
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
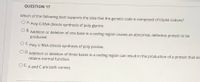
Transcribed Image Text:**Question 17**
Which of the following best supports the idea that the genetic code is composed of triplet codons?
- **A.** Poly G RNA directs synthesis of poly glycine
- **B.** Addition or deletion of one base in a coding region causes an abnormal, defective protein to be produced.
- **C.** Poly U RNA directs synthesis of poly proline.
- **D.** Addition or deletion of three bases in a coding region can result in the production of a protein that still retains normal function.
- **E.** A and C are both correct.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION 7 UUUUU..3' Rho-independent (intrinsic) terminators in bacterial transcripts consist of a sequence that forms a "hairpin" stem-loop structure, followed in the direction of transcription by a polyuridine (polyU) sequence, as shown in the figure above. Which of the following template strand DNA sequences, when transcribed, will form a terminator structure in the transcript? 5 CCGACGTATCCGACGTTTTTTTT3' 5'AAAAAAAACCGACGTATCGTCGG3' 5 CCGACGTATCGTCGGAAAAAAAA3' 5 TTTTTTTTCCGACGTATCGTCGG3' 5 AAAAAAAACCGACGTATGCAGCC3'arrow_forwardQUESTION 48 Identify the best match between the mutation description and term. a. Synonymous mutation: has the potential to cause large changes in transcription and subsequence amino acid sequence due to reading frameshifts b. Nonsense mutation: causes a drastic change in phenotype because the change causes a premature stop in the amino acid sequence c. Indel: a change in the DNA that changes the codon code from one amino acid to another amino acid d. Missense mutation: results in a change in single nucleotide from a purine to another purine or a pyrimidine to another pyrimidine but does not change the amino acid sequencearrow_forwardQUESTION 9 Which of the following step is NOT involved in eukaryotic MRNA synthesis? O Elongation O Polyadenylation O Rho-dependent termination Splicing Cappingarrow_forward
- Question 1: tRNA and amino acyl tRNA synthetases Part a: How many codons encode the amino acid Isoleucine (Ile, I)? Part b: How many codons encode the amino acid Valine (Val, V)? Part c: How many codons encode the amino acid Methionine (Met, M)? Part d: How many tRNAs decode the Ile codons? Part e: How many tRNAs decode the Val codons? Part f: How many tRNAs decode the Met codon?arrow_forwardQUESTION 16 CRISPR in nature evolved as a "bacterial immune system" or "genetic vaccine" to target infecting viruses. What aspect of the system can we now manipulate so that you can promote *more* transcription of a desired gene? O A nuclease deficient cas9 a single amino acid mutation in Cas9 o edit the PAM sequence supply a DNA template with the cas9/guide RNA use a special guide RNAarrow_forwardQuestion 12 What is the purpose of the inverted repeats at the ends of DNA-based transposons? A. The inverted repeats are recognized by restriction enzymes that cut out the transposon B. The inverted repeats are magnets for nucleases C. The inverted repeats are the sites of transfer on the target RNA D. The inverted repeats are recognized and cut by transposase to move the transposon from its original locationarrow_forward
- QUESTION 11 Which of the following statements about RNA interference pathways and mechanisms is FALSE? O A Investigators can load RISC and/or RITS complexes with artificial, designed RNAS in order to specifically target and silence a gene of interest as a way to see what the effect of that gene is when its expression is silenced. O B. Only a small section of a small interfering RNA, called the 'seed' sequence, is actually used to identify nucleic acid targets that are to be silenced. OC. Eukaryotic RNA interference pathways do not regulate genes from the genome itself (i.e. endogenous genes), they only respond to external infection events such as invading viruses. The piRNA pathway processes small RNAS out of long noncoding RNA transcripts and is important for suppression of repetitive element movement in germ cells. OD. O E. The micro (n RNA pathway and the short interfering (si) pathways load small RNAS into RISC or RITS complexes.arrow_forwardQuestion 10. A mRNA contains a codon with the sequence 5'-GAA-3'. Answer A and B for credit. A. What amino acid is encoded by this codon? B. What would be the most likely sequence of the anticodon in the tRNA that recognizes it? Write your answer starting with the 5' end and include 5' and 3' in your answer to get credit.arrow_forwardBefore the next elongation cycle can take place at a ribosome, the peptide chain of the peptidyl-tRNA has to be transferred to the ___ site and the deacylated tRNA has to move to the ___site. Question 46 options: A, P P, A A, E P, E there is no peptidyl transfer happening during protein translationarrow_forward
- 18arrow_forwardQuestion 6 of 10 can determine how an organism's The presence or absence of a single body works or how a cell does its tasks. O A. TRNA O B. ribosome O C. RNA O D. protein SUBMIT PREVIOUSarrow_forwardQuestion 7: At third codon positions, approximately what proportion of muations are synonymous? A. None B. 4% C.30% D. 70%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education