
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Protease is an enzyme that catalyzes the breaking of amide bonds which is very stable at “mild” conditions, namely body temperature and pH 7 (if done in the lab requires hot conditions, concentrated HCl for hours). Some proteases have two aspartic acid residues at their active sites. Write the reaction mechanism (which follows general acid-base catalysis)
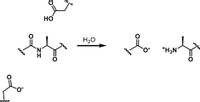
Transcribed Image Text:но
H20
'N'
*H3N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Prepare a schematic diagram and present it as though it were a Figure in a publication (scientificjournal or textbook) (20%). The Figure should illustrate the interactions made between thekey components of (a) total and (b) non-specific binding reactions. In preparing your figure,you should reflect on the role of each of the components of the reaction mixtures, and whythe subtraction of non-specific from total binding allows us to calculate specific binding.arrow_forwardPlease provide Typed solution in details, you can use only handwritten diagramarrow_forwardEnzymes are proteins that increase the rate of chemical reactions by lowering the energy activation required to facilitate the process. Explain the generalized and sequential enzyme mechanism of action (hint: from substrates to products).arrow_forward
- The hexokinases are a class of enzymes that catalyze the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of hexoses (sugars with six carbons). The hexokinases will bind only D-hexose sugars and not their L-counterparts. In general terms, describe the features of enzyme structure that make this specificity possible.arrow_forwardHow is it possible to determine the structure of an enzyme substrate complex by x ray crystallography when the reaction is over so quickly and the x ray analysis takes at least several minutes?arrow_forwardThe isoelectric point (pI) of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase is 6.0. Explain why the buffer used in DEAE cellulose chromatography must have a pH greater than 6 but less than 9 in order for the enzyme to bind to the DEAE resin.arrow_forward
- Chymotrypsin is an enzyme that is optimized to function in the small intestine (at a pH of ~7.4). Explain, given what you know about the chymotrypsin mechanism and what we learned about acid/base chemistry, why chymotrypsin would not be able to initiate catalysis if it were secreted into the stomach (pH ~2.5).arrow_forwardWhat type of reactions would involve a ligase? neither anabolic nor catabolic anabolic exergonic catabolicarrow_forwardY,G,I,F,L,Y what is the biochemical propities of this residues.arrow_forward
- give an example like the reaction mechanism of serin protease for example, with pictures & full explanationarrow_forwardWhat is the committed step of pyrimidine biosynthesis? Include the names and structures of any product(s), substrate(s), and cofactors, and the name of the enzyme responsible.arrow_forwardA student is attempting to add asparagine to a methionine that is connected to a solid polystyrene bead. They mix together the two components below with DCC, and some of the indicated product is generated. However, more happens in this mixture, resulting in multiple products. What reactivity is happening, and how can it be avoided (to give the indicated product in high yield)?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON