
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
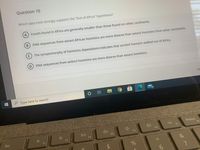
Transcribed Image Text:**Question 10**
Which data most strongly supports the “Out-of-Africa” hypothesis?
A) Fossils found in Africa are generally smaller than those found on other continents.
B) DNA sequences from extant African hominins are more diverse than extant hominins from other continents.
C) The synapomorphy of hominins (bipedalism) indicates that ancient humans walked out of Africa.
D) DNA sequences from extinct hominins are more diverse than extant hominins.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Out-of-Africa hypothesis -
Out-of-Africa hypothesis states that all modern human have been evolved from the single group of homo sapiens. This single group of homo sapiens have originated from the Africa. These homo sapiens originated from Africa. This species originated from Africa for about 2,000 generations ago.
These modern humans have spread to different parts of the world gradually in some years or generations.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The earliest hominins evolved toward the end of the Miocene or beginning of the Pliocene Epoch. True Falsearrow_forward66: The Vendija rockshelter and Krapina cave in Croatia contained ... Group of answer choices A: evidence that Aliens interbred with Neanderthals. B: elaborately ornamented modern human burials. C: evidence that dinosaurs ate Neanderthals. D: evidence that both Neanderthals and Modern Humans occupied them. E: fossils of Homo erectus.arrow_forwardHomo erectus … Group of answer choices: A.retained many arboreal adaptations not present in modern humans B.migrated to the island of Java by walking C.were about the same body size as chimpanzees D.reached Europe as early as 3 million years ago E.were the first hominids to reach the Americasarrow_forward
- A paleontologist finds a hominid fossil skull in a stratum dated at 4.4 MYA in eastern Africa. The skull has a relatively small braincasea and similarly-shaped teeth. Which of the following hominid species would the skull most likely be a fossil of? Homo erectus Ardipithecus ramidus Australopithecus africanus Homo neanderthalensisarrow_forwardPut the following hominins in order from the oldest to youngest in terms of when they first appear in the fossil record. The Denisovans Ardipithecus kadabbe Paranthropus Australopithecus aforensis Homo erectusarrow_forwardBecause the Laetoli footprints date to 3.6 mya and they are clearly made by a bipedal hominin, it is likely that they were made by Australopithecus afarensis, who appears to have been the only hominin around at that time. True O Falsearrow_forward
- The hominid evolutionary tree (Figure 20.19) Sahelanthropus tchadensis Orrorin tugenensis Ardipithecus ramidus Ardipithecus kadabba Au. anamensis Au. garhi Au. afarensis Au. africanus P. boisel - Homo Paranthropus = Australopithecus = early hominids = age of fossils - inferred relationships between hominid species -- relationships of major groups R aethiopicus P robustus H. ergaster H. habilis H. floresiensis Hrectus to H. neanderthalensis of hominids H. heidelbergensis H sapiens miocene pliocene pleistocene halocene 7. 5. 1. millions of years ago Figure 20.19 Evolutionary reconstruction of hominids; the human family tree. Age ranges of fossils are shown by red lines, and tan lines represent inferred relationships based on fossil evidence. Major groups are contained within colored boxes. Au. = Australopithecus; P. = Paranthropus; H. = Homo. %3D %3D %3D suggests that the genus Homo evolved a little over 2 million years ago. is reconstructed based on morphology and estimated age of…arrow_forwardWhat do you think about the hypothesis that language evolved as a way for early hominins to communicate about stone-tool manufacturing? What other hypothesis could you come up with as to why language evolved in our Hominini tribe?arrow_forwardHomo erectus was most likely the first hominid to successfully migrate to regions beyond Africa. Discuss how the biology and culture of Homo erectus led to its success on three major continents with varying environmentsarrow_forward
- Radiometric dating and the cranial capacity measurements are back from the paleolab for the specimen your friend at the museum called you about. She calls again to tell you the results. The cranial capacity is 442 cubic centimeters and it dates to 3 million years ago. After having identified the cranial traits present, you can now take this new information and provide, at least, the genus you think it could belong to in order to help your friend. Based on this information, choose from the options below, the category to which you think it most likely belongs. Group of answer choices Robust Australopithecine early Genus Homo Pre-Australopith Late Genus Homo Gracile Australopithecine Premodernarrow_forwardQUESTION 3 Which of the following are ways in which early hominins differed from apes? (select all correct answers) Increased bipedalism Decreased sexual dimorphism Lack of a tail Larger body sizearrow_forwardlist TWO similarities between early members of the genus Homo (e.g. H. habilis) and Homo erectus/ergaster that earlier hominins (e.g. gracile Australopithecines) do not have?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education