
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Falcons are excellent fliers that can reach very high speeds by diving nearly straight down. To pull out of such a dive, a falcon extends its wings and flies through a circular arc that redirects its motion. The forces on the falcon that control its motion are its weight and an upward lift force—like an airplane—due to the air flowing over its wings. At the bottom of the arc, as shown, a falcon can easily achieve an acceleration of 15 m/s2.
Suppose the falcon weighs 8.0 N and is turning with an acceleration of 15 m/s2 at the lowest point of the arc. What is the magnitude of the upward lift force at this instant?
A. 8.0 N B. 12 N
C. 16 N D. 20 N
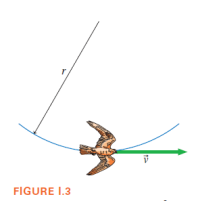
Transcribed Image Text:r
FIGURE I.3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You launch a projectile. It takes 3.9 seconds to reach its maximum height. What was the vertical component of the projectile's initial velocity? Neglect air resistance. 19 m/s 31 m/s 38 m/s 57 m/sarrow_forwardA soccer ball is kicked with a velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 45 degrees above the horizontal. What is the vertical component of its acceleration as it travels along its trajectory? A 9.8 m/s² downward B D 9.8 m/s² xsin (45°) downward 9.8 m/s² xsin (45°) upward 9.8 m/s² upwardarrow_forwardA package of mass m = 2.00 kg is released from rest at the top of an inclined plane as seen in the figure. The package starts out at height h = 0.100 m above the top of the table, the table height is H = 2.00 m, and 0 = 48.0°. H h m (a) What is the acceleration (in m/s²) of the package while it slides down the incline? m/s² m 0 (b) What is the speed (in m/s) of the package when it leaves the incline? m/s (c) At what horizontal distance (in m) from the end of the table will the package hit the ground? S (d) How long (in s) from when the package is released does it hit the ground? (e) Does the package's mass affect any of your above answers? Yes Noarrow_forward
- A basketball player jumps straight up for a ball. To do this, he lowers his body 0.320 m and then accelerates through this distance by forcefully straightening his legs. This player leaves the floor with a vertical velocity sufficient to carry him 0.880 m above the floor. (a) Calculate his velocity (in m/s) when he leaves the floor. (Enter a number.) m/s (b) Calculate his acceleration (in m/s2) while he is straightening his legs. He goes from zero to the velocity found in part (a) in a distance of 0.320 m. (Enter a number.) m/s2 (c) Calculate the force (in N) he exerts on the floor to do this, given that his mass is 108 kg. (Enter a number.)arrow_forwardA ball is kicked with an initial horizontal velocity of 16 m/s and initial vertical velocity of 10 m/s. What is the maximum height the ball goes above the ground? Use g = 10 m/s2.arrow_forwardA basketball player jumps straight up for a ball. To do this, he lowers his body 0.290 m and then accelerates through this distance by forcefully straightening his legs. This player leaves the floor with a vertical velocity sufficient to carry him 0.880 m above the floor. (a) Calculate his velocity (in m/s) when he leaves the floor. (Enter a number.) m/s (b) Calculate his acceleration (in m/s²) while he is straightening his legs. He goes from zero to the velocity found in part (a) in a distance of 0.290 m. (Enter a number.) m/s² (c) Calculate the force (in N) he exerts on the floor to do this, given that his mass is 114 kg. (Enter a number.) Narrow_forward
- You have put a sonar device at the top of a frictionless inclined plane. That device allows you to measure the distance an object is from the device, as well as the speed and the acceleration of that object. If we decide that the origin (h = 0) is at the sonar device, we want to know what the height change is as we slide down the incline. For an angle below the horizontal of 9.74°, we see that our object has slid a distance 0.54 m, as measured along the incline itself. - Calculate the height change and report your answer as a negative number. (This value would be useful for calculating the change in gravitational potential energy, as we will do in the lab.) h=o earrow_forwardA ball is kicked with an initial horizontal velocity of 16 m/s and initial vertical velocity of 10 m/s. What is the maximum height the ball goes above the ground? Use g = 10 m/s2.arrow_forwardA ball is suspended from a light 1.3 m string . The string makes an angle of 24 degrees with the vertical. The ball is then kicked up and to the right such that the string remains taut the entire time the ball swings upwards. This kick gives the ball an initial velocity of 1.1m/s. What will be the speed, in meters per second, of the ball when it reaches its lowest point (θ = 0)? What will be the maximum angle, in degrees, the string will make with the vertical?arrow_forward
- Falcons are excellent fliers that can reach very high speeds by diving nearly straight down. To pull out of such a dive, a falcon extends its wings and flies through a circular arc that redirects its motion. The forces on the falcon that control its motion are its weight and an upward lift force—like an airplane—due to the air flowing over its wings. At the bottom of the arc, as shown, a falcon can easily achieve an acceleration of 15 m/s2. A falcon starts from rest, does a free-fall dive from a height of 30 m, and then pulls out by flying in a circular arc of radius 50 m. Which segment of the motion has a higher acceleration?A. The free-fall diveB. The circular arcC. The two accelerations are equal.arrow_forwardAn astronaut exploring a distant solar system lands on a planet with a gravitational acceleration of 746 m/s. What is the maximum height an astronaut could reach when jumping straight up starting with an initial speed of 1.80 m/s?arrow_forwardYou are designing a high-speed elevator for a new skyscraper. The elevator will have a mass limit of 2400 kg (including passengers). For passenger comfort, you choose the maximum ascent speed to be 18.0 m/s, the maximum descent speed to be 10.0 m/s, and the maximum acceleration magnitude to be 3.40 m/s 2. Ignore friction. What is the minimum time it will take the elevator to ascend from the lobby to the observation deck, a vertical displacement of 640 m?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON