
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781337614085
Author: Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
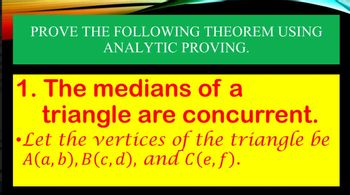
Transcribed Image Text:PROVE THE FOLLOWING THEOREM USING
ANALYTIC PROVING.
1. The medians of a
triangle are concurrent.
•Let the vertices of the triangle be
A(a, b), B(c,d), and C(e, f).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Show that the triangle with vertices A(1, 2), B(−2, −1), and C(−4, 4) is isosceles. We must first find the length of all three sides of the triangle by finding the distance between the vertices. d(A,B) d(B,C) d(A,C) Therefore, the following conclusion can be reachedarrow_forwardComplete the problem with a 2 column proofarrow_forwardLet 0(0,0), P(3,4), Q(6,0) be the vertices of the triangle OPQ. The point R lies inside the triangle OPQ such that the triangles OPR, PQR, OQR have the same area. The coordinates of point R are... A. G.3) (3.) (3) D. ) А. В. С. 4 2 B.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:9781285195698
Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:Cengage Learning