
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
propane is combined with 50% excess air in a mixer before being fed to a furnace. The propane (C3H5) enter the mixer at 25 degrees celsius at a rate of 300Kg/h and the air enters the mixer at 500 degrees celsius. Heat is lost form the mixer to the surroundeings at a rate of 8.5KW. Given MW(propane= 4.4; Cp(Propane)=0.068032KJ/mol. degrees celsius; Cp(air) =0.0289KJ/mol degrees celsius. Use table 8 for calculation.
a. Calculate the molar flow of air that enters the mixer.
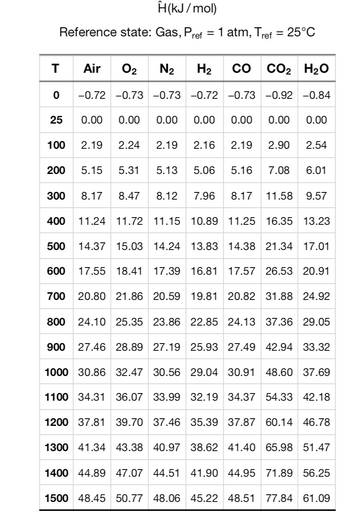
Transcribed Image Text:H(kJ/mol)
Reference state: Gas, Pref = 1 atm, Tref = 25°C
T
Air 0₂ N₂
-0.72 -0.73
-0.73
0.00 0.00 0.00
2.19 2.24 2.19
5.31 5.13
300 8.17 8.47 8.12 7.96 8.17 11.58 9.57
0
25
100
200
H₂
со CO2 H2O
-0.72 -0.73 -0.92 -0.84
0.00
0.00
2.16 2.19 2.90
5.15
500
5.06
5.16
0.00
7.08
0.00
2.54
6.01
400 11.24 11.72 11.15 10.89 11.25 16.35 13.23
14.37 15.03 14.24 13.83 14.38 21.34 17.01
600 17.55 18.41 17.39 16.81 17.57 26.53 20.91
700 20.80 21.86 20.59 19.81 20.82 31.88 24.92
800 24.10 25.35 23.86 22.85 24.13 37.36 29.05
900 27.46 28.89 27.19 25.93 27.49 42.94 33.32
1000 30.86 32.47 30.56 29.04 30.91 48.60 37.69
1100 34.31 36.07 33.99 32.19 34.37 54.33 42.18
1200 37.81 39.70 37.46 35.39 37.87 60.14 46.78
1300 41.34 43.38 40.97 38.62 41.40 65.98 51.47
1400 44.89 47.07 44.51 41.90 44.95 71.89 56.25
1500 48.45 50.77 48.06 45.22 48.51 77.84 61.09
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Saturated ammonia vapor at 25°C condenses on the outside surface of 16 thin-walled tubes, 2.5 cm in diameter, arranged horizontally in a 4 × 4 square array. Cooling water enters the tubes at 14°C at an average velocity of 2 m/s and exits at 17°C. Calculate (a) the rate of NH3 condensation, (b) the overall heat transfer coefficient, and (c) the tube length.arrow_forwardInsulated Sample Burning outside dish sample chamber Steel bomb Combustion (bomb) calorimeter. In an experiment, a 0.6629 g sample of phthalic acid ( C8H604) is burned completely in a bomb calorimeter. The calorimeter is surrounded by 1.046 x 10³ g of water. During the combustion the temperature increases from 24.04 to 26.63 °C. The heat capacity of water is 4.184 J-g¹. C-¹. The heat capacity of the calorimeter was determined in a previous experiment to be 788.9 J. ˚C-¹. Assuming that no energy is lost to the surroundings, calculate the molar heat of combustion of phthalic acid based on these data. C8 H6 O4(s) + (15/2) O2(g) → 3H₂O(l) + 8CO2 (g) + Energy kJ/mol Molar Heat of Combustion =arrow_forwardHeating Air by Condensing Steam. Air is flowing through a tube having an inside di- ameter of 38.1 mm at a velocity of 6.71 m/s, average temperature of 449.9 K, and pres- sure of 138 kPa. The inside wall temperature is held constant at 204.4°C (477.6 steam condensing outside the tube wall. Calculate the heat-transfer coefficient for a long tube and the heat-transfer flux. K) by Ans. h = 39.38 W/m² K (6.94 btu/h. ft².°F)arrow_forward
- Q2arrow_forwardFormaldehyde at 52.688 bar and 175.65 ℃ passes through a heater-expander and emerges at 39.516 bar and 420.45 ℃. There is no work into or out of the heater, but heat is supplied. Calculate the heat transfer into the heater-expander per mole of formaldehydearrow_forward1. (a) Hot oil at a flow rate of 5.5 kg/s (average cp = 1.92 kJ/kgK) enters an existing counter-flow exchanger at 435 K and is cooled by water entering at 325 K (under pressure) and flowing at a rate of 7.2 kg/s and the water exit temperature is 350 K. The overall heat transfer coefficient based on the outside area is 685 W/m²K (Average specific heat of water is 4.187 kJ/kgK). (i) Calculate the exit oil temperature. (ii) Calculate the heat transfer area. (b) The fluid in (a) enters an existing co-current-flow exchanger at the same conditions. (i) Calculate the heat transfer area. (ii) Explain the performance of both heat exchangers.arrow_forward
- The air at 20 ° C and 60% RH is heated using a heat exchanger to reach 70 ° C. Using a psychrometric chart, determine a. The amount of heat added per 1 m³ of initial air = (kJ). b. Condensation temperature = (° C)arrow_forwardCondensation of Steam on Vertical Tubes. Steam at 1 atm pressure abs and 100°C is condensing on a bank of five vertical tubes each 0.305 m high and having an OD of 25.4 mm. The tubes are arranged in a bundle spaced far enough apart so that they do not interfere with each other. The surface temper- ature of the tubes is 97.78°C. Calculate the average heat-transfer coefficient and the total kg condensate per hour. Ans. h = 15 240 W/m².Karrow_forward12.2-2. Heating of Oil by Air. A flow of 2200 lbm/h of hydrocarbon oil at 100°F enters a heat exchanger, where it is heated to 150°F by hot air. The hot air enters at 300°F and is to leave at 200°F. Calculate the total lb mol air/h needed. The mean heat capacity of the oil is 0.45 btu/lbm. °F. Ans. 70.1 lb mol air/h, 31.8 kg mol/harrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The