
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:QUESTIONS
Q1. Sodium sulphate decahydrate crystals (NażSO4.10H2O), DH are produced in a
continuous vacuum crystallizer. Concentrated sodium sulphate solution from an evaporation
system with a flow rate of 2000 kg/h at 80°C and 1 atm is mixed with 4000 kg/h of a saturated
aqueous recycle filtrate of sodium sulphate solution at 20°C and 1 atm. The mixture is sent to
the vacuum crystallizer, operating at 20°C and 50 mmHg, to produce water vapor and magma
of 25 wt% crystals and 75 wt% saturated solution. The magma is then sent to a filter, from
which filtrate is recycled.
a) Draw a block diagram of the process.
b) Define the streams and units in the block diagram.
c) Mark the streams on temperature versus concentration diagram and enthalpy
concentration diagram.
Determine:
d) crystal production rate (on a dry basis).
e) evaporation rate of water in vacuum crystallizer.
f) the energy required in vacuum crystallizer.
120
100
80
60
Na, so, + solution
solution
40
20
Na, so, 10H,O + solution
4
-20
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
Concentration of Na, SO,, kg Na,SO /kg solution
4"
Figure Q1-a. Solubility curve of sodium
sulfate in water.
Temperature, °c
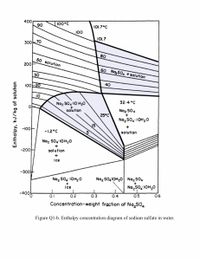
Transcribed Image Text:400
100°C
90
101.7°C
100
101.7
30070
80
50 solution
200
60 NazSO4 + solution
30
40
100-20
10
32.4°C
Na2 SOa 10 H20
solution
Na2 S04
+
25°C
Naz So4-1OH20
15
+
-100
-1.2°C
solution
Naz SO4 IOH20
+
-200
solution
+
ice
-300H
03H01.*os?ON
Naz SO¿IOH20 Noz sO4
ice
Na,so; 10H,0
-400!
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
Concentration-weight fraction of Na,SO,
Figure Q1-b. Enthalpy concentration diagram of sodium sulfate in water.
Enthalpy, kJ/kg of solution
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 100. mol/hr of a mixture of hexane (60.0 % by mol) and acetone are fed into a flash drum and separated into two streams. One exiting stream is composed of 80.0 % by mol acetone while the other exiting stream is composed of 90.0 % by mol hexane. Determine the total flow rates of both streams.arrow_forwardNaCl crystal is created from seawater within a series of evaporation and crystallization. A feed of 10 tons/hr of seawater containing 3.6% NaCl was mixed with a recycled stream of saturated brine solution at 40 Celcius before being fed to an evaporator where it is heated to 120 Celcius. The concentrated brine solution produced from the evaporator is 54% NaCl. This brine solution was fed to a crystallizer where it was cooled down to 40 Celcius to crystallize the NaCl. The crystals produced are 96.5% NaCl. The excess saturated liquor was mixed to the fresh seawater for recycle. The solubility of NaCl at 40 Celcius is 0.366 kg of water (H2O). Calculate: NaCI Crystals + H,0 Saturated Crystallizer Brine at 40°C Evaporator Mixer Seawater Concentrated Brine at 120°C Water Vapor a) crystals production rate kg/hr b) concentrated brine solution in kg/hr c) recycle stream flow rate in kg/hrarrow_forwardPlease note when values are sourced from an appendix/table. Include any assumptions.arrow_forward
- An inlet water solution of 800kg/h containing 12.0 wt % acetone is extracted with the solvent trichloroethane containing 0.5 wt % acetone in a countercurrent tray tower at 250C. The trichloroethane is essentially immiscible with water up to a concentration of acetone in water of 27 wt %. The exit concentration in the water stream is set at 1.0 wt % acetone. The equilibrium data is tabulated in Table 1. Table 1: The equilibrium data 0.0196 0.0467 0.0741 0.0909 0.0120 0.0294 0.0462 0.0571 0.0833 0.1081 0.1316 0.1304 0.1666 0.2000 a) Determine the minimum solvent rate needed for this extraction. b) Using 1.5 time the minimum rate, graphically determine the number of theoretical steps needed in the process. c) Calculate theoretical step using analytical equation d) For a packed tower with this sytem, the height of the transfer unit HoL has been estimated as 0.9m. calculate the number of transfer units NoL and the tower height in this process.arrow_forwardComplete the question by hand calculation(please show every step):-Do the mass balance, and find the flow rate of the vapour and liquid outlets of the last separator and purge stream and recycle stream flow rate for the following question by HAND CALCULATION:- Methanol can be produced from natural gas(syngas gas)the following syngas gas (feed) has the following conditions and composition 915 kgmole/hour Temperature 131.7 ºCPressure 1187 psiaComponent Composition (mol%)Carbon Monoxide 15.63Carbon Dioxide 7.93Hydrogen 73.31Nitrogen 0.33Methane 2.61Water 0.19TOTAL 100.00How the proccess flow diagram is attached to this question.Details of the process:- Firstly feed is mixed with the recycle stream using a mixer Output of the mixer is put into the reactorwhere the following two reactions occur:-CO2 + 3H2 <--> CH3OH + H2OANDCO + 2H2 <--> CH3OH Reactor output is cooled to from 246.3 degrees celcius to 37.78 degrees using a cooler(using 4.229e+007 of heatflow) Then the cooled…arrow_forwardA sealed 2-Liter container contains 1.2 L of water and 0.8 L of air. The temperature is 25°C. One hundred ug of a pollutant are added to the container. The container is then incubated until equilibrium is achieved between all two phases. KH is 10.7 L-atm/mol at 25°C. Assuming that no chemical or biological degradation occurs during incubation, what is the aqueous-phase concentration of the pollutant at equilibrium (mg/L)? R=0.08205 L-atm/mole-K.arrow_forward
- Consider an aerobic production of acetic acid (P) from ethanol (S) using Acetobacter aceti bacteria. Acetobacter aceti bacteria are added to vigorously-aerate medium containing 16 g/L ethanol. 3 g/L acetic acid is produced after 10 hours . Given the yield coefficient (YS/P) of 1.5, what is the concentration of ethanol after 10 hours ? Report your answer with two decimal places.arrow_forwardProblem 1. Air with 1.6 %mol SO₂ (you can assume very dilute conditions) is scrubbed with solute-free water in a packed column of 1.5 m² cross-sectional area and 3.5 m in height. The total gas flow rate is 0.062 kmol/s, the total liquid flow rate is 2.2 kmol/s, and the outlet air has an SO₂ mol fraction of 0.004. The equilibrium can be described by y*=40x. a) What is the minimum water flow rate required? b) How does the overall number of gas transfer units (NOG) compare to the number of theoretical stages required? c) What is the overall height of a gas transfer unit (HOG).arrow_forwardFastarrow_forward
- QUESTION 3 100 kg/s of solution containing 28 mass% CuSO4 is cooled slowly to 10°C to form crystals of CuSO4*5H2O. The solubility of CuSO4 at 10°C is 9.9 kg/ 100 kg water. It is estimated that 4% of the water entering the crystallizer is lost by evaporation. 3.1. Draw a diagram of the crystallizer showing all streams around it and use the yield method to calculate mass of crystals produced in the crystallizer. Additional information: Cu= 63.5 g/mol, H= 1 g/mol, S= 32 g/mol, O= 16 g/molarrow_forwardA liquid mixture of methanol and water contains 40 mole % methanol is fed into a flash vaporizationprocess operating at 82 C and 1 atm. The outlet vapour and liquid streams from the flash are inequilibrium and Raoult’s law is applicable for this system. (a) Draw the process and label it completely.(b) Examine the molar composition of the vapor and liquid phase and the ratio of liquid to feed stream. (c) If the temperature is further increased to 85 oC, examine the molar composition of the vapor and liquid phase and the ratio of liquid to feed stream. (d) Find the bubble point temperature of the feed stream at 1 atm.arrow_forwardQuestion: Consider the sugar–water phase diagram of Figure 10.1. (a) How much sugar will dissolve in 1000 g of water at 80°C (176°F)? (b) If the saturated liquid solution in part (a) is cooled to 20°C (68°F), some of the sugar will precipitate out as a solid. What will be the composition of the saturated liquid solution (in wt% sugar) at 20°C? (c) How much of the solid sugar will come out of the solution upon cooling to 20°C? Figure 10.1 is provided below.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The