 1 liter of a substance by 1°C c. The quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1°C d. The quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1°Farrow_forward00 IN L OUniversity Science Book: presented by Macmillan Learning Stry 4th Edition McQuarrie Rock Gallogly Consider an ideal gas enclosed in a 1.00 L container at an internal pressure of 18.0 atm. Calculate the work, w, if the gas expands against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm to a final volume of 18.0 L. Now calculate the work done if this process is carried out in two steps. 1. First, let the gas expand against a constant external pressure of 1.80 atm to a volume of 10.0 L. 2. From the end point of step 1, let the gas expand to 18.0 L against a constant external pressure of 1.00 atm. = M Question Source: McQuarrie, Rock, And Gallogly 4e - General Chemsitry Publisher. University Science Books MacBook Pro Q Search or enter website name { [ 7. $4 P. 5. 4. U E. K. H. B. gEarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY