
Concept explainers
Different species of crickets have distinct songs, and
they use these songs for mate recognition. Researchers
crossed two species of Hawaiian crickets (Laupala paranigra and L. kohalensis) whose songs are distinguished
by pulse rate (the number of pulses per second; Shaw et
al., Molecular Ecology 16, 2007, 2879–2892.) Then, they
mapped QTL in the F2 population derived from this
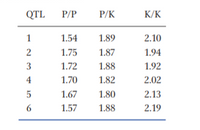
cross. Six autosomal QTL were detected. The mean trait
values (pulses per second) at the three genotypic classes
in the F2 for each QTL are shown in the table below,
where P indicates the L. paranigra allele and K indicates
the L. kohalensis allele.
a. Calculate the additive (A) and dominance (D) effects
and the D/A ratio for each of the six QTL.
b. Which of these QTL shows the greatest amount of
dominance?c. Which of these has the largest additive effect?
d. The mean pulse rate for L. kohalensis is 3.72, and it is
0.71 for L. paranigra. Do all six QTL act in the expected
direction with the L. kohalensis allele conferring a higher
pulse rate than the L. paranigra allele?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

- Entomologists at the New York State Department of Agriculture are interested in determiningthe connection between pest insects infesting crop plants with populations of the same insect-infesting native plants in natural habitats. Long-term trapping and monitoring studies have estimated that on average 3% of the populations move between habitats (farm to natural and vis versa) each generation. A new insecticide resistance allele (∆K) has begun to increase in frequency in agricultural populations. A genotyping survey at this locus of 50 individuals in each population has revealed the following genotype counts:4a. Based on the effects of migration alone, what will the frequency of ∆K be in the forestpopulation in the next generation? 4b. If migration was acting in here without selection, what would the frequency of ΔK be in the agricultural population in the next generation? 4c. If the natural forest population was substantially larger than the agricultural population, how might…arrow_forwardIn the Human Genome Project, researchers have collectedlinkage data from many crosses in which the male washeterozygous for molecular markers and many crosses wherethe female was heterozygous for the markers. The distancebetween the same two markers, computed in map units, isdifferent between males and females. In other words, thelinkage maps for human males and females are not the same.Propose an explanation for this discrepancy. Do you think thesizes of chromosomes (excluding the Y chromosome) in humanmales and females are different? How could physical mappingresolve this discrepancy?arrow_forwardThe question should be whether you reject or do not reject the Fisher test null hypothesis using data for all three institutions, not for two. Test that Mode ofInheritance is Autosomal Recessive forexperiments at each of three researchinstitutions At two research instructions, the parental cross is a affected(disease) male with an unaffected (wild‐type) female. Thecross of a male and female in the F 1generation produces thefollowing counts in the F 2generation: Question to be answered: Computethe Fisher Combined P‐value test using the data fromthe two sites, and draw a conclusion (reject, do notreject) the null hypothesis for the Fisher test, namelythat the specified MOI at each site is correct. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/aff2.68(only abstract) https://bigislandnow.com/2022/10/23/native-predatory-fish-help-control-invasive-species-in-hawaiian-fishpond-on-o%CA%BBahu/#:~:text=Jacks%20and%20barracuda%20in%20He%CA%BBeia,on%20the%20invasive%20mullet%20species.arrow_forward
- Please answer fastarrow_forwardParent Generation BB BB Bb Bb Bb Bb Bb Bb bb bb Rabbits with the brown coat color allele (B) are dominant over rabbits with the white coat color allele (b). A small population of rabbits (Parent Generation) has 2 individuals homozygous for B, 6 individuals that are heterozygous, and 2 individuals homozygous for b. What would you predict the frequencies of alleles B and b to be in the next (first) generation if this population is not evolving Edit View Insert Format Tools Tablearrow_forwardin a randomly mating laboratory population of Drosophila, 4% of the flies have black bodies, and 96% have brown bodies. Flies with brown bodies always have at least one parent with a brown body. What is the frequency of heterozygotes in this population? 0.04 0.16 0.08 0.32 The period gene of Drosophila melanogaster encodes for a stretch of Thr-Gly repeated in tandem. In natural populations, the three most common alleles encode for 17, 20 and 23 Thr-Gly repeats. The amplification by PCR of the allele encoding for 20 Thr-Gly repeats produces a fragment of 320 bp. Using the same set of primers, what is the size expected when amplifying the 17 Thr-Gly allele? 317 303 314 302 in a certain species of plant loci A, B and C have an additive effect on the colour of the flower. Alleles A, B, and C are dominant and alleles a, b and c are recessive. Knowing that a plant with genotype AAbbCc has a…arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





