
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
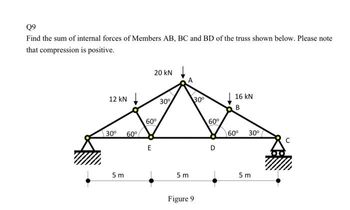
Transcribed Image Text:Q9
Find the sum of internal forces of Members AB, BC and BD of the truss shown below. Please note
that compression is positive.
12 kN
30⁰ 60°
5m
20 kN
60°
E
30%
5m
30⁰
Figure 9
60°
D
16 KN
B
60⁰ 30⁰
5m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 1. For the grid shown in Figure below, determine the nodal displacements and the local element forces. Let E = 30 x 106 psi, G = 12 x 106 psi, I = 200 inª, and J = 100 in for both elements. 5000 lb 7 2 10 ft 10 ft Xarrow_forwardConsider the frame shown in (Figure 1). Suppose that w = 410 N/m. Figure 1.5 m y 2m D E 3 m N 3m F 1.5 m B v W 1 of 1 Part A Determine the x and y components of force which the pin A exert on the frame using scalar notation. Express your answers using three significant figures separated by a comma. Ax, Ay = Submit Part B Ba, By = Submit ΑΣΦ Request Answer Determine the x and y components of force which the pin B exert on the frame using scalar notation. Express your answers using three significant figures separated by a comma. < Return to Assignment ΑΣΦ Request Answer ↓↑ vec ↓↑ vec ? Provide Feedback kN ? kNarrow_forwardGiven the loading criteria in the figure below, find all reaction forces. |80 kN 30 kN/m A B 2m 3m 2marrow_forward
- A force of Fi = (180 i -250j + 190k) lb is applied to the pipe assembly at point B. A force of F2 -250j + 250k) lb is applied to the pipe assembly at point D. The pipe assembly is supported by a fixed support at point A. (180 ? F1 В d3 C d1 d2 y F2 Values for the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale. Variable Value di 1 ft d2 2 ft dz 3.5 ft a. Determine the normal force at point C, Nc. Express as a Cartesian Vector. b. Determine the normal force at point C, Vc. Express as a Cartesian Vector. c. Determine the Torsional Moment at point C, Tc. Express as a Cartesian Vector. d. Determine the Bending Moment at point C, Bc. Express as a Cartesian Vector.arrow_forwardA shaft is composed of elements made of S355 with a modulus of elasticity of 2.1×1052.1×105 N/mm² and a Poisson's ratio of 0.3. As shown in the picture, on the right side, there are two forces of 10,000 N each, acting at an angle of 15° upwards, creating a moment that is statically compensated by the force F2 on the left side. The shaft is supported at positions A and B. In the same position (for simplicity), there are two critical cross-sections leading to stress concentrations. The sleeve near F2 is shrink-fitted. The dimensions there are d=50 mm, D=120 mm, and the length of the sleeve is 50 mm. Ha=1 µm and Hn=1 µm. The fit is H7/s6. Determine breell.arrow_forward2 B 2arrow_forward
- The structure is subjected to the loadings shown. Member AB is supported by a ball-and-socket at A and smooth collar at B. Member CD is supported by a pin at C. Suppose that F₁ = 280 N. (Figure 1) Figure 2 m 4 m 1.5 m 60° D B 60° C Z 45 F₁ 800 N-m 3 m ▼ Determine the z, y, z components of reaction at A using scalar notation. Express your answers using three significant figures separated by commas. ΓΙΑΣΦ Az, Ay, Az = Submit Part B Request Answer Cz. Cy. Cz = ΠΕ ΑΣΦ vec P Pearson Determine the x, y, z components of reaction at C using scalar notation. Express your answers using three significant figures separated by commas. → O ↓1 vec SMK ? SAVE ? N Narrow_forwardThe truss below is subject to the loads as shown. All of the members are attached at plates and can be treated as pin connected. The truss is attached to the ground at a pin joint at G and a roller at D. The applied load H is 335 N. The applied load Jis 211 N. What is the internal resultant normal force in member CD in N? (tension is positive, compression is negative) E F G A 3 m B |● ● H] 3 m 3 m D 5 marrow_forwardParvinbhaiarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY