
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
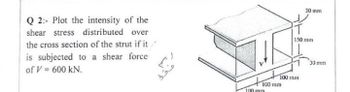
Transcribed Image Text:Q2: Plot the intensity of the
shear stress distributed over
the cross section of the strut if it
is subjected to a shear force
of V = 600 KN.
+100 mm
100 mm
100 mm
30 mm
150 mm
30 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question Three The three-bar truss ABC shown in the figure part a has a span L = 3 m and is constructed of steel pipes having cross-sectional area A = 3900 mm² and modulus of elasticity E = 200 GPa. Identical loads P act both vertically and horizontally at joint C, as shown. (a) If P=475 kN, what is the horizontal displacement of joint B? (b) What is the maximum permissible load value Pmax if the displacement of joint B is limited to 1.5 mm? P A 45° 45° B L (a)arrow_forwardA pin-jointed 2-D truss is loaded with a vertical load of 10 kN as shown in figure. The crosssectional area of the horizontal member is 150 mm² and cross-section areas of the members AC and BC are 200 mm² each. Modulus of elasticity of the truss material is 200 kN/mm². The magnitude of horizontal displacement (in mm, round off to two decimal places) of joint Cis A -6m 10 KN 5 m 4.5 marrow_forwardFor the beam and loading shown, determine the magnitude of the deflection at point C. The length of the beam, L, is 1,000 mm. The moment, M, is 55 kN·m. The flexural rigidity, EI, is 4.5X108 kN·mm2.arrow_forward
- A beam is subjected to equal bending moments of M, = 3500 N-m. The cross-sectional dimensions are b = 165 mm, c = 29 mm, d = 72 mm, and t = 3 mm. Determine: (a) the centroid location (measured with respect to the bottom of the cross-section), the moment of inertia about the z axis, and the controlling section modulus about the z axis. (b) the bending stress at point H. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. (c) the bending stress at point K. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. (d) the maximum bending stress produced in the cross section. Tensile stress is positive, while compressive stress is negative. M2 M2 H d (tур) K Answer: (a) y= i mm z= i mm4 S= i mm3 (b) OH = i MPa (c) σκ-i MPa (d) Omax i MPaarrow_forwardStructure analysisarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning