
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Question: Car BB is traveling along the curved road with a speed of 15 m/s while decreasing its speed at 2 m/s^2. At this same instant car C is traveling along the straight road with a speed of 30 m/s while decelerating at 3 m/s^2. (Figure 1)
Part A: Determine the direction of the velocity of car B relative to car C.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
Part B:
Determine the magnitude of the velocity of car B relative to car C.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
Part C:
Determine the direction of the acceleration of car B relative to car C.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
Part D:
Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of car B relative to car C.
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
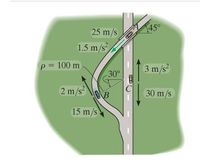
Transcribed Image Text:25 m/s
145°
1.5 m/s
p 100 m
3 m/s
30°
2 m/s
B
30 m/s
15 m/s
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How should the kinematic diagrams look for these two problems?arrow_forwardThis is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. A motorist starts from rest at Point A on a circular entrance ramp when t = 0, increases the speed of her automobile at a constant rate and enters the highway at Point B. Her speed continues to increase at the same rate until it reaches 85 km/h at Point C. Determine the speed at Point B. (You must provide an answer before moving on to the next part.) The speed at Point B is km/h. Note: please show step by step solution. Hence, double check the solution. For correction purposes!. I require handwritten working out please!. Kindly, please meticulously, check the image for conceptual understanding and for extra information purposes!. Also on occasions, I receive wrong answers!!. Please go through the question and working out step by step when you finish them. Appreciate your time!.arrow_forwards v(t) = {0.8t²i + 12t¹/²j+5k} m/s. The velocity of a particle is defined asarrow_forward
- At the instant shown, car A is traveling at a constant speed of va = 55 mph. At the instant shown, car B is mi traveling at a speed of vB = 20 mph, which is increasing at a rate of 1200 h2 * Hint: 1. Use the coordinate axes given in the image. VB y VA A Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value 0.75 miles 01 30 degrees a. Determine the velocity of car B relative to car A, VE, express as a Cartesian vector. b. Determine the acceleration of car B relative to car A, ag, express as a Cartesian vector. A c. Determine the magnitude of the velocity of car B relative to car A, VE d. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of car B relative to car A, agarrow_forwardAt a given instant A has the motion shown in (Figure 1). Figure 3 ft 1.5 ft- PA-3 ft/s -X a₁-681/² 1 of 1arrow_forwardPlease show step by steparrow_forward
- (b) The disc in Figure 3.2 has diameter 1 m and is rolling on the level ground with angular velocity 4 rad/s. Bar AB has length 1 m and is attached to the disc at A, while B slides on the ground. Determine the angular velocity of bar AB and the velocity of point B. 4 rad/s 1 m 1 m Figure 3.2arrow_forwardsolve part c and darrow_forwardQ.1 An object moves along the x-axis according to the equation x (1) =~ 3t +12t 6. where tis in seconds. For the time interval t=0 to t=3 s, (1) find the acceleration: (2) calculate the distance traveled: and (3) determine the displacement of the particle.arrow_forward
- Question: At the instant shown car A is traveling with a velocity of 30 m/s and has an acceleration of 2 m/s^2 along the highway. At the same instant, B is traveling on the trumpet interchange curve with a speed of 15 m/s, which is decreasing at 0.8 m/s^2. (Figure 1) Part A: Determine the direction of the relative velocity of B with respect to A at this instant. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units Part B: Determine the magnitude of the relative velocity of B with respect to A at this instant. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Part C: Determine the direction of the relative acceleration of B with respect to A at this instant. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Part D: Determine the magnitude of the relative acceleration of B with respect to A at this instant. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the…arrow_forwardTwo tractors leave point O at the same time and drive in the directions shown. Tractor A is traveling at a m m constant speed of va = 15 -. Tractor B is traveling at a constant speed of vz = 23 * Hint: 1. Use constant acceleration equations to find time. VA y VB А В 02 Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value 40 degrees 02 40 degrees a. Determine the velocity of tractor A relative to tractor B, VÁ, express as a Cartesian vector. b. Determine the magnitude of the velocity of tractor A relative to tractor B, VÁ. c. How long after leaving point O will the tractors be 600 m apart?arrow_forwardBar AB has the angular motions shown. Suppose that wAB = 3.8 rad/s and AB = 6.9 rad/s². (Figure 1) Figure AB AB 0.5 m 45° B 1m 60° 1 of 1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY