
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
please urgent I want to briefly summarize what he is talking about and what you conclude
about the two graph (ventilation system)

Transcribed Image Text:0.6
0.59
0.58
0.57
0.56
0.55
comparison of diameter of the duct
Between the Software and the
Calculated Duct
equivelent diameter Software (m) equivelent Diameter Calculated
(m)
Figure 3-22 comparison of diameter of the duct Between the Software and the
Calculated Duct
Through these parametric studies, researchers gained valuable insights
into the complex interactions between various factors influencing the
ventilation system's performance. By systematically analyzing each parameter,
they were able to refine the system design and optimize its operation to meet
the specific requirements of the sports hall, ensuring optimal air quality and
comfort for occupants.
3.6. CONCLUSION
In summary, the components of a ventilation system, including fans,
ductwork, dampers, and control systems, work together to ensure effective air
circulation, temperature regulation, and air quality management within indoor
spaces. Also, delved into the intricacies of ventilation system design,
employing parametric studies and fundamental equations to elucidate key
relationships governing system performance. Through comprehensive
analyses, the chapter underscored the importance of various parameters on
ventilation efficacy. The parametric studies revealed proportional expansions
in exhaust flow, duct area, and pressure drop, highlighting the direct
correlations between factors such as occupancy, room size, duct dimensions,
and system resistance
Transcribed Image Text:Prresure Drop (Pa)
Variation of pressure drop (Pa) as Length
of Duct Varies in (m)
350
275
300
242
250
250
200
150
100
50
300
308
0
50
55
70
85
90
Lenght of Duct (m)
pressure drop (Pa)
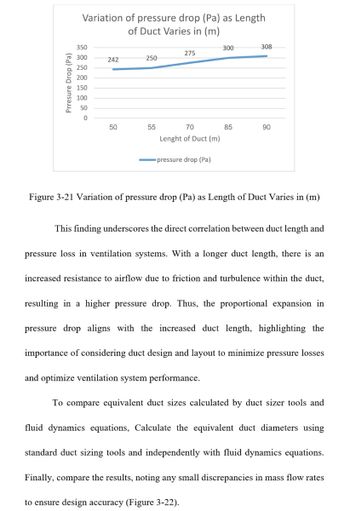
Figure 3-21 Variation of pressure drop (Pa) as Length of Duct Varies in (m)
This finding underscores the direct correlation between duct length and
pressure loss in ventilation systems. With a longer duct length, there is an
increased resistance to airflow due to friction and turbulence within the duct,
resulting in a higher pressure drop. Thus, the proportional expansion in
pressure drop aligns with the increased duct length, highlighting the
importance of considering duct design and layout to minimize pressure losses
and optimize ventilation system performance.
To compare equivalent duct sizes calculated by duct sizer tools and
fluid dynamics equations, Calculate the equivalent duct diameters using
standard duct sizing tools and independently with fluid dynamics equations.
Finally, compare the results, noting any small discrepancies in mass flow rates
to ensure design accuracy (Figure 3-22).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Hello I’m trying to make the graph that you see in the picture but I am having trouble on make the two lines that you see on the graph to over lap each other, I don’t want the two lines to be separate I want the two lines on top of eachother like you see in the picture please fix the code so that the Diesel line is on top of the Petrol line as seen on the picture. % Sample data for Diesel and Petrol cars carPosition = linspace(1, 60, 50); % Assumed positions of cars % Fix the random seed for reproducibility rng(45); % Assumed positions of cars CO2Diesel = 25 + 5*cos(carPosition/60*2*pi) + randn(1, 50)*5; % Random data for Diesel CO2Petrol = 20 + 5*sin(carPosition/60*2*pi) + randn(1, 50)*5; % Random data for Petrol % Fit polynomial curves pDiesel = polyfit(carPosition, CO2Diesel, 3); pPetrol = polyfit(carPosition, CO2Petrol, 3); % Generate points for best fit lines fitDiesel = polyval(pDiesel, carPosition); fitPetrol = polyval(pPetrol, carPosition); % Plotting the data figure; hold on;…arrow_forwardI am attaching both questions for 4 and 5 with the question in the image. thank you. NOTE : So the last person answered this question WITHOUT refencing the answer for whether question 4 or 5 answeres were given, so i am asking for question 5(or the answer for the question that was NOT solved because it was not referenced.) These were the following answers given to me from the last person on bartleby who answered my question without referencing whether it was the answer for question 4 or 5. 1 pass 2 fail 3 fail 4 passarrow_forwardAn electric hot water heater consumes 3.1 kilowatts of electricity and converts it to heat. How long will it take the water heater to heat a 67 gallon tank of water from 10 degrees Celsius to 50 degrees Celsius? (1 kilogram of water is 0.37 gallons, 1 Calorie = 4200 J). It may be helpful to refer back to the weekly handout for guidance on this problem. Your final answer should be in minutes (rounded to the nearest 10 minutes).arrow_forward
- Thermodynamics question. please help (2nd Attachment is the table question B is referring to)arrow_forwardPlease explainarrow_forwardProjects A and B are mutually exclusive. The minimum attractive rate of return (MARR) is 12%. Using rate of return analysis, which project should be selected? If the image fails to load here, go to https://www.dropbox.com/s/ld6wctqieu8jgwp/ROR.jpg Year 0 1 2 3 4 ROR A - $750 $200 $200 $200 $600 17.68% B - $1,150 $300 $350 $400 $700 16.44% O Project A O Project B O Both Project A and B O Select none of the project. O Insufficient information to make a decision. B-A - $400 $100 $150 $200 $100 13.69%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY