Arsenate is structurally and chemically similar to inorganic phosphate (Pi), and many enzymes that require phosphate will also use arsenate. Organic
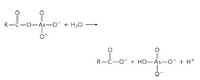
compounds of arsenate are less stable than analogous phosphate compounds, however. For example, acyl arsenates decompose rapidly by hydrolysis: On the other hand, acyl phosphates, such as 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, are more stable and undergo further enzyme-catalyzed transformation in cells.
(a) Predict the effect on the net reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase if phosphate were replaced by arsenate.
(b) What would be the consequence to an organism if arsenate were substituted for phosphate? Arsenate is very toxic to most organisms. Explain why.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- Pyrolysis gas chromatography is a particularly valuabletechnique for characterizing paint’s (binder, pigments).arrow_forwardMy question is in the picture.arrow_forwardBy now you’ve noticed that the cards represent charged ions. If you want to combine these ions to make a stable material, what does the total charge need to be on the final product? Ionic materials share similar properties when it comes to how they respond to forces, melting/boiling temperatures, how they interact with light, and how they conduct electricity. What are those properties, and what are the electrons doing that cause those observed behaviors?arrow_forward