
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Question
2 (cont'd)
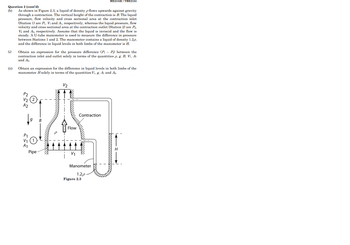
(b) As shown in Figure 2.3, a liquid of density p flows upwards against gravity
through a contraction. The vertical height of the contraction is B. The liquid
pressure, flow velocity and cross sectional area at the contraction inlet
(Station 1) are P₁, V₁ and A₁, respectively, whereas the liquid pressure, flow
velocity and cross sectional area at the contraction outlet (Station 2) are P₂,
V2 and 42, respectively. Assume that the liquid is inviscid and the flow is
steady. A U-tube manometer is used to measure the difference in pressure
between Stations 1 and 2. The manometer contains a liquid of density 1.2p,
and the difference in liquid levels in both limbs of the manometer is H.
(i)
(ii)
Obtain an expression for the pressure difference (PP) between the
contraction inlet and outlet solely in terms of the quantities p, g, B, Vi, A₁
and A₂.
ME2134E/TME2134
Obtain an expression for the difference in liquid levels in both limbs of the
manometer H solely in terms of the quantities V₁, g, A₁ and A₂.
V₂
A2
Contraction
14
Flow
Pipe
V/₁
Manometer
1.2p
Figure 2.3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Where necessary, assume air as an ideal gas and consider R = 287 J/(kg.K), Cp = 1005 J/(kg.K), Cv = 718 J/(kg.K). a) A nozzle is a device that is used to increase the velocity of a fluid by varying the cross-sectional area. At the last section of a jet engine (Fig Q1.a, section 5), air with a mass flow rate of 50 kg/s at a pressure of 500 kPa and a temperature of 600 K enters a nozzle with an inlet cross-sectional area of 5 m2. The exit area of the nozzle is 20% of its inlet area. The air leaves the nozzle at a velocity of 300 m/s. The nozzle is not well-insulated and during this process, 5 kJ/kg heat is lost.Figure Q1.a: Schematic of a Jet engine.(v) Calculate the pressure of the air as it leaves the nozzle.arrow_forward7. Blood is flowing through point P (Figure 2.5), which is connected to a catheter tip manometer system. Blood enters the manometer and equilibrates the pressure of the various fluids within the system (as denoted in the figure). Calculate the pressure within the blood vessel. Blood density is 1050 kg/m³, atmospheric pressure is 760 mmHg 25 cm Blood Fluid 1, P₁ = 879 kg/m³ Ja 45 cm 2 1 10 cm ✓ Fluid 2. P2 = 1200 kg/m³ Atmospheric pressure Figure 2.5 Schematic of a catheter tip manometer to measure intravascular blood pressurearrow_forwardM T M H₂0 2 blocks in water The figure shows two blocks of wood (A and B) connected by a string in a tank of water. The masses are equal (M 0.5 kg). 75% of block A is under water. The volume of block B is 454 cm^3. (a) Determine the tension force of the string. (b) Determine the density of block A. =arrow_forward
- The flow between two horizontal infinite parallel plates is a two-dimension, steady-state, incompressible and fully- developed flow. The distance between the plates is h m. The bottom plate is stationary and the top plate velocity is U. m/s in the x-direction. The flow is driven by the top moving plate and there is, therefore, no pressure gradient in the direction of the flow. Velocity in the y-direction, v = 0. Note: Align the x-axis to the bottom wall. Use the x-momentum equation to show that the velocity profile equation is (a) u(y) = ay + b and find the values of a and b. Use the energy equation to derive the temperature distribution T(y) for the flow if the surface temperature and temperature gradient on the bottom plate are both zero. (b)arrow_forwardA turbine model has the following characteristics: Effective power: 13, 6 kW; Rotor Diameter: 0.38 meters, Flow: 0.34 ms, Energy Jump: 26.5 J / Kg and 3 R.P.S. rotation It is desired to construct a geometrically similar 1.20 meter diameter turbine that provides a power on the 656 kW axis, we ask: to calculate and justify its answers: a) the specific rotation; b) the unit quantities (rotation, flow and power); c) the rotation, flow and power of the model (bi-unit quantities).arrow_forwardIf 10 m^3 of atmospheric air at 1 degree centigrade temperature are compressed to a volume of 1m^3 at 100°C, what will be the pressure of air?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY