
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
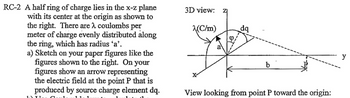
Transcribed Image Text:RC-2 A half ring of charge lies in the x-z plane
with its center at the origin as shown to
the right. There are λ coulombs per
meter of charge evenly distributed along
the ring, which has radius 'a'.
a) Sketch on your paper figures like the
figures shown to the right. On your
figures show an arrow representing
the electric field at the point P that is
produced by source charge element dq.
I TI Cul
3D view: zl
(C/m)
X
a
b
View looking from point P toward the origin:
y
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A very long straight thread is oriented at right angles to an infinite conducting plane; its end is separated from the plane by a distance 1. The thread carries a uniform charge of linear density X. Suppose the point O is the trace of the thread on the plane. Find the surface density of the induced charge on the plane (a) at the point O. (b) as a function of a distance r from the point O.arrow_forwardThe two sides of the DNA double helix are connected by pairs of bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). Because of the geometric shape of these molecules, adenine bonds with thymine and cytosine bonds with guanine. The figure (Figure 1) shows the thymine- adenine bond. Each charge shown is te, and the H-N distance is 0.110 nmarrow_forwardDon't Use Chat GPT Will Upvotearrow_forward
- A 47.0-m length of coaxial cable has an inner conductor that has a diameter of 2.58 mm and carries a charge of 8.10 µC. The surrounding conductor has an inner diameter of 7.27 mm and a charge of -8.10 µC. Assume the region between the conductors is air. (a) What is the capacitance of this cable? C = nF (b) What is the potential difference between the two conductors? AV = KVarrow_forwardA rod and two balloons A very thin glass rod 4 meters long is rubbed all over with silk cloth. It gains a uniformly distributed charge 1.2 x 10-6 C. Two small spherical rubber balloons of radius 1.2 cm are rubbed all over with wool. They each gain a uniformly distributed charge of -4 x 10-8 C. The balloons are near the midpoint of the glass rod, with their centers 3 cm from the rod. The balloons are 2 cm apart (4.4 cm between centers). Length 4 m (drawing not to scale) 2 cm 3 cm Radius 1.2 cm 0,6 cm (a) Find the net electric field at the location marked by the x, 0.6 cm to the right of the center of the left balloon. Things to think about: Which objects make nonzero contributions to E at this location? What are the correct distances from sources to the observation location? What is the direction ofE due to the rod? (The drawing is not to scale; read the problem statement carefully. Assume the +x axis is to the right, the +y axis is up, and the +z axis is out.) N/C What approximations…arrow_forwardAs shown in (Eigure 1), metal sphere A has 4 units of negative charge and metal sphere B has 2 units of positive charge. The two spheres are brought into contact. A T Touch B ♥ Part A What is the final charge state of each sphere? Express your answers in units of charge separated by a comma. 9A.9B = Submit 195] ΑΣΦ Request Answer 0 ?arrow_forward
- (b) When the silicon is in a certain position, the probe is 3.5 mm from it. The silicon must remain within 0.70 mm of this position. Determine the maximum allowable percentage decrease in the charge on the capacitor. k=2.8 x 10-15 Fm (4)arrow_forwardDon't Use Chat GPT Will Upvote And Give Handwritten Solution Pleasearrow_forwardA cube has sides of length L = 0.390 m. It is placed with one corner at the origin as shown in the figure (Figure 1). The electric field is not uniform but is given by E=(-4.40 N/(C. m))+(3.10 N/(C-m))ak Part A Find the electric flux through each of the six cube faces S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, and S6- Enter your answers in ascending order separated by commas. Figure S₁- (left side) L S₂ (top) 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46 = Submit Request Answer Part B Η ΕΕ ΑΣΦ Find the total electric charge inside the cube. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ q= <1 of 1 Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback So (back) S3 (right side) S4 (bottom) Ss (front) y ? C ? (N/C) m²arrow_forward
- A uniform electric field of magnitude 260 V/m is directed in the positive x direction. A +15.0 μC charge moves from the origin to the point (x, y) = (20.0 cm, 50.0 cm). (a) What is the change in the potential energy of the charge field system? ] (b) Through what potential difference does the charge move? varrow_forwardA charged nonconducting rod, with a length of 2.52 m and a cross-sectional area of 4.76 cm², lies along the positive side of an x axis with one end at the origin. The volume charge density p is charge per unit volume in coulombs per cubic meter. How many excess electrons are on the rod if p is (a) uniform, with a value of -4.66 µC/m³, and (b) nonuniform, with a value given by p= bx², where b = -2.18 µC/m²? (a) Number i (b) Number i Units Unitsarrow_forwardTwo point charges are on the y axis. A 4.90-µC charge is located at y = 1.25 cm, and a -2.04-µC charge is located at y = −1.80 cm. (a) Find the total electric potential at the origin. V(b) Find the total electric potential at the point whose coordinates are (1.50 cm, 0).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY