
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A particle of mass m moves in a circle of radius R at a constant speed υ as shown P11.13. Time t = 0 is defined as when the particle is at point Q. Determine the
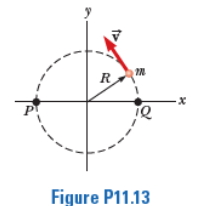
Transcribed Image Text:R
Figure P11.13
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 8arrow_forwardA circular disc of mass M and radius R is rotating about its axis with angular speed ω1 . If another stationary disc having radius R/2 and same mass M is droped co-axially on to the rotating disc. Gradually both discs attain constant angular speed ω2. The energy lost in the process is p% of the initial energy. Value of p isarrow_forwardA smooth rod of mass M, length L= 1 (m), is rotated at one end with a constant angular velocity w = 3 (rad/s) as shown in the figure. At t 0, an insect of m 0.02 (kg) moves from point O to the other end of the rod with a constant velocity of v = 2 (m/s) and stops at the end of rod. The angular velocity of the rod remains constant during the movement. Find the torque acting on the rod in (N.m) when the insect reaches to the end of rod (just before it stops). m M x = L A) 0.48 В) 0.16 C) 0.72 D) 0.24 E) 0.96arrow_forward
- The figure shows a device that can be used to measure the speed of a bullet. The device consists of two rotating disks, separated by a distance of d = 0.922 m, and rotating with an angular speed of 90.8 rad/s. The bullet first passes through the left disk and then through the right disk. It is found that the angular displacement between the two bullet holes is = 0.360 rad. From these data, determine the speed of the bullet. Number i Bullet Units 19 kd + Motorarrow_forwarda top with radius 10cm, mass 2 kg has a string around the edge and is initially at rest. assume the top can be reasonably approximated as a solid cylinder. the top is held in place as the string is pulled. the string applies a force of 10N tangential to the edge for 2s. what is the angular velocity (in radians per second) of the top after 3 seconds? what is the angular momentum of the top after the string is pulled? after the string is pulled, the top is released. it travels away from its initial position at a linear velocity of 10m/s. what is the rotational velocity (in radians per s) at this top? assume no frictionarrow_forwardPlease help mearrow_forward
- A solid cylinder of mass 4 kg and radius 2 m rotates with constant angular velocity of 5 rad/s about an axis through its center. What is the angular momentum of the cylinder?arrow_forwardA circular disc of mass M and radius R is rotating about its axis with angular speed ω1 . If another stationary disc having radius R/2 and same mass M is droped co-axially on to the rotating disc. Gradually both discs attain constant angular speed ω2. The energy lost in the process is p% of the initial energy. Value of p isarrow_forwardA ring (mass 4 M, radius 2 R) rotates in a CCw direction with an initial angular speed 2 w. A disk (mass 4 M, radius 2 R) rotates in a CW direction with initial angular speed 2 w. The ring and disk "collide" and eventually rotate together. Assume that positive angular momentum and angular velocity values correspond to rotation in the CCw direction. What is the initial angular momentum Lj of the ring+disk system? Write your answer in terms of MR2W. MR2W Submit Answer Tries 0/3 What is the final angular velocity wf of the ring+disk system? Write your answer in terms of w. Submit Answer Tries 0/3arrow_forward
- Two particles, each of mass 3.45 x 104 kg and speed 6.22 m/s, travel in opposite directions along parallel lines separated by 7.50 cm. (a) What is the magnitude L of the angular momentum of the two-particle system around a point midway between the two lines? (b) Is the value different for a different location of the point? If the direction of either particle is reversed, what are the answers for (c) part (a) and (d) part (b)? (a) Number Units (b) (c) Number i Units (d)arrow_forwardTwo particles, each of mass 3.45 x 10-4 kg and speed 6.22 m/s, travel in opposite directions along parallel lines separated by 7.50 cm. (a) What is the magnitude L of the angular momentum of the two-particle system around a point midway between the two lines? (b) Is the value different for a different location of the point? If the direction of either particle is reversed, what are the answers for (c) part (a) and (d) part (b)? (a) Number i Units (b) no : (c) Number Units (d) yes :arrow_forward(hrw8c11p28) A particle P with mass 9 kg has position vector r (r = 6.0 m) and velocity v (v = 35.0 m/s) as shown in the figure. It is acted on by force F (F = 11.0 N). All three vectors lie in the xy plane. About the origin, what is the z-component of the angular momentum of the particle? About the origin, what is the z-component of the torque acting on the particle?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON