
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
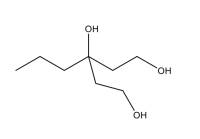
Propose a multistep synthetic route to the following structure that includes all reagents, substrates, as well as the products in each step.
Transcribed Image Text:### Chemical Structure of Glycerol
The image above displays the structural formula of Glycerol, also known as propane-1,2,3-triol. Glycerol is a simple polyol compound with the molecular formula C3H8O3. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic.
#### Structure Description:
- There are three carbon (C) atoms in the backbone.
- Each carbon atom is bonded to one hydroxyl group (OH), indicating that glycerol contains three hydroxyl groups.
- The first carbon atom is bonded to two hydrogen (H) atoms and one hydroxyl (OH) group.
- The second carbon atom is bonded to one hydrogen atom, one hydroxyl group (OH), and a carbon atom on each side.
- The third carbon atom is bonded to two hydrogen atoms and one hydroxyl (OH) group.
### Educational Significance:
Glycerol is an important molecule in biology and chemistry. It serves as a building block for triglycerides and phospholipids, which are essential components of cell membranes. In industries, glycerol is used in food sweeteners, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. Understanding its structure is vital for comprehending its role in various chemical reactions and biological processes.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Propose a sequence of synthetic steps that would efficiently accomplish the conversion shown below. You can use any inorganic reagents you like, but the only organic compound you are allowed to use is cyclopentane. multiple stepsarrow_forward4. Propose a synthetic route for the following transformation with explanationarrow_forward9. Propose reagents and conditions for the following multistep synthesis, one of steps will be Witting reaction. Propose a mechanism for the Witting reaction.arrow_forward
- Which of the methods shown will successfully complete the following synthesis? OH NH 1) 1) PBR3 1) H2CrO4 ОН 2), NH2 OH 2) SOC2 3) 2 3) aqueous NaOH NH2 1) H2CRO4 2) 1) PCC, CH2CI2 2) SOCI2 4) HO. 3) 2 NH2 2) HO. NH2 4) LİAIH4 ether followed by H2O H+arrow_forward2. Provide a synthetic route for the transformation below. More than one step is required. Show al steps clearly with reagents and products. OHarrow_forwardMuscone synthesis is possible via an intramolecular Prins reaction. The starting point is cyclododecatriene, which his subjected topartial ozonolysis.With one aldehyde group protected,the other is reacted with isobutenyl magnesium chloride, and the protecting group is hydrolysed off. Then follows what is formally a Prins reaction,and etherification results in cyclisation to the bicyclic dihydropyran. Hydrogenation (at high T) finally gives racemic muscone. a. What is the protective group used in the muscone synthesis above? b. What is the name of the reagent used as the protecting group? c. What groups are protected in the above muscone synthesis ?arrow_forward
- Provide a detailed mechanism for the following reactions. H₂SO4 CI 1.NaOH, Heat, pressure 2. HC1, H₂O CH₂ LOH CH₂ H₂O OHarrow_forwardDraw the MAJOR organic product(s) for each of the following reactions/sequence of reactions. OEt ΕΙΟ OEt OH 1) PCl3 / Br₂ NH2 2) / pyridine 1) EtONa / EtOH 2) H3O+ (dilute) 1) EtONa / EtOH 2) Ph 3) NaOH / H₂O Br 4) H2SO4/H₂O/heat OH 1) SOCI₂ 2) HO- / Et₂N NO2 1) MCPBA / CF3SO₂H 2) Ph-NH2/pyridine 1arrow_forwardDraw the major organic product of the reaction. Show the stereochemistry, if applicable. Omit byproducts such as water or bromide ion.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY