
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
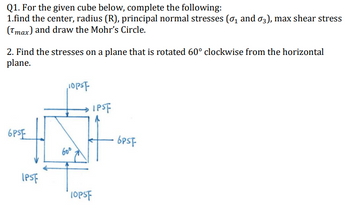
Transcribed Image Text:Q1. For the given cube below, complete the following:
1.find the center, radius (R), principal normal stresses (σ and σ3), max shear stress
(Tmax) and draw the Mohr's Circle.
2. Find the stresses on a plane that is rotated 60° clockwise from the horizontal
plane.
6PSE
IPSF
10pst
60⁰
TOPST
IPSF
6PSF
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- HWK 4-2.2-3: Find the shear stress about the neutral axis if V = 2000karrow_forwardJust complete the last part of this problem please (part 4). The mohr's circle drawing will help with a complete understanding of these types of problems.arrow_forwardGiven the stress element shown, determine the maximum in-plane shear stress, 0x = 54 MPa Oy = 30 MPa Txy = 40 MPa (Use the stress orientation shown in the figure to determine the sign on the stress values.) 58 MPal 65 MPa 74 MPa 88 MPa 96 MPa + 148 MPaarrow_forward
- Need only handwritten solution only (not typed one).arrow_forwardAn element in plane stress is subjected to stresses: 0 = 85 MPa, o, = -30 MPa, and Try = 32MPa, as shown in the figure below. (1) Determine the principal stresses and show them on a sketch of a properly oriented element; (2) Determine the maximum shear stresses and show them on a sketch of a properly oriented element. 30MPA 85MPA 32MPа 1arrow_forwardDetermine the stress resultants N(x), V(x), M(x) and draw the diagrams of the stress resultants and calculate the extremal values. At first, consider all parameters (F, a, L, ...) as variables and fill in their actual values at the end of your calculation.arrow_forward
- Find the Normal Stress at points A, B, and C in the Rod below. Dimensions given are diameters.arrow_forwarduse angle of 92 pleasearrow_forwardFor a plane stress state, in the original Oxy system we know the component Ox = 120 MPa and Txy = 60 MPa. After the element (see the left figure) is rotated counterclockwise by 45°, we know the stress component Txryı = -60 MPa in the new Ox'y' system (see right figure). Determine the two principal stresses and the absolute maximum shear stress (ra). y Oy Txıy! x' Txy Ox 45 хarrow_forward
- Problem 3. Strains are measured on the surface of a structural component as &A = = 1200 x 10-6. EB = 500 x 10-6, &c = 300 × 10-6. E = 200 GPa and v = 0.3. b) a) Find the principal stresses and show these on a sketch of a properly oriented element. Use Mohr's Circle to find the stresses at 0 = 30° counterclockwise from the x axis and show these on a sketch of a properly oriented element. y 60° C B A Xarrow_forwardConsider the following plane stress state: Ox=30 MPa, y= -60 MPa, Txy= 30 MPa cw Calculate the following: 1. The coordinates of the center of the Mohr's circle C The location of the center of the Mohr's circle Cis ( 2. Principal normal stresses (01, 02) The principal normal stresses are σ₁ = 39.08 3. Maximum shear stress (7) The maximum shear stress is 54.08 MPa. 4. The angle from the x axis to 0₁ (p) The angle from the x axis to 0₁ (p) is -16.85 5. The angle from the x axis to 7 (s) The angle from the x axis to T (s) is 28.15 6. The radius of the Mohr's circle The radius of the Mohr's circle is 54.08. ✰ MPa. MPa and 02 = -69.08 MPa. O -15 MPa, CW CCW O MPa).arrow_forwardAt a point on the free surface of a machine part (E = 214 GPa, G = 83 GPa), the state of the stress is illustrated in the figure below. For the given plane stress condition determine: -all 3 principle stresses, the max in plane stress, average noemal stress and the absolut max shear stress. - Show the principle stress, the max inplane shear stress and the average normal stress on an appropriate schematicarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY