
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
This is an
PLEASE SHOW STEP BY STEP, WITH ARROWS! ALSO PLEASE INCLUDE ALL ELECTRON LONE PAIRS AND CHARGES FOR STRUCTURES IF NECESSARY!
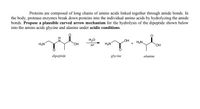
Transcribed Image Text:Proteins are composed of long chains of amino acids linked together through amide bonds. In
the body, protease enzymes break down proteins into the individual amino acids by hydrolyzing the amide
bonds. Propose a plausible curved arrow mechanism for the hydrolysis of the dipeptide shown below
into the amino acids glycine and alanine under acidic conditions.
H20
H+
HO
H2N.
H2N
H2N
+
HO,
dipeptide
glycine
alanine
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 22-71 Which amino acid side chain is most frequently involved in denaturation by reduction?arrow_forward22-91 Which amino acid does not rotate the plane of polarized light?arrow_forward22-49 Based on your knowledge of the chemical properties of amino acid side chains, suggest a substitution for leucine in the primary structure of a protein that would probably not change the character of the protein very much.arrow_forward
- On complete hydrolysis, a polypeptide gives two alanine, one leucine, one methionine, one phenylalanine, and one valine residue. Partial hydrolysis gives the following fragments: Ala-Phe, Leu-Met, Val-Ala, Phe-Leu. It is known that the first amino acid in the sequence is valine and the last one is methionine. What is the complete sequence of amino acids?arrow_forwardUsing both three- and one-letter codes for amino acids, write the structures of all possible peptides containing the following amino acids: (a) Val, Ser, Leu (b) Ser, Leu2, Proarrow_forward22-9 What is the difference in structure between tyrosine and phenylalanine?arrow_forward
- 22-97 Gelatin is derived from collagen by denaturation. Is a gelatin dessert likely to be a good source of dietary protein?arrow_forward22-61 Polyglutamic acid (a polypeptide chain made only of glutamic acid residues) has an a-helix conformation below pH 6.0 and a random-coil conformation above pH 6.0. What is the reason for this conformational change?arrow_forwardBoth norepinephrine and epinephrine are synthesized from the same protein-derived amino acid. From which amino acid are they synthesized? What types of reactions are involved in their biosynthesis? н он H OH H HO. NH, НО. CH3 (a) (b) HO НО Norepinephrine Epinephrine (Adrenaline)arrow_forward
- Which of the following amino acid side chains can aid the departure of a leaving group?arrow_forwardAll amino acids have two ionizable functional groups: an a-amino group (average pK, of 9.4) and an a-carboxylic acid group (average pK, of 2.2). Tyrosine also has an ionizable side chain (R group) with a pK, of about 10.1. One of the possible ionization states of tyrosine is shown. H3N-CH -C-OH CH2 ÓH At what pH would the structure be the predominant ionization state? Consider the ionization state of all three of the functional groups. The protonated form of the R group of tyrosine is shown in the structure. The ratio of the protonated form to the charged (deprotonated) form depends on the pK, of the R group and the pH of the solution. Select the pH value at which the charged form of the R group would predominate.arrow_forward(a) Which of the common amino acids have more than one carboxyl group?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning