
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
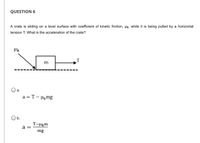
Transcribed Image Text:## Question 6
A crate is sliding on a level surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction, \( \mu_k \), while it is being pulled by a horizontal tension \( T \). What is the acceleration of the crate?
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows a crate with mass \( m \) on a flat surface. There is a horizontal arrow labeled \( T \) indicating the tension pulling the crate to the right. An arrow labeled \( \mu_k \) points leftwards at the crate, representing the direction of kinetic friction opposing the motion.
**Options:**
- **a.** \( a = T - \mu_k mg \)
- **b.** \( a = \frac{T - \mu_k m}{mg} \)
![The image presents a multiple-choice question related to physics, specifically focusing on the calculation of acceleration. The expressions provided are different equations for acceleration dependent on parameters such as tension, mass, gravitational acceleration, and kinetic friction.
The choices are labeled from c to e:
- **Choice c:**
\[
a = \frac{T + \mu_k mg}{m}
\]
- **Choice d:**
\[
a = \frac{T - \mu_k mg}{m}
\]
- **Choice e:**
\[
a = \frac{T}{m} - \mu_k g
\]
Where:
- \( a \) is acceleration.
- \( T \) is tension.
- \( m \) is mass.
- \( \mu_k \) is the coefficient of kinetic friction.
- \( g \) is the acceleration due to gravity.
Each equation provides a different approach to calculating the resultant acceleration of an object considering the forces acting upon it, such as tension and friction.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/679cbec7-7cf2-49ce-8f3f-bf2473fe518f/a84a5918-8b6c-4bfa-aaac-7bed2f65fedd/rw9aeuo_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:The image presents a multiple-choice question related to physics, specifically focusing on the calculation of acceleration. The expressions provided are different equations for acceleration dependent on parameters such as tension, mass, gravitational acceleration, and kinetic friction.
The choices are labeled from c to e:
- **Choice c:**
\[
a = \frac{T + \mu_k mg}{m}
\]
- **Choice d:**
\[
a = \frac{T - \mu_k mg}{m}
\]
- **Choice e:**
\[
a = \frac{T}{m} - \mu_k g
\]
Where:
- \( a \) is acceleration.
- \( T \) is tension.
- \( m \) is mass.
- \( \mu_k \) is the coefficient of kinetic friction.
- \( g \) is the acceleration due to gravity.
Each equation provides a different approach to calculating the resultant acceleration of an object considering the forces acting upon it, such as tension and friction.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Problem 1: Two objects are connected as shown, and the surface is frictionless. m1 = 121 kg, and m2 = 2 kg. m1 m2 Part (a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the masses in m/s2? Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression. a = Part (b) What is the tension in the cable in N? Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression. T =arrow_forwardThe top block is accelerated across a frictionless table by the falling mass m. The string is massless, and the pulley is both massless and frictionless. The tension in the string is Select one: a. T = mg %3D O b. T mgarrow_forwardThis time we have a crate of mass 47.8 kg on an inclined surface, with a coefficient of kinetic friction 0.289. Instead of pushing on the crate, you let it slide down due to gravity. What must the angle of the incline be, in order for the crate to slide with an acceleration of 3.66 m/s^2? a. 37.1 degrees b. 22.3 degrees c.59.4 degrees d. 29.7 degreesarrow_forward
- Pls help ASAParrow_forwardQuestion 3 A 18.0-kg crate is being pushed across a level frictionless horizontal floor by a force 150 N at an angle of 20.0° as shown. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the crate, in m/s27 Use g = 10.0 m/s2. Your answer needs to have 3 significant figures, including the negative sign in your answer if needed. (No unit is needed in your answer, it is already given in the question statement.) 20.0arrow_forwardmg m2g Example: In the figure below, two forces, pull a 50.0 kg crate. The magnitude of F is 215 N and it is applied at an angle 0 = 42.0°. The magnitude of F2 is 55.0 N. If the crate is accelerating to the right at a rate of 0.500 m/s2, find the friction between the crate and thé floor. Fiy= Fi sin42 = 215 sin 42 0 = 42° Fix F cos42 = 215 COs 42 W =mgarrow_forward
- Problem 2 Assuming that the system is in equilibrium and the rope with T is horizontal, find the tensions T1, T2, T3. 60.0° T T3 10.0 kgarrow_forwardPlz use g = 9.8 m/s2arrow_forwardThree boxes are pulled along a horizontal frictionless floor by a constant horizontal pull P. The boxes are connected by very light horizontal strings having tensions T1 and T2 as shown in the figure. Which of the following statements about the tensions is correct? T₂ T₁ 10 20 N N 100 N O A.T1 > T2 OB.T1 = P OC. T2 = P O D. T2 > T1 Parrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON