
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
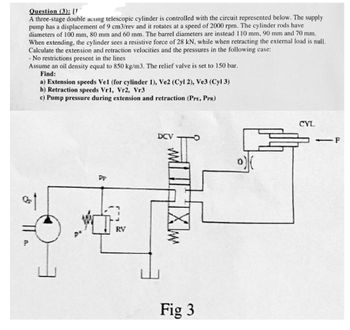
Transcribed Image Text:Question (3): [1
A three-stage double acung telescopic cylinder is controlled with the circuit represented below. The supply
pump has a displacement of 9 cm3/rev and it rotates at a speed of 2000 rpm. The cylinder rods have
diameters of 100 mm, 80 mm and 60 mm. The barrel diameters are instead 110 mm, 90 mm and 70 mm.
When extending, the cylinder sees a resistive force of 28 kN, while when retracting the external load is null.
Calculate the extension and retraction velocities and the pressures in the following case:
A.
- No restrictions present in the lines
Assume an oil density equal to 850 kg/m3. The relief valve is set to 150 bar.
Find:
a) Extension speeds Vel (for cylinder 1), Ve2 (Cyl 2), Ve3 (Cyl 3)
b) Retraction speeds Vr1, Vr2, Vr3
c) Pump pressure during extension and retraction (PPE, PPR)
πT
www
P
PP
RY
DCV
HXw
Fig 3
CYL
-F
-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step 1: determine the extension and retraction velocities
VIEW Step 2: Calculate flow rate of pump
VIEW Step 3: Calculate the extension and retraction speeds for each cylinder stage
VIEW Step 4: Calculate the pressure during extension and retraction for each stage
VIEW Step 5: Calculate the pump pressure during extension
VIEW Solution
VIEW Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 20 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- feedback--- difference between the setpoint and the measured position so the feedback can -- ----- result in violent and sustained oscillations within the system Positive/decrease/positive Positive/increase/positive Negative/increase/negative Negative/decrease/negativearrow_forwardAssume that you are to design a 3V V-belt drive. Given that input speed as 1750 rpm and nominal output speed as 725 rpm. Starting with belt linear velocity 4000 ft/min, specify the output sheeve D2 once you specify D1 from last question. D2 = ___ in. Provide write down steps including equations.arrow_forwardSuppose we have determined that the lowest natural frequency of a particular helical compression spring is 20286 rpm. According to the prescription in our book and according to the presentation in class, find the highest recommended operating frequency of a machine that utilizes this spring. Give your answer in rpm, but do not include units--Blackboard will not understandarrow_forward
- a lever with an input of 2 meters has a mechanical advantage of 4. What is the output arms length?arrow_forwardA manipulator’s end-effector position is calculated as follows:x = q0 cos q1 + l2 cos(q1 + q2),y = q0 sin q1 + l2 sin(q1 + q2),where q0,1,2 represent joint displacements and l2 is a constant positive parameter.Which of the following describes this manipulator:1) This is a robot-manipulator with 3 revolute joints.2) This is a robot-manipulator with 2 revolute and 1 prismatic joints.3) This is a robot-manipulator with 1 prismatic and 3 revolute joints.4) This is a robot-manipulator with 2 revolute joints. A robot’s end-effector’s tool position is defined asx = L1 cos(q1) + q3 sin(q1 + q2)where L1 = const, q1 = q1(t), q2 = q2(t) and q3 = q3(t) with t defining time. Calculate ∂x / ∂q3 1) it is impossible to calculate as the equation for the y and z positions are missing.2) cos(q1 + q2).3) it is impossible to calculate as time is not given.4) sin(q1 + q2).arrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forward
- For the spherical manipulator shown in the Fig. 1, derive the link parameters using D-H convention. Also find T. Fig.1arrow_forwardThe following EOMS describe the behavior of an electric motor attached to a torsional spring and damper: [Li + Rz + vb = Vin(t) IÖ= k0b0 + T Importantly, the equations are coupled by the fact that 7 = k₁z and v₂ = k₂0. Here, L, R, kv, I, k, b, and kt are constants. z is the current in the motor, and is the angular displacement of the motor (clearly then, is the motor's angular velocity). Finally, the input to the system is vin (t). Your tasks: A Substituting in the coupling terms (7 = ktz and v k0) into the EOMs, write the state space form of the system x = Ax + Bu, assuming your states are x₁ = z, x₂ = 0, and x3 = 0. Clearly identify your matrices. B Assume that the desired outputs of the system (to be measured) are the current z, the angle and the input Vin all as separate elements in the vector y. Write the output equation y = Cx + Du. Hint: D will NOT be zero in this case. Clearly identify your matrices C Assume there is no stiffness to the spring (k = 0). Using w(t) to represent…arrow_forwardQUESTION 1 Consider the equations of motion of an armature controlled DC motor given by Jw(t)+bw (t) Ki (t) = di (l) L + Ri (t) + Kw (t) = -Tfriction - Tload (t) Vin (t), dt where vin(t) is the input voltage and Tload(t) is the input load torque. The outputs are the armature current i(t) and the motor speed w(t). When the input voltage and torque are constant, the transient response of this system has the form of the homogeneous solution. What is the time constant of the transient response? Find the characteristic roots of this system first. Keep 3 significant figures, and do not include units. Use scientific notation. The constants are given below: Nominal voltage, Vin(t) = 17 V Moment of inertia of the rotor, J = 0.02 kg-m² Motor viscous friction constant, b = 0.009 N-m-s Friction torque, Tfric = 0.003 N-m Armature inductance, L = 0.1 H Armature resistance, R = 0.35 Back emf constant and motor torque constant, K = 0.21 N-m/A. **Recall that the time constant (or relaxation time) is…arrow_forward
- 5- Describe how would you check the degree of freedom for a system with multi masses.arrow_forwardA rotary actuator has the following physical data: Outer radius of rotor = 0.75 in Outer radius of vane = 1.5 in Width of vane = 0.75 in If the torque load is 1000 in lb, what pressure must be developed to overcome the load?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY