
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
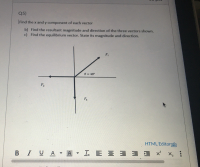
Transcribed Image Text:Q5)
Find the x and y component of each vector
b) Find the resultant magnitude and direction of the three vectors shown.
c) Find the equilibrium vector. State its magnitude and direction.
F1
e = 48°
%3D
F2
F3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Let the four compass directions north, east, south, and west be represented by unit vectors ne . . and respectively. Vertically up and down are represented as u and d. Let us also identify unit vectors that are halfway between these directions such as for northeast. Rank the magnitudes of the following cross products from largest to smallest. If any are equal in magnitude or are equal to zero, show that in your ranking, (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)arrow_forwardLet us name three perpendicular directions as right, up, and toward you as you might name them when you are facing a television screen that lies in a vertical plane. Unit vectors for these directions are r. u. and L respectively. Consider the quantity (-3 2t ). (i) Is the magnitude of this vector (a) 6, (b) 3, (c) 2, or (d) 0? (ii) Is the direction of this vector (a) down, (b) toward you, (c) up, (d) away from you, or (e) left?arrow_forwardUse the component method to add the vectors A and B shown in Figure P3.9. Both vectors have magnitudes of 3.00 m and vector A makes an angle of = 30.0 with the x axis. Express the resultant A+B in unit-vector notation.arrow_forward
- Vector A has a magnitude of 4.50 m and makes an angle of 64.0 with the positive x axis. Vector B, with a magnitude equal to that of vector A, points along the negative y axis (Fig. P3.16). Graphically find the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector a. A+B, b. AB, c. BA, and d. 2AB.arrow_forwardLet vector point from the origin into the second quadrant of the xy plane and vector point from the origin into the fourth quadrant. The vector must be in which quadrant, (a) the first, (b) the second, (c) the third, or (d) the fourth, or (e) is more than one answer possible?arrow_forwardA young boy throws a baseball through a window. a. Sketch the problem and pick a reference point. b. Use this reference point to draw a vector representing the initial and final position of the ball. c. Draw the displacement vector. d. Which of these vectors change if you pick a different reference point?arrow_forward
- A Three vectors all have the same magnitude. The symbol for the magnitude of each of these vectors is M. The first vector A points in the positive x direction. The second vector B points in the negative y direction. The third vector C points in the positive z direction. These three vectors added together are equal to a fourth vector D. What is the magnitude of the fourth vector?arrow_forwardThe displacement vectors A and B shown in Figure P3.9 both have magnitudes of 3.00 m. The direction of vector A is = 30.0. Find graphically (a) A+B, (b) AB, (c) BA, and (d) A2B. (Report all angles counterclockwise from the positive x axis.)arrow_forwardSee attached image. Please help me solve a and b. Don't need help with c and darrow_forward
- The direction of force P is given by an in-plane and out-of-plane angle. The direction of force Q is given using a similar triangle that is in the yz plane.a) Find the vector forms of P and Q.b) Find the resultant force and its direction cosine angles.arrow_forwarda.) Find the angle of the sum of the three vectors shown in the figure, measured counterclockwise from the positive x-axis.arrow_forwardA) Write the vector form of D, E, and F. B) Find F x D · E 7 in E 15 in 12 in F 10 inarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning