
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:**Text Transcription:**
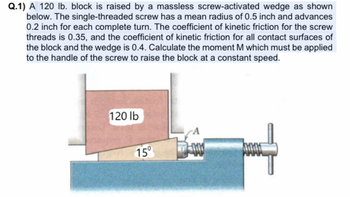
Q.1) A 120 lb. block is raised by a massless screw-activated wedge as shown below. The single-threaded screw has a mean radius of 0.5 inch and advances 0.2 inch for each complete turn. The coefficient of kinetic friction for the screw threads is 0.35, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for all contact surfaces of the block and the wedge is 0.4. Calculate the moment M which must be applied to the handle of the screw to raise the block at a constant speed.
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram illustrates a setup where a 120 lb block rests on a wedge inclined at 15 degrees. The wedge is connected to a screw mechanism. As the screw turns, it moves the wedge horizontally, which in turn raises the block vertically. The problem requires calculating the moment (torque) needed to apply to the screw handle to lift the block at a constant speed, taking into account the friction between the surfaces involved.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The uniform cylindrical drum D weighs 42.0 lb. The coefficient of static friction at all surfaces is 0.600, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.500 at all surfaces. The cylinder is pushed by force P applied to a pad as shown, and it is intended for the cylinder to translate horizontally without rotation. a) Calculate the minimum force P required.b) Calculate the acceleration of the drum.arrow_forwardDont forget to draw the FREE BODY DIAGRAMS ALSO PLEASE! (:arrow_forwardB1arrow_forward
- A uniform ladder 5 m long and weighing 80N rests against on a vertical wall at B and one end at A (on the ground). The angle of friction at all contact surfaces is 21.8°. Find the smallest angle 0 at which the ladder can be inclined with the horizontal before it is on its verge of slipping.arrow_forwardHelp Please.arrow_forwardPlease solve this question in handwritting. Again in handwritingarrow_forward
- The following lead screw and saddle arrangement is used to lift aload of 550 kg. The square thread has a pitch of 3 mm and a diameter of 15 mm. The coefficient of friction is 0.2. Calculate the torque required to rotate the screw on raising and lowering.arrow_forwardHigh-strength bolts are used in the construction of many steel structures. For a 1-in.- nominal-diameter bolt, the required minimum bolt tension is 51 kips. Assuming the coefficient of friction to be 0.30, determine the required couple that should be applied to the bolt and nut. The mean diameter of the thread is 0.94 in., and the lead is 0.125 in. Neglect friction between the nut and washer, and assume the bolt to be square-threaded. You must show a free body diagram of your block and incline analysis of the bolt and nut, and clearly indicate your force triangle, if any.arrow_forward4.) A flat belt makes contact with an 16 in. diameter pulley through half its circumference. If the coefficient of friction is 0.45 , and a torque of300ft−bsis to be transmitted, calculate the belt tensions. (please type answer not write by hend)arrow_forward
- An arrangement of three boxes is shown in figure below. Box A weighs 25 N and rests on an inclined plane, while box B weighs 50 N and rests on a horizontal plane. The coefficient of friction between box A and the inclined plane is 0.3, and between box B and the horizontal plane is 0.4. The pulleys are all frictionless. Determine the range of weight of box C for which no motion will occur. Consider both sliding and tipping of boxes A and B. 0.6 m 0.75 m 25 N 5 A 4 C pome 0.8 m 0.6 m 50 N B 1.2 marrow_forwardA 150lb man stands on a 60lb bar to which a cable is fixed at B. The cable passes over two fixed pegs with coefficients of friction indicated. Assume that the arrangement of the pegs permits the cable to contact each peg over a total angle of 90-degrees (90-degrees per peg). Assume that the normal force exerted by the man on the bar acts downward through A. Find the largest force the man can exert on the cable and maintain the bar horizontal.arrow_forwarddraw free body diagram and A and B please. picture is pretty clear! Block is labeled A (under A is 25 degrees) above is 45 degrees and F pulling down is 50 degreesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY