
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
(a) Find the point (A, B, C, D, or E) that corresponds to the profit maximizing
(b) Which number corresponds to
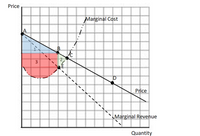
Transcribed Image Text:Price
Marginal Cost
2
3
Price
Marginal Revenue
Quantity
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The table below gives the quantity of fancy widgets demanded and the quantity supplied for selected prices. (a) Find the linear equation that gives the price as a function of the quantity demanded. (b) Find the linear equation that gives the price as a function of the quantity supplied. (c) Use these equations to find the market equilibrium price. Price Quantity ($) Demanded (thousands) Supplied (thousands) 40 50 60 70 100 Quantity 270 250 230 210 150 0 160 320 480 960 C (a) What is the price as a function of the quantity demanded? p=0 (Type an expression using q as the variable. Type your answer in slope-intercept form.) (b) What is the price as a function of the quantity supplied? p= (Type an expression using q as the variable. Type your answer in slope-intercept form.) (c) What is the market equilibrium price?arrow_forward25. According to the following points on a demand curve, which would be the ideal price for a company to sell its product to get the maximum amount of revenue or total income before substituting cost? A. At $75, the quantity demanded per month is five. B. At $50, the quantity demanded per month is 10. C. At $100, the quantity demanded per month is two. D. At $25, the quantity demanded per month is 12.arrow_forwardMULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Table 3-1 Loose Leaf Tea Price per lb. (dollars) Sunil's Quantity Demanded (lbs) Mia's Quantity Demanded (lbs) Rest of Market Quantity Demanded (lbs) Market Quantity Demanded (lbs) $8 4 0 30 6 7 2 40 5 9 3 51 4 12 5 64 3 15 8 90 12) Refer to Table 3-1. The table above shows the demand schedules for loose-leaf tea of two individuals (Sunil and Mia) and the rest of the market. At a price of $5, the quantity demanded in the market would be 12) ______ A) 51 lbs. B) 63 lbs. C) 76 lbs. D) 146 lbs.arrow_forward
- Question attahed in imagearrow_forward1. The graph below shows the Demand Curve and Supply Curve for a particular item (a) Label the Demand Curve and the Supply Curve. (b) Explain how you know which curve is the Demand curve and which curve is the Supply curve. (c) Label the Equilibrium Point (re. Pe) and mark z, and p, on the appropriate axes. (d) Shade and label the region whose area represents the Producer Surplus. (e) Shade and label the region whose area represents the Consumer Surplus. Show Transcribed Text S 2. The demand function for a product is p product is p²+12r+23. C and the supply function for the same (a) Sketch the graph of both the supply and demand functions (on the same axes) for 0 ≤ ≤ 10. Clearly label the axes and the curves (b) Find the equilibrium point (hint: do this with your calculator). Label the equi- librium point on your graph above. (c) Find the consumer's surplus at the equilibrium point. Show your organized work.arrow_forward3. Consider a market for custom plastic cups. The demand function is D(p) = 100 - 2p and supply is S(p) = 4p - 20. a. Calculate the elasticity of demand at any price. b. What is the equilibrium price? C. What is the elasticity of demand in equilibrium? d. Are revenues maximized at the equilibrium price? How do you know? If not, what should firms do to increase revenues?arrow_forward
- 1. Consider a linear demand curve D(p) = 60 - 3p. 1. Draw this demand curve on a graph. 2. When the price changes from 4 to 3, what is the associated change in consumer’s surplus?arrow_forwardWhich of the following factors would impact a buyer's reservation price for a given good or service? check all that apply Peer influenceunanswered The cost of producing the itemunanswered The price of a goodarrow_forwardEvaluate how the following situations will affect the demand curve for iPods. (a) Income statistics show that income of 18–25-year-olds have increased by 10 percent over the last year. (b) Efforts of music artists wanting greater protection of their music result in more stringent enforcement of copyrights and the shutdown of numerous illegal downloading sites. (c) Believing that it has significant control of the market for portable digital music players, Apple decides to raise the price of iPods with the goal of increasing profits. (d) The price of movie tickets decreases.arrow_forward
- Assume gadgets are sold in a competitive market, the equilibrium price is $6, and the equilibrium quantity is 500 units. (a) Using the numerical values above, draw a correctly labeled graph of the market for gadgets and show each of the following. (i) The equilibrium price (ii) The equilibrium quantity (b) At a price of $8 per unit, will there be a surplus or a shortage in the market? Explain. (c) Assume gadgets now become more popular. On your graph in part (a), show the effect of the increase in gadgets' popularity on the equilibrium price and quantity of gadgets. (d) Assume instead there is an increase in the price of tin, a major input in producing gadgets. What will be the effect of an increase in the price of tin on the market for gadgets? (e) If both changes in part (c) and part (d) occurred simultaneously, will the equilibrium quantity of gadgets increase, decrease, remain unchanged, or be indeterminate? Explain.arrow_forwardThe quantity demanded isA) the amount of a good that consumers plan to purchase at a particular price.B) independent of the price of the good.C) independent of consumers' buying plans.D) always equal to the equilibrium quantity.arrow_forward10. If supply changes from S2 to S1 and demand changes from D1 to D2 (a) equilibrium price falls to $ 14. (b) equilibrium quantity increases to 16. (c) equilibrium price increases to $19. (d) supply has increased. 11. if demand changed from D1 to D2 as a result of an increase in buyers' income this product is (a) a normal good. (b) a free good. (c) an inferior good. (d) a complementary good. 12. If demand for this product changed from D2 to D1 as a result of a increase in price of a related product, then these two products are (a) complements. (b) inferior goods. (c) economic goods. (d) substitutes. (e) public goods.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education