
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
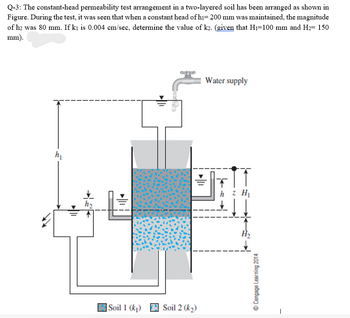
Transcribed Image Text:Q-3: The constant-head permeability test arrangement in a two-layered soil has been arranged as shown in
Figure. During the test, it was seen that when a constant head of h₁= 200 mm was maintained, the magnitude
of h2 was 80 mm. If ki is 0.004 cm/sec, determine the value of k2. (given that H₁-100 mm and H₂= 150
mm).
h₂
h₂
Soil 1 (k₁)
Soil 2 (K₂)
Water supply
TT
h z H₁
ⒸCengage Learning 2014
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A soil profile is shown in Figure P3.3 along with the standardpenetration numbers in the clay layer. Use Eqs. (3.8b)and (3.9) to determine the variation of cu and OCR withdepth. What is the average value of cu and OCR?arrow_forward9. A falling head permeability test was performed on a sand sample and the following data were recorded: = Cross-sectional area of permeameter = 100 cm2; length of the soil sample 15 cm; area of the stand pipe 8 min, = 1 cm2, time taken for the head to fall from 150 cm to 50 cm = temperature of water = 25°C; dry mass of the soil specimen 2.2 kg and its Gg = 2.68. Compute the coefficient of permeability of the soil for a void ratio of 0.70 and standard temperature of 20°C. (2 x 10 cm/s) =arrow_forwardPlease help answer problem 1,2 & 3 Thank youarrow_forward
- A falling head permeability test was carried out on a 15cm long of silty clay. The diameter of the sample and the stand pipe were 9.8cm and 0.75cm respectively. The water level in the stand pipe was observed to fall from 7ocm to 45cm in 12minutes. Determine the coefficient of permeability of the soil in m/day and the height of water level in stand pipe after 20minutes.arrow_forwardA constant head permeability test is performed on soil that is 4 cm2, and 2.5cm long. The head difference applied during the test is 20 cm and 7 cm3 is collected over a time of 100 sec. Then, falling head test is conducted on the same soil specimen at the same time (t1 – t2 = 100 sec), and the standpipe diameter is 0.8 cm. If the average head during the test should be 18 cm, what are h1 and h2 values, provide step by step solution solving h1 and h2 values.arrow_forwardThree CU tri-axial tests were performed oa samples retrieved from a 4-meter-thick layer of saturated clay layer (ysat-20.7 KN cubic meter). The top of the clay and the water level are at the ground surface. The results of these three tests (in kN/sq. m) are summarized ia the following table: Test Chamber Pressure, o3 Deviator Stress, Aod Pore Pressure@ Failure AU, (KNsq m) (KNsq m) 1) 82 171 -13 2) 156 302 -56| 3) 257 414 -84 a. Determine graphically and by formula the Motr-Coulomb effective shear strength parameters e (in kN'sq m) aad o b. Estimate the shear strength in the middle of the clay layer in kN/sq m.arrow_forward
- Homeworks 2. The following results were obtained from an oedometer test on a specimen of saturated clay: Pressure (kN/m?) 27 54 107 214 429 214 107 54 Void ratio 1.243 1.217 1.144 1.068 0.994 1.001 1.012 1.024 A layer of this clay 8m thick lies below a 4m depth of sand, the water table being at the surface. The saturated unit weight for both soils is 19kN/m3. A 4m depth of fill of unit weight 21 kN/m3 is placed on the sand over an extensive area. Determine the final settlement due to consolidation of the clay. -1 e -eo 1+e, o'y-o'vo my S = i=larrow_forwardPlease answer my homework problem. show all work so I can understand. thank you!arrow_forwardProb. In a constant head permeability test following results observed - Distance between piezometer tappings = 100 mm Difference of water levels in piezometers = 60 mm Diameter of test sample = 100 mm Quantity of water collected = 350 ml in 270 sec Determine the coefficient of permeability of the soil.arrow_forward
- The 2nd picture is the continuation of the question in the 1st picture.arrow_forward3-8 A 1-ft3 of undisturbed soil sample has a dry weight of 107 lbs. The specific gravity of the soil solids is 2.70. Need Vs VT = 1 To solve for Vs = use the following equation Ws=Vs*Gs*yw (solve for Vs) a) Calculate the void ratio of the sample. b) Calculate the porosity of the sample. DCarrow_forwardIn a falling permeameter, the sample used is 20 cm long having a cross-sectional area of 24 cm2. The sample of soil is made of three layers. The thickness of the first layer from the top is 8 cm and has a value of k1 = 2 x 10-4 cm/s, the second layer of thickness 6 cm has k2 = 5 x 10-4 cm/s and the bottom layer of thickness 4 cm has k3 = 7 x 10-4 cm/s. Assume the flow is taking perpendicular to the layers. Estimate the average hydraulic conductivity of soil in the vertical direction. a.3.12 x 10-4 cm/s b.5.69 x 10-4 cm/s c.2.35 x 10-4 cm/s d.4.28 x 10-4 cm/s e.6.69 x 10-4 cm/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning