
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Are the following statements true or false? Explain your reasons.
For a firm with
If marginal cost is rising with increasing output, average cost must also be rising.
Fixed cost is the same at each output level except when no output is produced. When a firm produces no output, there are no fixed costs.
Allsmart’s demand curve is given by Q=10-P for its dishwashers. The marginal and average cost is $3 per dishwasher produced. Complete the following table.
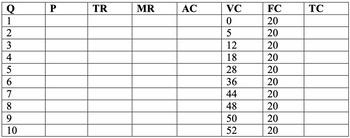
Transcribed Image Text:Q
P
TR
MR
AC
VC
FC
TC
12
0
20
5
20
3
12
20
4567
18
20
28
20
36
20
44
20
8
48
20
9
50
20
10
52
20
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The graph below shows the marginal cost (MC), average variable cost (AVC), and average total cost (ATC) curves for a firm in a competitive market. These curves imply a short-run supply curve that has two distinct parts. One part, not shown, lies along the vertical axis (quantity-0); this represents a condition of production shutdown. Where is the other part? Use the straight-line tool to drawit. To refer to the graphing tutorial for this question type, please click here Price and cost 18 15 14 13 12 10 19/21 SUBMIT ANSWER 13 OF 21 QUESTIONS C OMPLETED 28 MacBook Pro 금□ F7 F8 F9 F1o F2 F3 F5arrow_forwardDo not give handwriting solution.arrow_forwardWhen the marginal cost curve intersects the average variable cost curve, which of the following is true? Marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue. This is the quantity a firm would choose to produce in the short run. Average total cost is at its lowest point. Average total cost is at its highest point. Average variable cost is at its lowest point.arrow_forward
- assume your price is equal to marginal cost and marginal cost slopes upwards. in the short run, a firms profit max can only lie on the downward sloping part of its marginal cost curve. true or falsearrow_forwardUsing price (P), quantity (q), and average total cost (ATC), define profit rate (per unit profit), and total profits? Now assume you own a small business. Explain the difference between economic profits and accounting profits as concerns your business. What does it mean to say economic profit equals zero for your business and why does the firm continue to operate if economic profit equals zero (normal profit)?arrow_forwardScenario 15-2 The information below applies to a competitive firm that sells its output for $40 per unit. When the firm produces and sells 140 units of output, its average total cost is $24.5. When the firm produces and sells 141 units of output, its average total cost is $24.60. Refer to Scenario 15-2. Suppose the firm is producing 140 units of output and its fixed cost is $975. Then its variable cost amounts to O a. $9,360.25. O b. $2,455.00. O c. $3,430.00. O d. $7,500.00.arrow_forward
- For the pizza seller whose marginal, average variable, and average total cost curves are shown in the graph below, what is the profit-maximizing level of output and how much profit will this producer earn if the price of pizza is $1.50 per slice?Instructions: In the graph below, label all three curves by clicking on the dropdown to select the appropriate label. Instructions: Enter your response as a whole number. If you are entering a negative number, be sure to include a negative sign (−). When the price is $1.50 per slice, the profit-maximizing level of output is slices per day. Instructions: Enter your response rounded to the nearest penny (two decimal places). At the profit-maximizing level of output, the producer's profit is: $ per day.arrow_forwardThe two side by side graphs are for two firms that between them supply all the original grown advocados for a local area. With vigorous competition between the firms, the price per pound has settled at a point where both firms are just breaking even. For each firm, the marginal cost (mc) average variable cost (avc) and average total (atc) curves are shown In the blank graph below, use the straight line tool to draw a straight line representing the short run market supply curve for quantities above zero. (that is Dont worry about operating points for which the quantity is zero)arrow_forwardWhat is the firm’s total variable cost at this level of output? $ e. What is the firm’s fixed cost at this level of output? $ f. What is the firm’s profit if it produces this level of output? Instructions: If the firm is taking a loss, enter this as negative (−) profits. $ g. What is the firm’s profit if it shuts down? Instructions: If the firm is taking a loss, enter this as negative (−) profits. $ h. In the short run, should this firm continue to operate or shut down?arrow_forward
- Find the marginal cost, marginal revenue, and marginal profit functions. C(x) = 7x²; R(x) = x³ + 11x + 15 marginal cost marginal revenue marginal profit Find all values of x for which the marginal profit is zero. Interpret your answer. (Enter your answers as a comma-separated list.) X =arrow_forwardProblem 2. Restaurants in Baltimore operate under a total cost function TC(q) = 3q + 5q^2 + 30 Which part of the cost is fixed cost and which part of the cost is variable cost? What is the marginal cost, MC? What is the average total cost, ATC? What is the average variable cost, AVC? In the long run, calculate the equilibrium price and restaurants’ profits. Below what price will restaurants shut down? (Hint: Consider the AVC.)arrow_forwardConsider the market for ice cream. Suppose that this market is perfectly competitive. The cost structure of the typical ice cream producer is as follows. Average total cost is equal to 50 1 1 ATC(Q) +÷Q, average variable cost is equal to AVC(Q) =;Q, and marginal cost is equal to 2 MC(Q) = Q. Now, suppose that a new scientific study comes out that shows that soil pollution from rock salt (a key input for making ice cream) is extremely hazardous to human health. In response, the government decides to impose harsh re-zoning restrictions on any land once used for making ice cream. This reduces the market rent for land used to make ice cream, which in turn lowers the opportunity cost of operating an ice cream factory. This reduction in the opportunity cost of capital causes the total fixed cost of ice cream production to fall to 32, but there is no change to variable cost. Give formulas for the typical ice cream producer's new average total cost curve ATC(Q) and marginal cost curve MC(Q).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education