
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
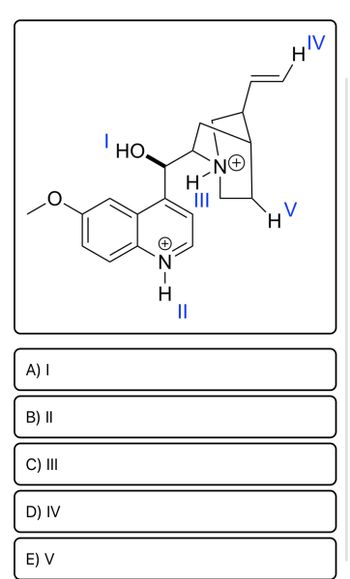
Transcribed Image Text:**Determine the most basic Nitrogen atom in this structure:**
The diagram provided is a chemical structure with several labeled hydrogen atoms (H) attached to nitrogen atoms (N+), marked with roman numerals I, II, III, IV, and V.
Underneath the structure, there are multiple-choice options:
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Please select the hydrogen atom that is attached to the most basic nitrogen atom in the structure.

This diagram shows the molecular structure of quinine, with certain protons labeled as I, II, III, IV, and V. The structural features include:
- A quinoline ring system on the left.
- A vinyl group (-CH=CH2) extending from the right side of the structure.
- A methoxy group (OCH3) and an alcohol group (OH).
- Two nitrogen atoms, one in the ring structure and one in a bridgehead position.
**Choices for the Most Acidic Proton:**
- **I:** Proton attached to the hydroxyl group (-OH).
- **II:** Proton attached to the nitrogen of the quinoline ring.
- **III:** Proton attached to the nitrogen of the bridgehead.
- **IV:** Proton attached to the terminal carbon in the vinyl group.
- **V:** Proton attached to the methine group (carbon adjacent to a double bond).
#### Answer Choices:
- **A) I**
- **B) II**
- **C) III**
- **D) IV**
- **E) V**
When evaluating the acidity of protons in a molecule, factors such as the stability of the conjugate base after deprotonation, resonance stabilization, and inductive effects must be considered. An acidic proton is typically one whose removal yields a stable conjugate base.
### Explanation of the Most Acidic Proton:
To solve for the most acidic proton in quinine, let's analyze each position:
1. **Proton I (OH Group):** The hydroxyl group can donate a proton to form a resonance-stabilized phenoxide ion, which can make this proton relatively acidic.
2. **Proton II (NH Group):** Protons attached to nitrogen can be relatively acidic due to the nitrogen's ability to stabilize the negative charge.
3. **Proton III (Bridgehead NH):** Similarly, this proton would be somewhat acidic due to nitrogen stabilization but may be less accessible.
4. **Proton IV (Vinyl CH):** A vinyl proton tends to be less acidic because removing this proton does not lead to significant resonance stabilization.
5. **Proton V (Methine CH):** This proton is also less acidic compared](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/468a1036-9eac-47e7-b3af-5f844e8c7d46/92f386a2-e1e2-477e-b3c6-eca4fc669c18/sv340i_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:### Organic Chemistry Exercise: Analyzing Quinine
**Quinine, found in tonic water, is shown below. Identify the most acidic proton from the choices I–V.**
#### Molecular Structure of Quinine

This diagram shows the molecular structure of quinine, with certain protons labeled as I, II, III, IV, and V. The structural features include:
- A quinoline ring system on the left.
- A vinyl group (-CH=CH2) extending from the right side of the structure.
- A methoxy group (OCH3) and an alcohol group (OH).
- Two nitrogen atoms, one in the ring structure and one in a bridgehead position.
**Choices for the Most Acidic Proton:**
- **I:** Proton attached to the hydroxyl group (-OH).
- **II:** Proton attached to the nitrogen of the quinoline ring.
- **III:** Proton attached to the nitrogen of the bridgehead.
- **IV:** Proton attached to the terminal carbon in the vinyl group.
- **V:** Proton attached to the methine group (carbon adjacent to a double bond).
#### Answer Choices:
- **A) I**
- **B) II**
- **C) III**
- **D) IV**
- **E) V**
When evaluating the acidity of protons in a molecule, factors such as the stability of the conjugate base after deprotonation, resonance stabilization, and inductive effects must be considered. An acidic proton is typically one whose removal yields a stable conjugate base.
### Explanation of the Most Acidic Proton:
To solve for the most acidic proton in quinine, let's analyze each position:
1. **Proton I (OH Group):** The hydroxyl group can donate a proton to form a resonance-stabilized phenoxide ion, which can make this proton relatively acidic.
2. **Proton II (NH Group):** Protons attached to nitrogen can be relatively acidic due to the nitrogen's ability to stabilize the negative charge.
3. **Proton III (Bridgehead NH):** Similarly, this proton would be somewhat acidic due to nitrogen stabilization but may be less accessible.
4. **Proton IV (Vinyl CH):** A vinyl proton tends to be less acidic because removing this proton does not lead to significant resonance stabilization.
5. **Proton V (Methine CH):** This proton is also less acidic compared
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- One water molecule can donate a proton to another in a process called the equilibrium constant expression for this reaction is O a. #,0* ][ OF] [H,0] он autoionization; Ob. [H,0* ][ O] [H,0]° protonation; Oc. [H,0* ][O ] [H,0] hydrolysis; Od. autoionization; [H30*][OH] Oe. [H,0* ][O ] [H,0] OHO neutralization;arrow_forwardWhich Represents the acid ionization constant of H3PO4arrow_forward15. Which of the following is the strongest acid? H OH OH О 16. Which of the following is the weakest acid? OH OH HH О 17. Which of the following is the strongest base? 18. Which of the following is the weakest base?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY