
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
propose a mechanism--not the name of the mechanism, but showing electron movement-for following reaction. Your mechanism must account for both products and show intermediates
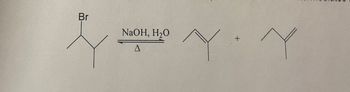
Transcribed Image Text:### Organic Chemistry Reaction: Dehydrohalogenation of Alkyl Halides
**Reaction Overview:**
This reaction depicts the dehydrohalogenation of an alkyl halide using sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in the presence of water (H₂O) and heat (indicated by the delta symbol, Δ). The alkyl halide shown is a bromide, which undergoes elimination to form alkenes.
**Chemical Equation:**
- **Reactant:**
- **2-Bromo-2-methylpropane** (C₄H₉Br)
- **Reaction Conditions:**
- **Reagents:**
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
- Water (H₂O)
- **Conditions:**
- Heated (Δ)
- **Products:**
- **Alkenes:**
- 2-Methylpropene
- 1-Butene
**Mechanism:**
The reaction involves the removal of a hydrogen atom and a bromine atom from the adjacent carbon atoms (dehydrohalogenation), resulting in the formation of a double bond and the production of alkenes.
**Outcome:**
Two alkenes are formed as products due to the possible formation of more than one alkene during the elimination reaction. The major product in many cases is the more substituted alkene (the Zaitsev product), but other factors such as sterics and reaction conditions can influence the distribution of products.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- b) Provide a detailed mechanism (with arrows) and show all relevant reaction intermediates for the following azo coupling reaction. -ZEZ Br NO CIO N Br 'N-arrow_forward3) Any compound or ion with at least one lone pair can be considered a base and/or a nucleophile. The relative basicity and nucleophilicity of the species is one of the most important factors that determine the mechanism of a reaction on sp³-carbon atoms. Please show an example of a) a reagent that is a strong nucleophile and a strong base, b) a reagent that is a weak nucleophile and a strong base, c) a reagent that is a strong nucleophile and a weak base, d) a reagent that is a weak nucleophile and a weak base. Which nitrogen atom in the structure below is most nucleophilic? Please explain by discussing the electron density around each nitrogen atom. Show at least three resonance structures of the compound. N.arrow_forwardSubstitution and elimination: predict the product Maximum allowed tries per question: Unlimited (7) Draw the major organic product of the reaction. Follow this procedure: determine whether the reaction conditions are acidic or basic; identify the most nucleophilic/basic atom, the electrophilic atom, and the leaving group; predict whether elimination or substitution will occur; and then draw the product. Indicate the stereochemistry at every stereocenter with a single wedged (up), hashed (down), or wavy (a mixture of up and down; either) bond. Launch MarvinJSTM viewer or click image to copy source CH3 H3C EtONa EtOH Brarrow_forward
- 4. Draw the mechanism that accounts for the formation of the product under the conditions shown. You may not add any other reagents. Be sure to show: all intermediate structures that occur in the course of the mechanism, any important resonance structures that play a role in the process, what if anything is added or lost in each step, and all formal charges on the structures. CHO H+ HO-C-H HO OH H-C-OH CH,OH НО 1 2 = 3arrow_forwardPlease do not give hand writing solutions.arrow_forwardHelp me draw in the arrows, thank you.arrow_forward
- Substitution and elimination: predict the product Maximum allowed tries per question: Unlimited (3) Draw the major organic product of the reaction. Follow this procedure: determine whether the reaction conditions are acidic or basic; identify the most nucleophilic/basic atom, the electrophilic atom, and the leaving group; predict whether elimination or substitution will occur; and then draw the product. Indicate the stereochemistry at every stereocenter with a single wedged (up), hashed (down), or wavy (a mixture of up and down; either) bond. Launch MarvinJSTM viewer or click image to copy source H₁₂C CH3 EtOH Brarrow_forwardShow the mechanism and give the expected products for the following reaction.arrow_forwardPropose a mechanism to account for the product listed using ONLY THE REACTANTS SUPPLIED. Be sure to use arrow notation and include any transition states if required. ОН -Brarrow_forward
- Complete the Reaction below and provide the following (i) a detailed stepwise mechanism to account for the product(s), including all steps involved (ii) Clearly show all the resonance structures and intermediates formed leading to the product. OH acetic anhydridearrow_forwardCompound (a) is formed by the reduction of what compound? HS соон COOH b oxidation HS COOH reduction SH HS .COOH COOH darrow_forwardPredict Products. Using line structures, give the major product of each 1.[ reaction below. DON'T SHOW MECHANISMS HERE. Use scratch paper if needed. H2 a) Pt/C b) HBr H2SO4 HOarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY