
Database System Concepts
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780078022159
Author: Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:public static int countLeaves (BinaryTree tree)
Returns the number of leaf nodes in the tree.
public static int countNonLeaves (BinaryTree tree)
Returns the number of non-leaf nodes in the tree.
public static int getHeight (BinaryTree tree)
Returns the height of the tree.
public static void print PreOrder (BinaryTree tree)
Prints the elements of the tree using a pre-order traversal.
public static void printInOrder (BinaryTree tree)
Prints the elements of the tree using an in-order traversal.
public static void print PostOrder (BinaryTree tree)
Prints the elements of the tree using a post-order traversal.
public static void removeLeaves (BinaryTree tree)
Removes all leaf nodes from the tree. Use print PreOrder,
printInOrder, or print PostOrder after calling removeLeaves to show
that removeLeaves successfully removed all leaves.
Transcribed Image Text:7
4
2
4
2
Tree #1
1
5
Tree #2
6
3
6
8
8
9
5
7
9
1
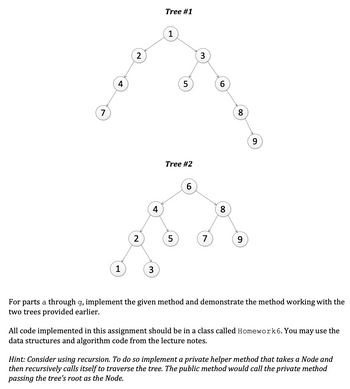
For parts a through g, implement the given method and demonstrate the method working with the
two trees provided earlier.
All code implemented in this assignment should be in a class called Homework 6. You may use the
data structures and algorithm code from the lecture notes.
Hint: Consider using recursion. To do so implement a private helper method that takes a Node and
then recursively calls itself to traverse the tree. The public method would call the private method
passing the tree's root as the Node.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2-3-4 Trees Java Programming Given the following sequence of numbers: 4.0 5.0 6.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 2.5 3.5 7.0 3.9 8.0 3.8 6.5 6.7 9.0 Show what the 2-3-4 tree looks like after each insert. This means you start with a blank tree and then show the 2-3-4 tree after inserting 4.0. Then, from that 2-3-4 tree, show what it looks like after you insert 5.0 into it. Repeat for the remaining numbers. There are 15 numbers to insert so you should be showing 15 trees progressively being built. Assume we are maintaining numbers in ascending order correctly within the tree as discussed in the slides. From the tree you have from completing question 1, which of the following is true (remember that more than one answer may apply) There are 6 leaf nodes in the tree No matter what the next number is to insert, there will definitely be a node that will be split Each non-leaf node in the final tree has exactly 2 children None of the above Finally, which of the following concepts about a 2-3-4 tree are…arrow_forwardJava - The node (80, 85, 90) is split. Enter each node's keys after the split, or "none" if the node doesn't exist.arrow_forwardthe Java code that removes the top BinaryTree of a tree andreturns the root of the resulting treearrow_forward
- Please, help. I'm working with notebook python. class Tree: """A rooted binary tree""" def __init__(self): self.root = None self.left = None self.right = None def is_empty(tree: Tree) -> bool: """Return True if and only if tree is empty.""" return tree.root == tree.left == tree.right == None def join(item: object, left: Tree, right: Tree) -> Tree: """Return a tree with the given root and subtrees.""" tree = Tree() tree.root = item tree.left = left tree.right = right return tree The following code builds a binary tree, MORSE, which implements the upper-case Morse code, as per the image below. More information on Morse code can be found on Wikipedia. You will need to run this code block to use in your solutions. In [33]: EMPTY = Tree()arrow_forwardplease, can you help me, I'm working with notebooks python. class Tree: """A rooted binary tree""" def __init__(self): self.root = None self.left = None self.right = None def is_empty(tree: Tree) -> bool: """Return True if and only if tree is empty.""" return tree.root == tree.left == tree.right == None def join(item: object, left: Tree, right: Tree) -> Tree: """Return a tree with the given root and subtrees.""" tree = Tree() tree.root = item tree.left = left tree.right = right return tree The following code builds a binary tree, MORSE, which implements the upper-case Morse code, as per the image below. More information on Morse code can be found on Wikipedia. You will need to run this code block to use in your solutions. EMPTY = Tree()H = join('H',EMPTY,EMPTY)V = join('V',EMPTY,EMPTY)F = join('F',EMPTY,EMPTY)L = join('L',EMPTY,EMPTY)P = join('P',EMPTY,EMPTY)J = join('J',EMPTY,EMPTY)B = join('B',EMPTY,EMPTY)X =…arrow_forwardJava / Trees: Which node in a tree does not have a parent? Multiple chocie. center null root leafarrow_forward
- True or False: Any node in a tree can be viewed as being the root of its own tree.arrow_forwardUse Java to create a Binary Search Tree Class with the following Operations: Insert(int n) : add a node the tree with value n. Its O(lgn) Find(int n) : find a node the tree with value n. Its O(lgn) Delete (int n) : delete a node the tree with value n. Its O(lgn) Display(): prints the entire tree in increasing order. O(n).arrow_forwardCreate the corresponding counting trees with the following traversals:1. Pre: IAMHEDBCFLPost: EHDMALFCBIIn: AHEMDICFLB2. Pre: ABDGCEHIFIn: DGBAHEICF3. Post: CBFEGDAIn: CBAEFDG4. Post: FABG/+CD - ^*In: F/AGB*+^C-Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education