
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
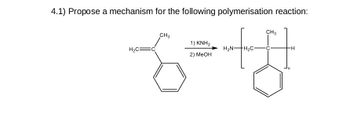
Transcribed Image Text:4.1) Propose a mechanism for the following polymerisation reaction:
1) KNH₂
HẸN—†H,C-
2) MeOH
=+H
H₂C=
CH3
CH3
-H
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- HC CH CH3CO2H H,SO, H3C-C-O-C=CH2 H HgSO, Acetylene Acetic Acid Vinyl acetate Acetylene reacts with acetic acid in the presence of H,SO4 and HgSO4 to yield vinyl acetate, a monomer used in the production of poly(vinyl acetate). The reaction mechanism includes the following steps: 1. Formation of a bridged mercurinium ion intermediate between Hg- and acetylene; 2. Addition of acetic acid to open the three-membered ring; 3. Proton transfer to solvent to give an organomercury vinyl ester3; 4. Addition of H to the alkene to form a carbocation; 2+ 5. Expulsion of Hg²+ to form the alkene. Diagram the mechanism on a separate sheet of paper, and then draw the structure of the product(s) of step 3. • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • Draw organic species only. • Do not include counter-ions, e.g., Na, I, in your answer.arrow_forwardU, NH, 14.) The shown reaction is an example of: (A) anti addition, forming a Z-alkene (B) anti addition, forming an E-alkene (C) syn addition, forming a Z-alkene (D) syn addition, forming an E-alkene (E) both A and Care true Iarrow_forwardWhich of the following reactions will not yield a carboxylic acid as a product? он (B) owool CrO3/H,0 (1) Oz/CH;Ch, -78°C (1) Mg, ether, A (A) Br (C) (2) H20 (2) CO2 (3) H* (dil /H¿O он H* /H2O A (D) Reaction D Reaction A Reaction Carrow_forward
- Only Carrow_forward(a) (b) HO N N-H Catalytic H+ (-H₂O) ? (c) NH2 HO N (d)arrow_forwardFollowing is a balanced equation for bromination of toluene.(a) Using the values for bond dissociation enthalpies given in Appendix 3,calculate ∆H0for this reaction.(b) Propose a pair of chain propagation steps and show that they add up to theobserved reaction.(c) Calculate ∆H0for each chain propagation step.(d) Which propagation step is rate-determininarrow_forward
- CH3 CH3CH₂CH=CCH2CH3 2- Give the common names for the following Alkenes: Ethene, Propene, 2-Methyl propene, and 2-Methyl, 1,3- butadiene. 3- Draw the correct structures of the following: 1-1,2-Dimethylcyclohexene 2-4,4-Dimethylcycloheptene 4- Write the complete mechanism of electrophilic addition of HI to 2-Methyl propene. Show the directions of the electron flow with the proper arrow orientation. Name the final product. 3- Cis-2-Butene and Trans-2-Hexene 4- cis-9-tricosene 5- Trans-9-tricosene 5- What is the sole product of the reaction of HC1 with 2-Methyl propene? Show the reaction with the reactant on the left side and the product on the right side and the intermediate between them. 1 Dashboard 900 Calendar To Do D Notifications Inboxarrow_forwardThe rate of hydration of 2-butene and 2-methylpropene differ by several orders of magnitude. Whcih alkene is more rapidly hydrated and why?arrow_forwardSome of the most useful compounds for organic synthesisare Grignard reagents (general formula R-MgX, where X is ahalogen), which are made by combining an alkyl halide, R-X,with Mg. They are used to change the carbon skeleton of a start-ing carbonyl compound in a reaction similar to that with R-Li:.(a) What is the product, after a final step with water, of thereaction between ethanal and the Grignard reagent of bromo-benzene? (b) What is the product, after a final step with water, ofthe reaction between 2-butanone and the Grignard reagent of2-bromopropane? (c) There are often two (or more) combina-tions of Grignard reagent and carbonyl compound that will givethe same product. Choose another pair of reactants to give theproduct in (a). (d) What carbonyl compound must react with aGrignard reagent to yield a product with the -OH group at theendof the carbon chain? (e) What Grignard reagent and carbonylcompound would you use to prepare 2-methyl-2-butanol?arrow_forward
- For each pair of ions, determine which ion is more stable. Use resonance forms to explain your answers. (a) CH;-CH-CH, or CH,-CH-OCH, (b) CH;-N-CH, CH3-CH-CH; or CH;-C-CH; CH;-C-CH, (c) CH=CH-ČH-CH, or CH,=CH-CH;-CH2 (d) CH-CH, or CH,-C N: (e) CH2 CH2 () or orarrow_forwardFor each alkane, which mono brominated derivatives could you form in good yield by free-radical bromination?(a) cyclopentane (b) methylcyclopentane(c) 2-methylpentane (d) 2,2,3,3-tetramethylbutanearrow_forward4-47 Questions e) and questions f) onlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning