
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
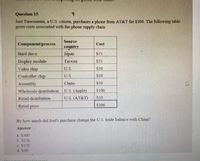
Transcribed Image Text:Question 15
Joel Tuoroniemi, a US. citizen, purchases a phone from AT&T for $300. The following table
gives costs associated with the phone supply chain
Source
Component/process
Cost
country
Hard dnve
Japan
S75
Display module
Video chip
Controller chip
Taiwan
$25
US
$20
U.S
$10
Assembly
China
$20
US (Apple)
US (AT&T)
Wholesale distrnbution
$100
Retail distribution
S50
Retail price
$300
By how much did Joel's purchase change the US trade balance with China?
Answer
a. $300
b. S150
e S120
d $30
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- DECREASING MARGINAL COST OCCUR FROM 0 TO20 TONS OF STEEL BECAUSE THE WORKERS A. WORK OVERTIME B. PRODUCE OUTPUT C. EARN A SALARY D. SPECIALIZE. ONLY TYPED SOLUTIONarrow_forwardFor distract drivingarrow_forwardThe owner of Barb’s Burgers has suggested the firm should invest in more moderntechnology and created a list of potential changes she thinks may be helpful as aninvestment. She has asked you to analyze the four potential choices and comment onwhat this would change in terms of cost:1. Build kiosks in the dining area for people to place their orders without having tointeract with a cashier. The kiosks would need also need to be integrated into thepoint of sales system to track orders for the kitchen Question: Argue how each of these is likely to change the cost of the firm once implemented (i.e. are any of these a fixed cost or a variable cost). How this adjust theamount of labour and/or capital currently necessary for the firm? Would the technology be a general technology, labour-saving, or capital-saving?arrow_forward
- Q) Economic Costs Owner/operators of small gas stations rarely pay themselves an hourly wage. How does this practice affect the economic cost of dispensing gasoline?arrow_forwardUse the diagrams to answer the following questions. Price and cost 20- 18 16- 14- 12 10 8 6 4 2+ o Market 1 488888 MC NO₂ MR 40 55 an in en nn minn Price and cost 20- 18- 16- 14 12- 10- 8- 6- 4- 2- 0 Market 2 0000000 MC NMR Annnnn in ED ORA on noinn If the firm wants to maximize profits, what price will it charge in Market 1, and what quantity will it sell? The firm will charge a price of $ using integers). Q and will sell a quantity of units. (Enter numeric responsesarrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- help please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forwardWorse than useless Europe's Emissions trading Scheme (ETS) has too many carbon emission permits trading at too low a price. Source: The Economist, January 25, 2014 Under what conditions would the ETS, a cap-and-trade system, reduce carbon emissions to the efficient quantity. Use a graph to illustrate your explanation. Also, show the outcome of issuing too many permits. The efficient quantity of emissions would be produced if the quantity of permits was set such that_ price O A. carbon emissions were eliminated; equal to marginal benefit OB. marginal private cost of electricity equals marginal benefit; above marginal external cost OC. marginal private cost of electricity equals marginal benefit; equal marginal external cost OD. marginal social cost of electricity equals marginal benefit; equal to marginal external cost OE. marginal social cost of electricity equals marginal benefit; below marginal external cost The graph shows the market for electricity production in the European Union…arrow_forwardPRICE (Dollars per room) 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 Demand 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Hotel rooms) Graph Input Tool Market for Lakes's Hotel Rooms Price (Dollars per room) Quantity Demanded (Hotel rooms per night) Demand Factors Average Income (Thousands of dollars) Airfare from DSM to ACY (Dollars per roundtrip) Room Rate at Mountaineer (Dollars per night) 350 150 50 100 200 ? For each of the following scenarios, begin by assuming that all demand factors are set to their original values and Lakes is charging $350 per room per night. If average household income increases by 10%, from $50,000 to $55,000 per year, the quantity of rooms demanded at the Lakes rooms per night to rooms per night. Therefore, the income elasticity of demand is from , meaning that hotel rooms at the Lakes are If the price of an airline ticket from DSM to ACY were to increase by 50%, from $100 to $150 roundtrip, while all other demand factors remain at their initial values,…arrow_forward
- (a) What is the profit-maximizing level of output and how much daily profit will the producer below earn if the price of pizza is $ 2.50 per slice? MC S/lice ATC AVe 2.50 1.40 slices/day S70arrow_forwardPRICE (Dollars per room) 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 Demand + 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Hotel rooms) Graph Input Tool Market for Oceans's Hotel Rooms Price (Dollars per room) Quantity Demanded (Hotel rooms per night) Demand Factors Average Income (Thousands of dollars) Airfare from DSM to ACY (Dollars per roundtrip) Room Rate at Meadows (Dollars per night) 300 200 40 200 rooms per night to ,hotel rooms at the Oceans and hotel rooms at the Meadows are 200 For each of the following scenarios, begin by assuming that all demand factors are set to their original values and Oceans is charging $300 per room per night. If average household income increases by 50%, from $40,000 to $60,000 per year, the quantity of rooms demanded at the Oceans rooms per night to rooms per night. Therefore, the income elasticity of demand is Oceans are ? from meaning that hotel rooms at the If the price of a room at the Meadows were to decrease by 20%, from $200 to $160,…arrow_forwardno handwritten notesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education