Question
The resultant vector R has an angle that is determined by
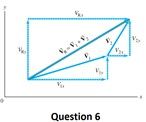
Transcribed Image Text:The image depicts a vector addition diagram, typically shown in physics or mathematics to illustrate the process of combining vectors. It features a grid with a horizontal \( x \)-axis and a vertical \( y \)-axis. Here is a detailed breakdown:
1. **Vectors:**
- \( \mathbf{V_1} \) is horizontally aligned from the origin towards the right on the \( x \)-axis.
- \( \mathbf{V_2} \) originates at the tip of \( \mathbf{V_1} \) and makes a diagonal upwards and to the right.
- The resultant vector \( \mathbf{V_r} \) is shown as a diagonal from the origin to the endpoint of \( \mathbf{V_2} \).
2. **Components:**
- \( \mathbf{V_{1x}} \) represents the horizontal component of \( \mathbf{V_1} \).
- \( \mathbf{V_{2x}} \) represents the horizontal component of \( \mathbf{V_2} \), depicted along the \( x \)-axis starting from the tip of \( \mathbf{V_1} \).
- \( \mathbf{V_{2y}} \) is the vertical component of \( \mathbf{V_2} \), shown as a vertical line from the tip of \( \mathbf{V_{2x}} \) up to the tip of \( \mathbf{V_2} \).
3. **Equation:**
- The diagram includes an equation \( \mathbf{V_r} = \mathbf{V_1} + \mathbf{V_2} \), which denotes the vector addition.
4. **Question Label:**
- Below the diagram, the text "Question 6" is displayed, indicating that it is part of a larger set of problems or exercises.
This diagram effectively demonstrates how individual vector components combine to form a resultant vector using the parallelogram or triangle method of vector addition.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Given
Two vectors and its resultant and their components along the x and y axis
We have to find what determines the angle made by resultant vector.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Vector A has a magnitude of 34 units and points in the positive y-direction. When vector B is added to A, the resultant vector A+B points in the negative y-direction with a magnitude of 18 units. Find the magnitude of B?arrow_forwardA unit vector is defined as a fixed vector which locates a point in space relative to another point. True Falsearrow_forwardTwo vectors A⃗ and B⃗ are at right angles to each other. The magnitude of A⃗ is 2.00. What should be the length of B⃗ so that the magnitude of their vector sum is 5.00?arrow_forward
- Vector A has a magnitude of 23 units and points in the positive y-direction. When vector B is added to A, the resultant vector A + B points in the negative y-direction with a magnitude of 15 units. Find the magnitude and direction of B.arrow_forwardA vector has a magnitude of 2.8 m and points in a direction that is 135 counterclockwise from the a axis. You may want to review (Page 71).arrow_forwardConsider two vectors A and B. A = 11 + 133 and B = 14 - 16 Find the unit vector that points in the same direction as the vector A + 2B. Write the unit vector in the form (U‚Î + U‚ĵ) N = U₁ =arrow_forward
- Vector A has magnitude 27 and direction 168°. Vector B has magnitude 39 and direction 270°. Find the resultant vector R, which is the sum of these two vectors.arrow_forwardFind the magnitude and angle of the resultant vector.arrow_forwardLet vector a= <-2,1> and vector b= <-4,-5>. Find the vector 3a+barrow_forward
- Vector A has magnitude 11 and angle 24°. Vector B has magnitude 11 and angle 114°. (a) What is the magnitude of the resultant vector? (b) What is the angle of the resultant vector in degrees?arrow_forwardDisplacement vector A points due east and has a magnitude of 3.87 km. Displacement vector points due north and has a magnitude of 6.59 km. Displacement vector & points due west and has a magnitude of 6.70 km. Displacement vector points due south and has a magnitude of 2.45 km. Find (a) the magnitude of the resultant vector A+++, and (b) its direction as a positive angle relative to due west. (a) Number (b) Number MI i Units Units <arrow_forwardFind the magnitude and angle of the resultant vector.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios