
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Boyle's law can be represented graphically in several ways. Which of the following plots does not correctly represent Boyle's law (assuming constant Tand n)? Explain.
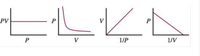
Transcribed Image Text:PV
P
V
V
1/P
1/V
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A sample of hydrogen gas at a pressure of 903 torr and a temperature of 26.9°C, occupies a volume of 692 mL. If the gas is allowed to expand at constant temperature until its pressure is 633 torr, the volume of the gas sample will be | mL.arrow_forward7. A container fitted with a movable piston is used to demonstrate Avogadro's law. As gas is introduced into the cylinder, the piston moves upward and the volume increases. Why does the pressure of the gas remain constant during this experiment? Is there any other variable that remains constant?arrow_forwardA 6.751 L gas cylinder contains hydrogen (H2) at a pressure of 8.339 atm and a temperature of 23.502ºC. What is the mass of hydrogen gas in the cylinder?arrow_forward
- A sample of an ideal gas at Pi is initially confined to one chamber of the apparatus represented above, and the other chamber is initially evacuated. The valve connecting the chambers is opened, and the gas expands at constant temperature to fill both chambers. Which of the following best describes AS for the process? A. S < 0 because the pressure of the gas decreases by half. B. S = 0 because there is no change in the total number of particles of the gas. C. S = 0 because the average kinetic energy of the gas particles is unchanged. D. S > 0 because the gas particles become dispersed in a larger volume.arrow_forwardP 8.98 atm Vị 8.95 L T; 610. K P; 4.38 atm V; 6.98 L T; ?K Tf = Karrow_forward15. answer question in pic pls :)arrow_forward
- Please help mearrow_forwardCLESS the soction in your e lext. Part A What is the pressure in millimeters of mercury of 0.0125 mol of helium gas with a volume of 213 mL at 40. °C? (Hint: You must convert each quantity into the correct units (L, atm, mol, and K) before substituting into the ideal gas law.) Express your answer with the appropriate units. Value Units Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remalining Next > Provide Feedback MacBook Air F7 吕口 F3 esc * & $ % 9 @ # 6 3 4 P T Y E R Q Garrow_forwardHow many grams of iron are needed to completely consume 36.4 L of chlorine gas according to the following reaction at 25 °C and 1 atm?iron ( s ) + chlorine ( g ) iron(III) chloride ( s )arrow_forward
- 7. A sample of nitrogen gas is collected over water at 20°C and a pressure of 1.00 atm. The volume of the collected gas is 250.0 L. What is the partial pressure of the nitrogen gas? (At 20°C, the vapor pressure of water is 17.5 torr) Dalton's Law: Protal = P, Solving this problem: Pnitrogen = Ptotal - Pwater + P. nitrogen water 8. A sample of hydrogen gas is collected Over water at 22°C. The pressure of the resultant mixture is 765torr. What is the pressure that is exerted by the dry hydrogen alone?arrow_forward) What mass of Al(BrO.), is required to produce 44.76 liters of O,which is collected over water at 40 C and a total pressure of 1.23 atm (vapor pressure of water at 40 C is 55.3 torr). Al(BrO.). -> AIBr, O,arrow_forwardThe average kinetic energy of the molecules in a gas sample depends only on the temperature T. R=8.314. What is the rms speed 02 molecules at 443 K? What is the rms speed of He atoms at 443 K?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY