
Concept explainers
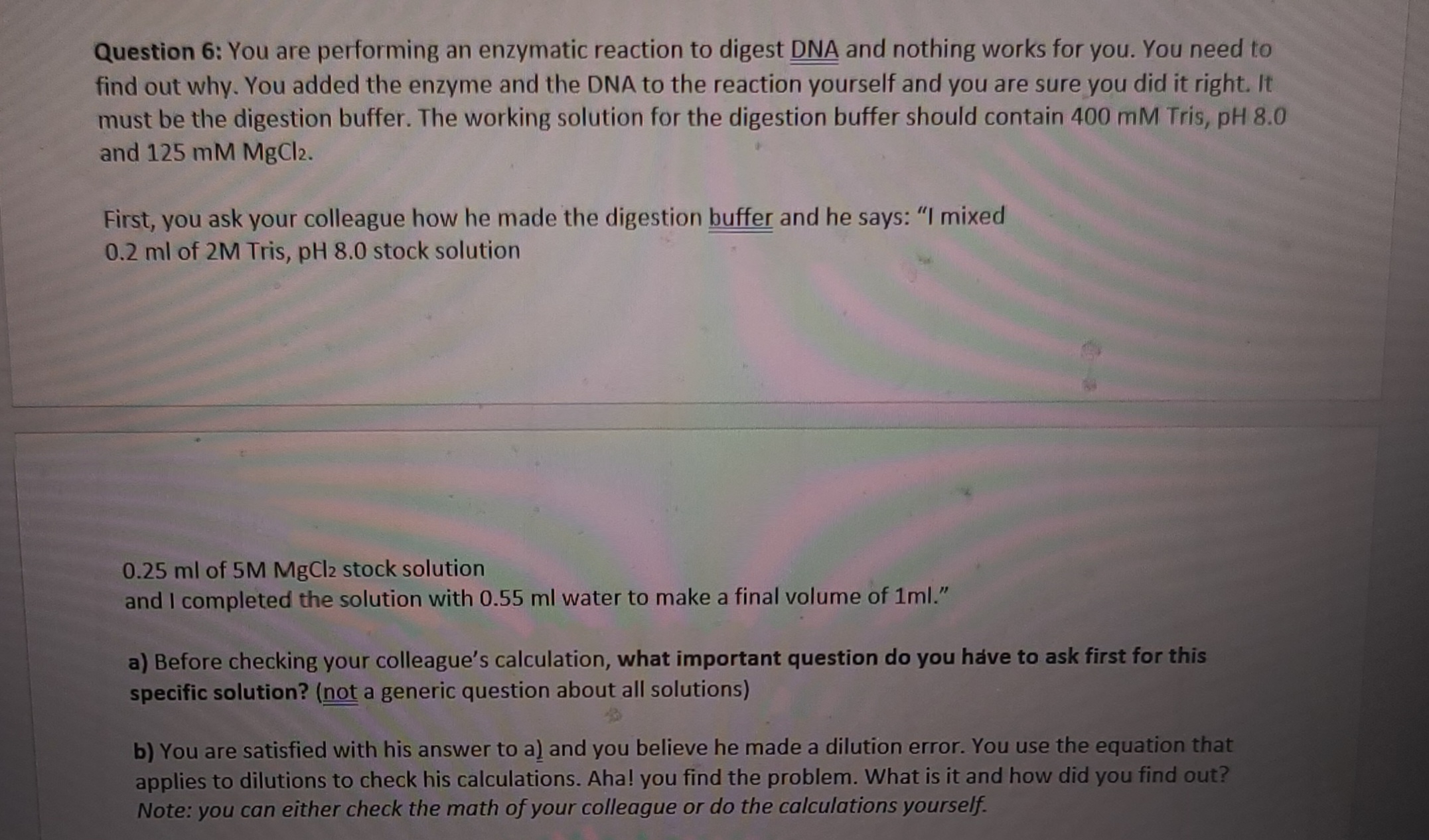
I could use some help with my biology lab assignment. I attached a picture of the question. I'm not sure how to solve and would love an explanation!
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions in living organisms. They function by lowering the activation energy required for a chemical reaction to occur, thereby speeding up the reaction without being consumed in the process. Enzymes are highly specific in the reactions they catalyze and can be regulated in various ways, such as through the presence of inhibitors or activators, post-translational modifications, or changes in pH or temperature. Enzymes are essential for many biochemical processes in the body, such as digestion, energy production, and DNA replication.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- Can i get a help answering this question: The case study tells you that the HIV virus exits the cell by budding, but how can you tell that just based on the structure of the HIV virus? (see attached for the case study)arrow_forwardI need help with the following question I dont understand a) and b)!!!!! Dr. Sharon Martin and her company have spent years working to identify how the gene for albinism works. The mutation in this gene causes no pigment to be produced in the hair, skin or eyes. Identifying the gene would open the door to curing the condition. Finally, her team succeeds. But, the years of research have been expensive. One way to make back the money is to patent the gene that the team members have identified. Then, anyone who wanted to develop either treatments or tests would have to pay a fee to use the gene. a) Do you think the government should allow this gene to be patented? Explain. b) If Dr. Martin’s company develops a test for this gene, should they be allowed to patent the test? Explain.arrow_forwardI need help getting the right answer for the queshtion typed out pleasearrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





